Oceanix City: This Concept Of Floating City Includes Food Production And Farming
Linked by Michael Levenston
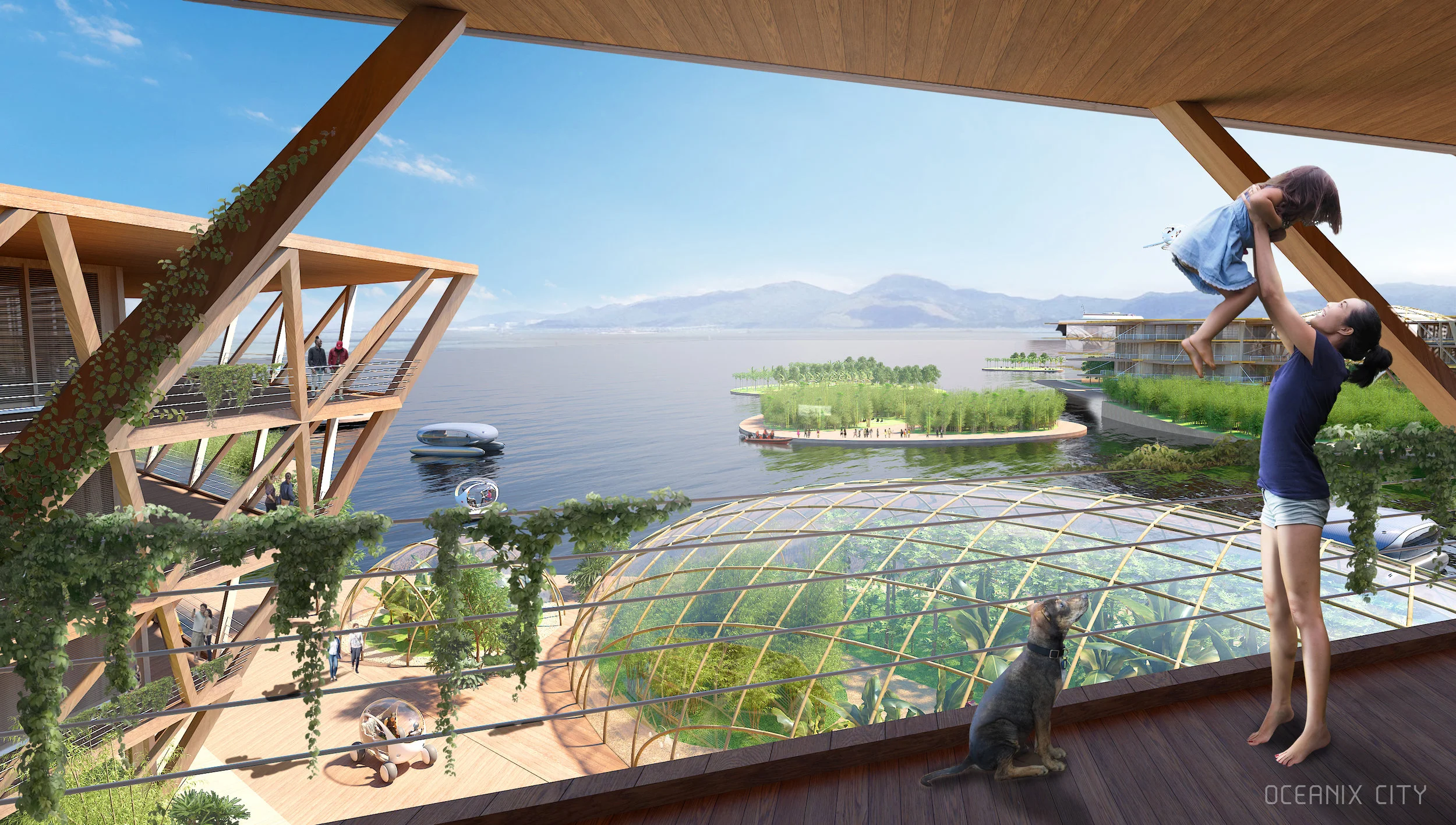
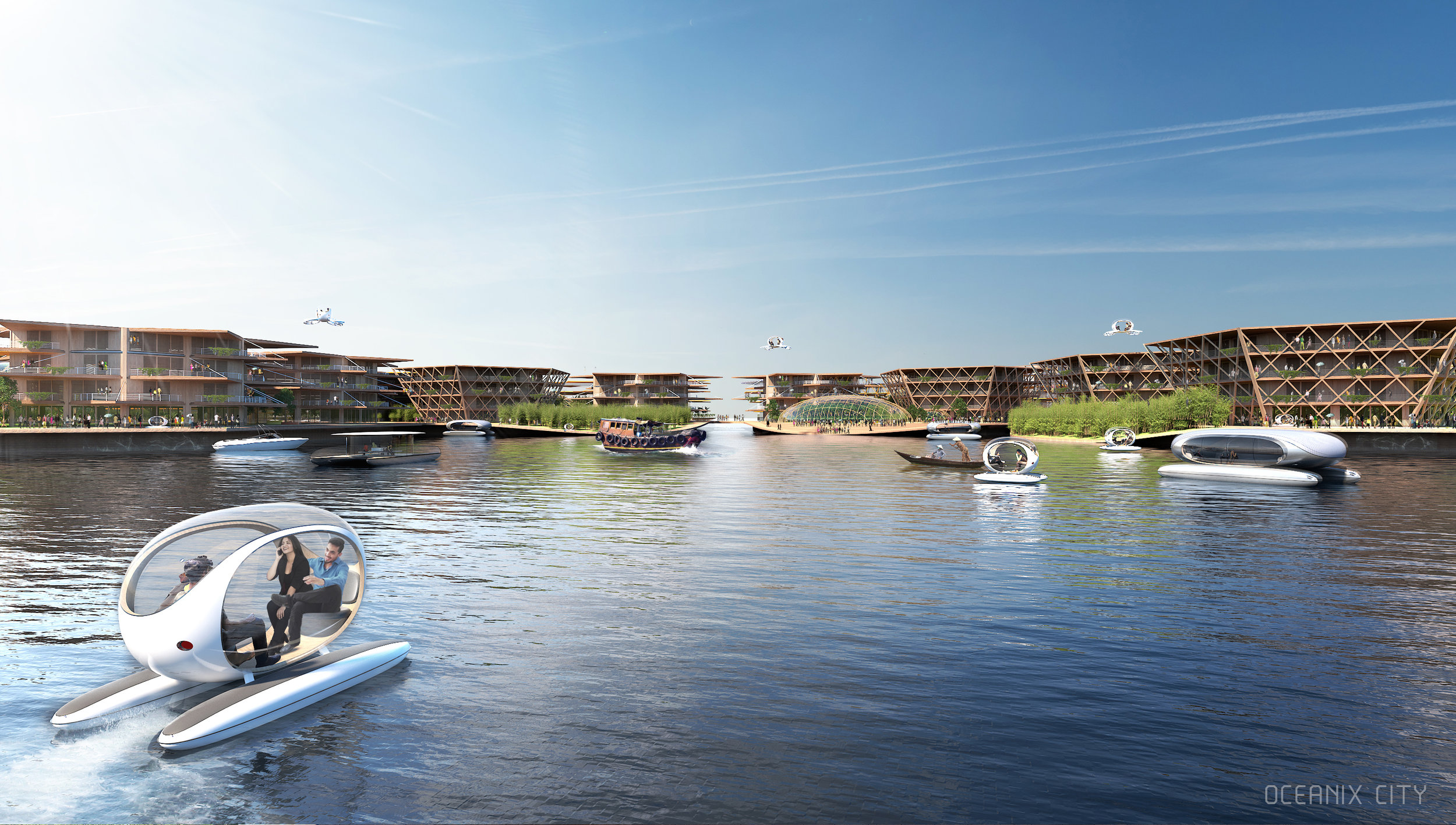
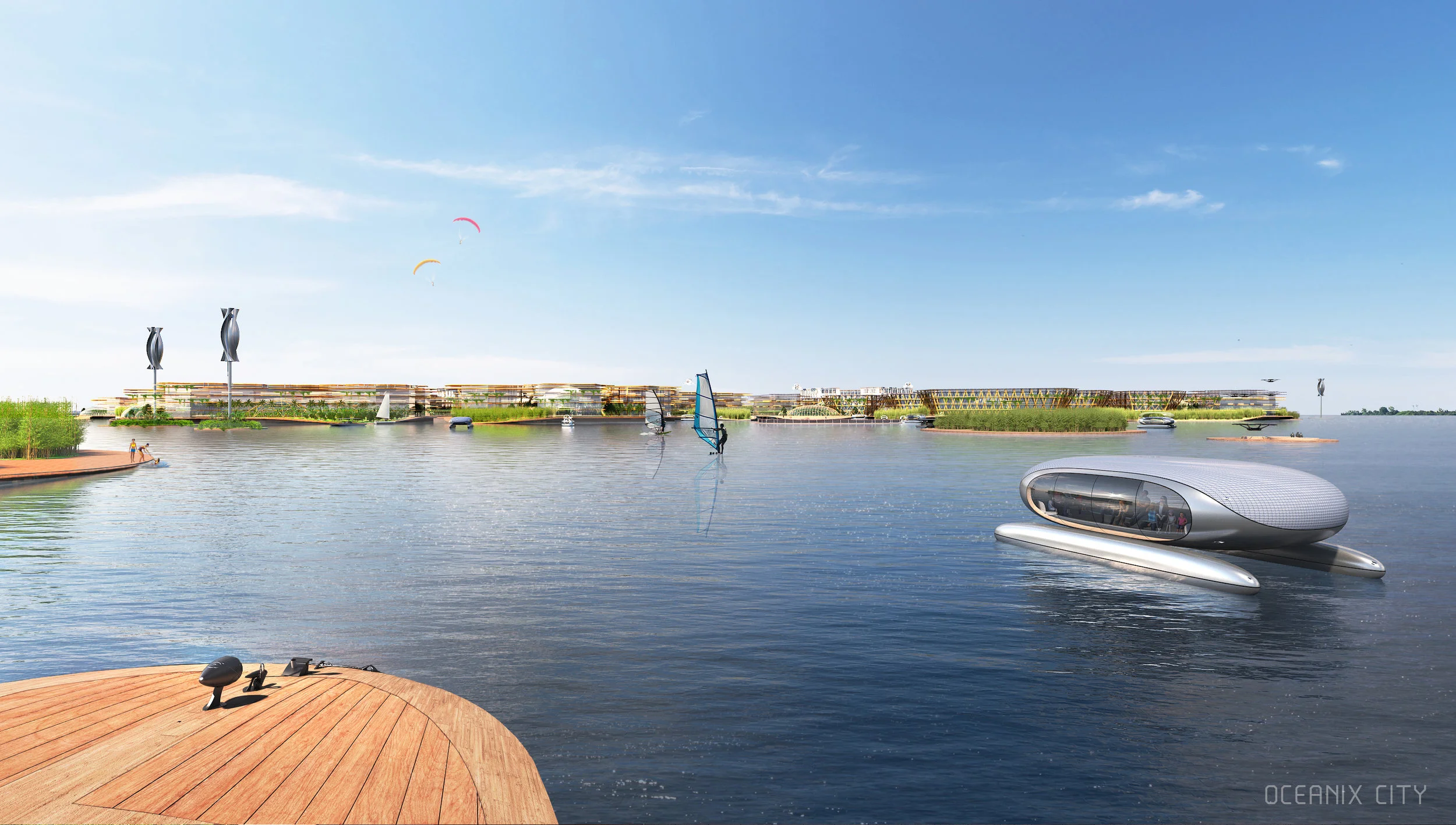
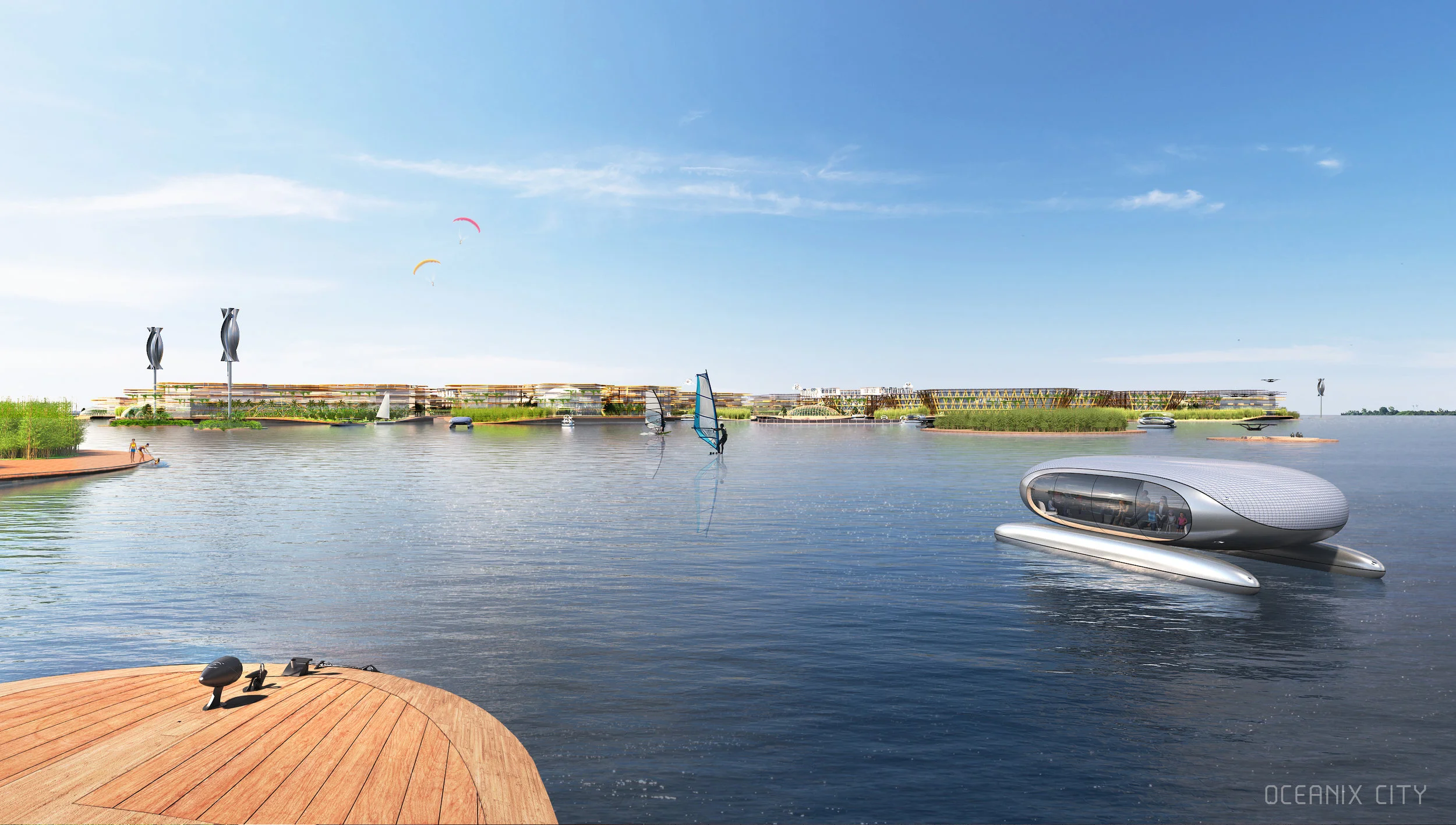
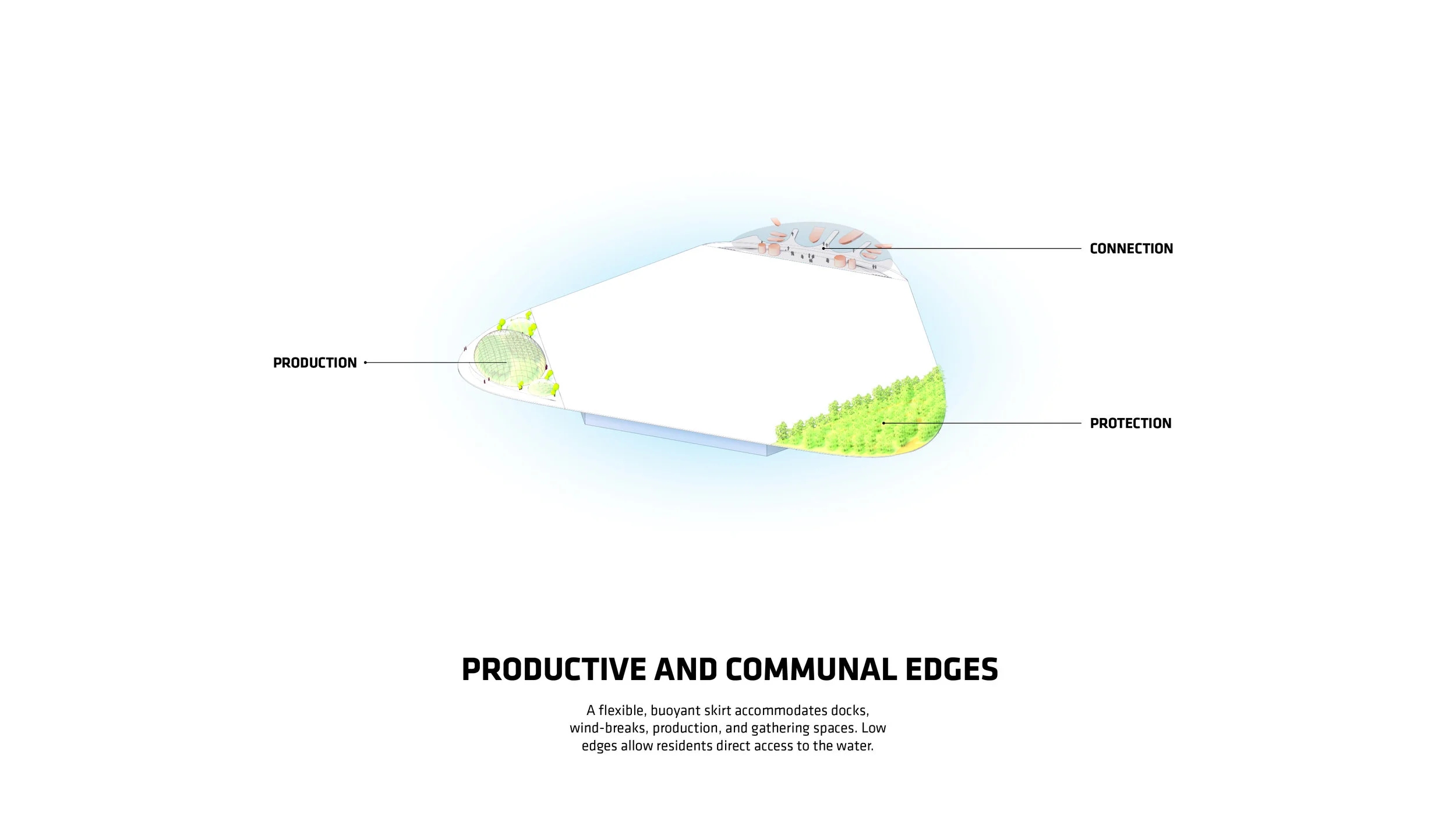
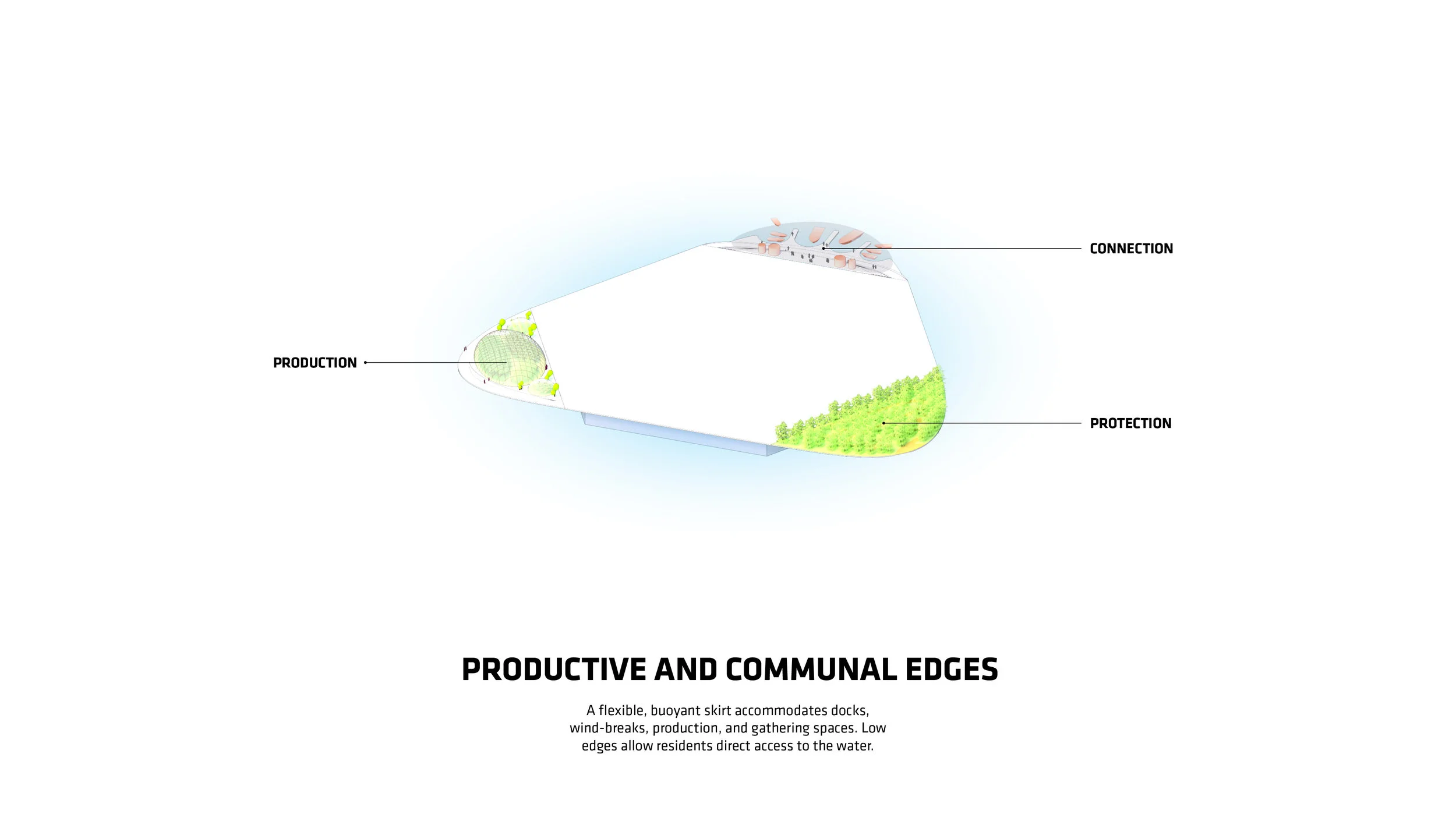
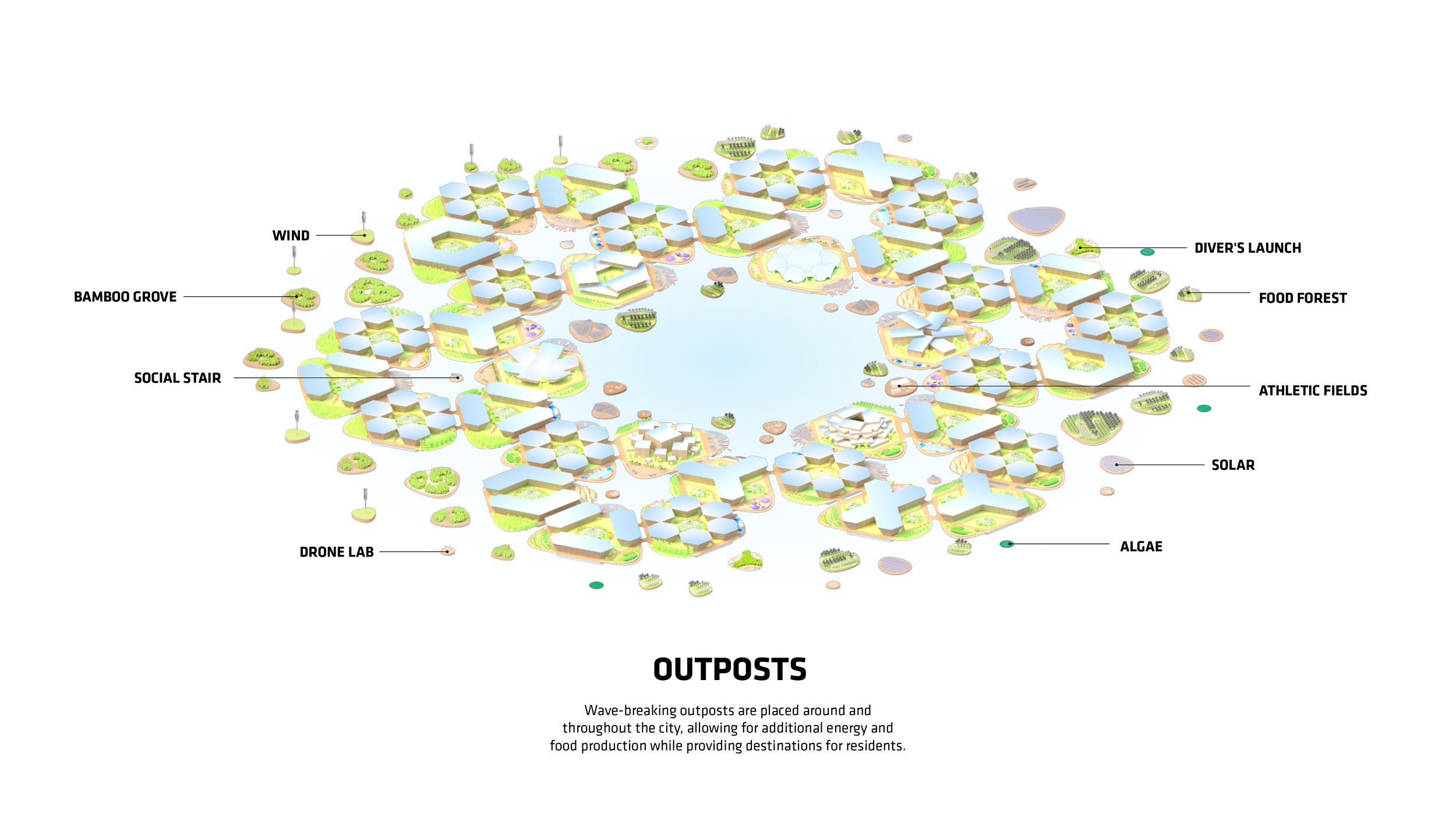
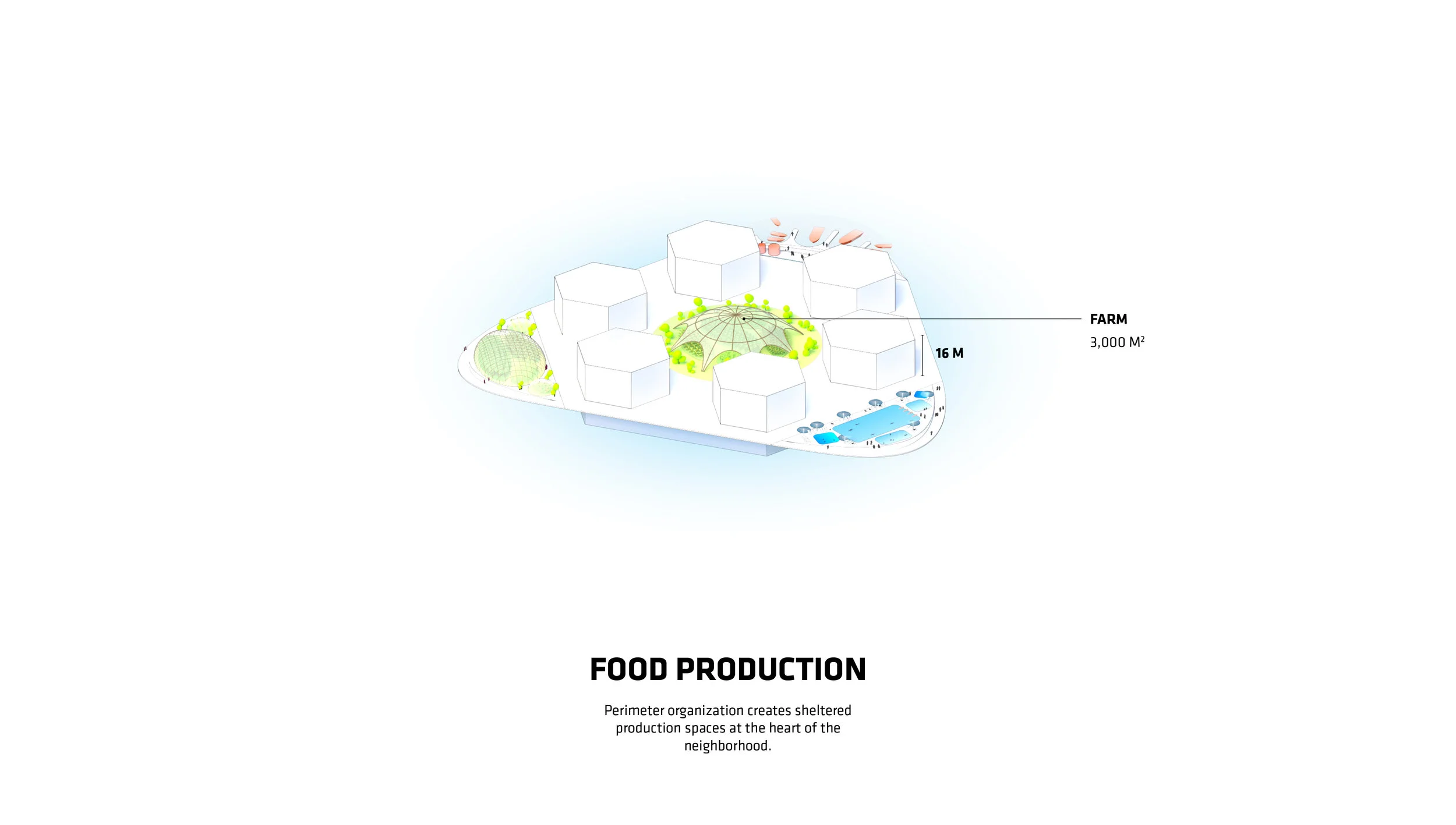
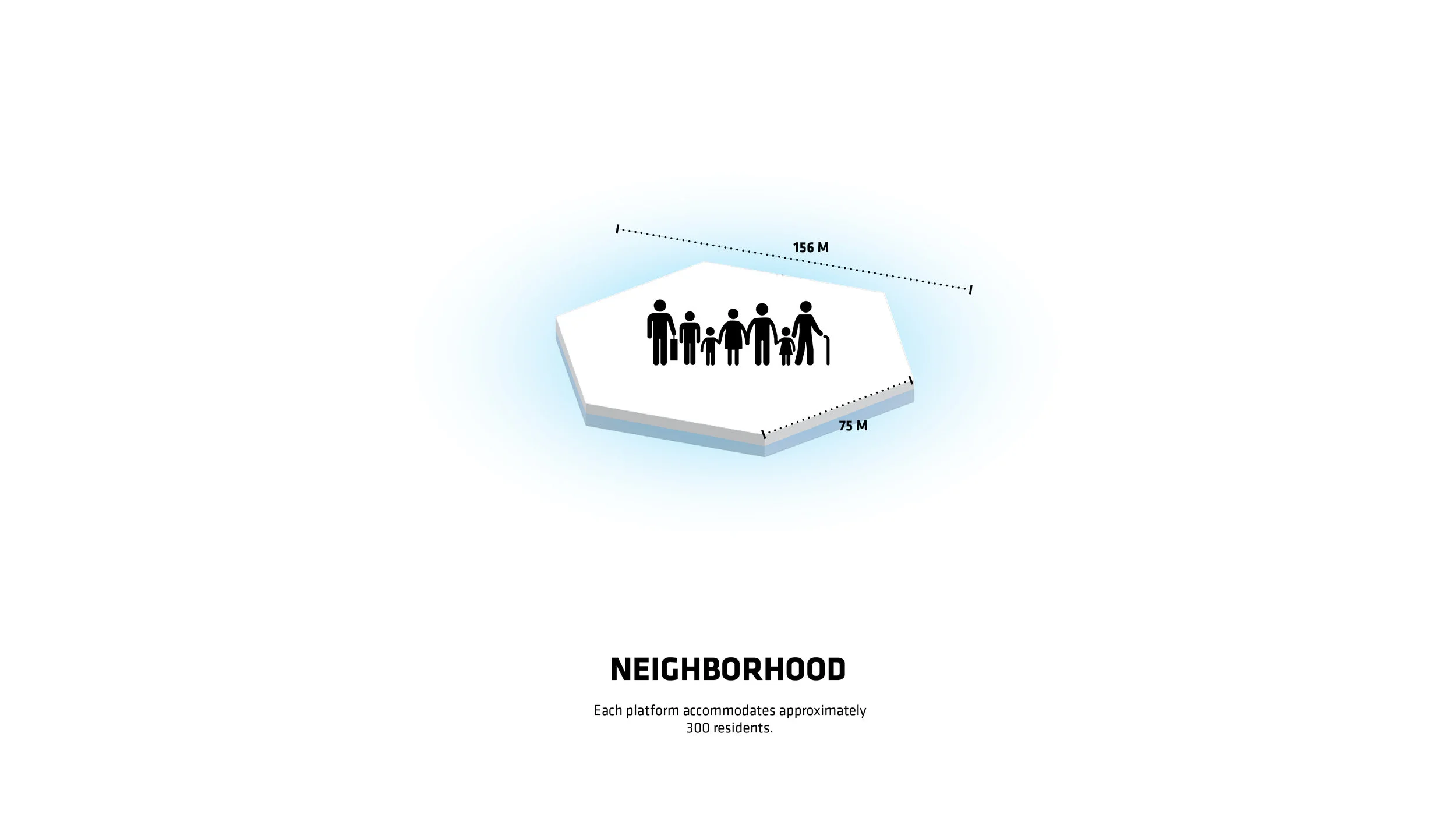
“Every island has 3,000 square metres of outdoor agriculture that will also be designed so that it can be enjoyed as free space,” said Ingels.
By Katharine Schwab
Fast Company
Apr 4, 2019
Excerpt:
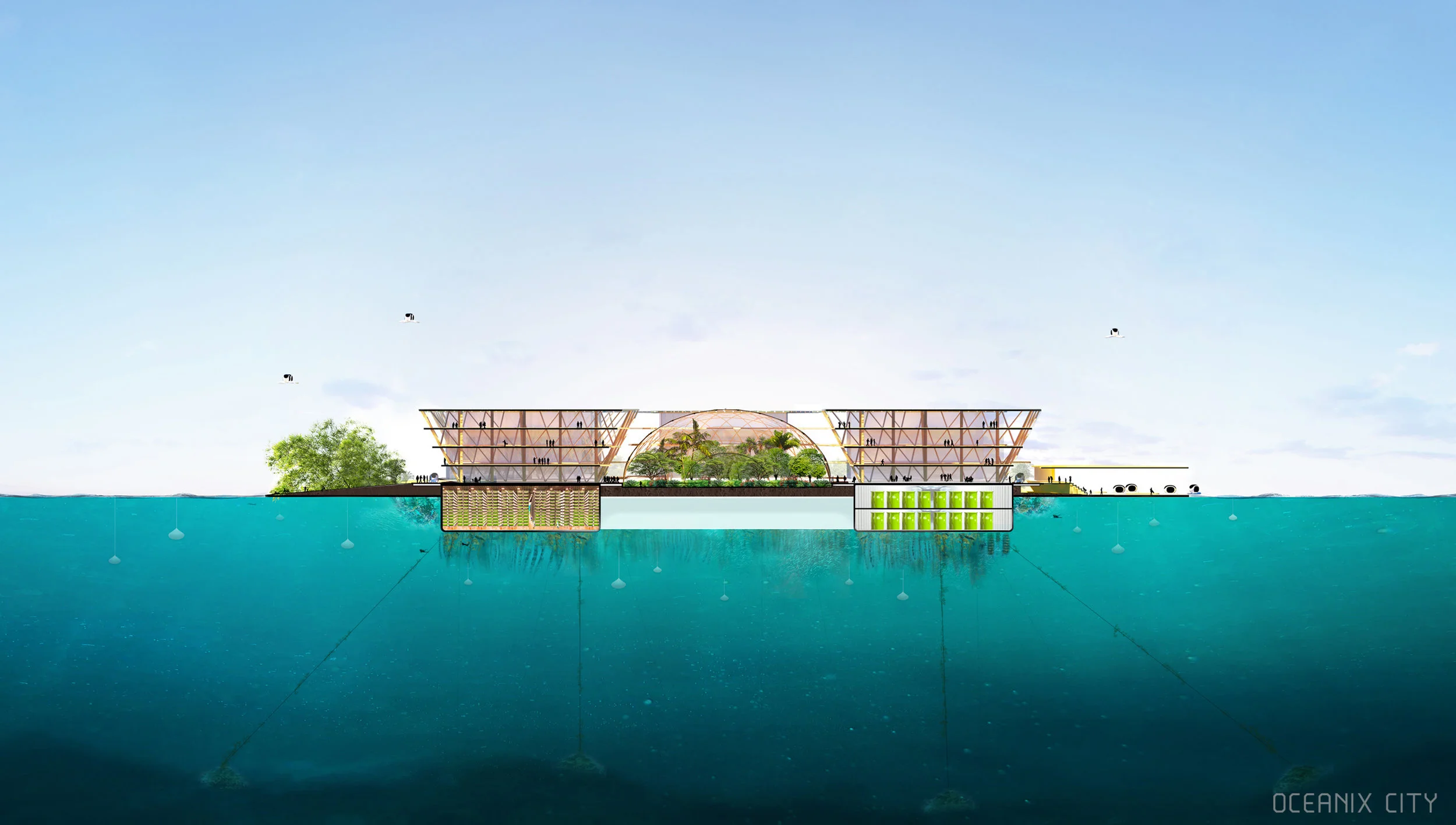
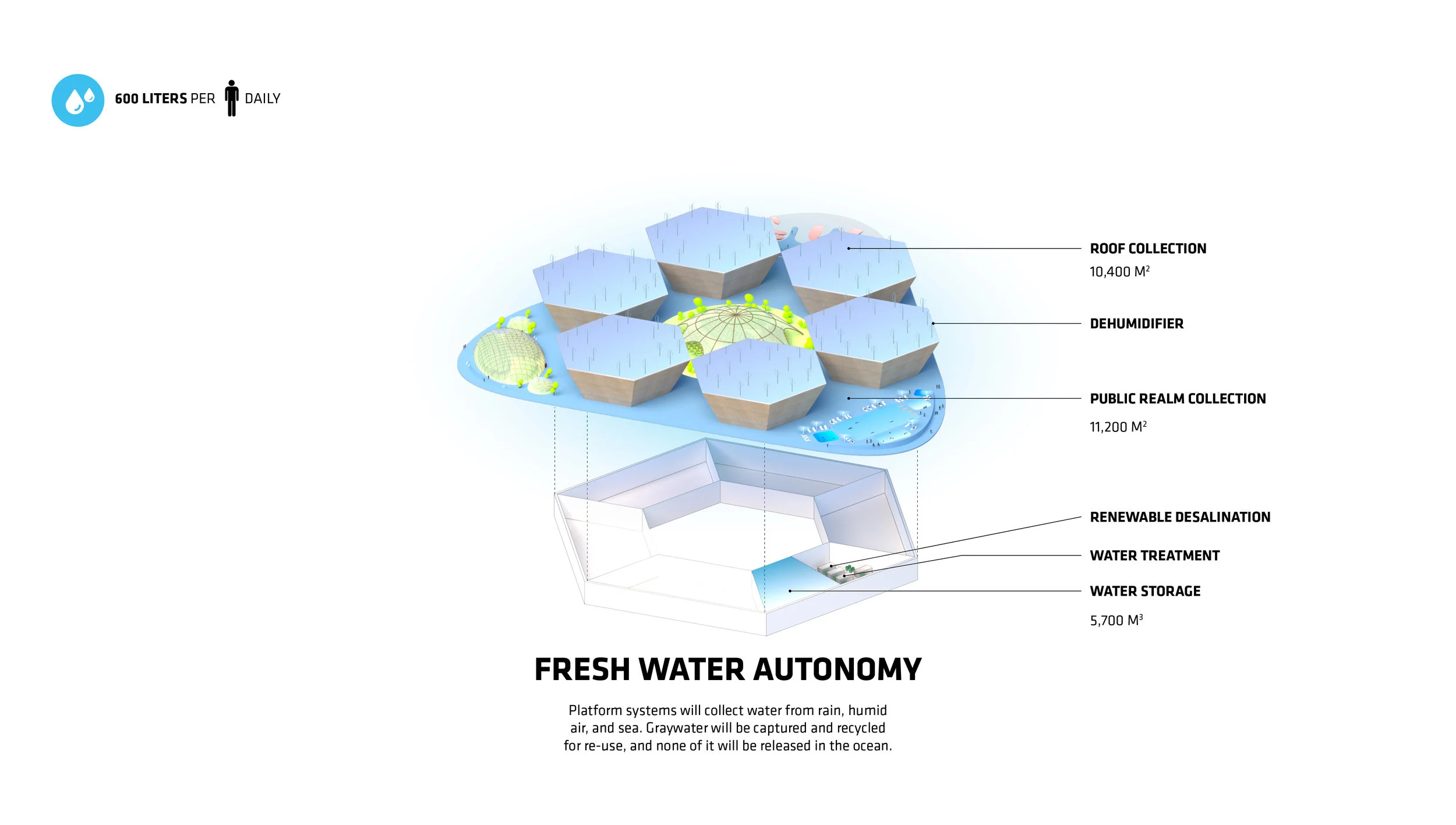
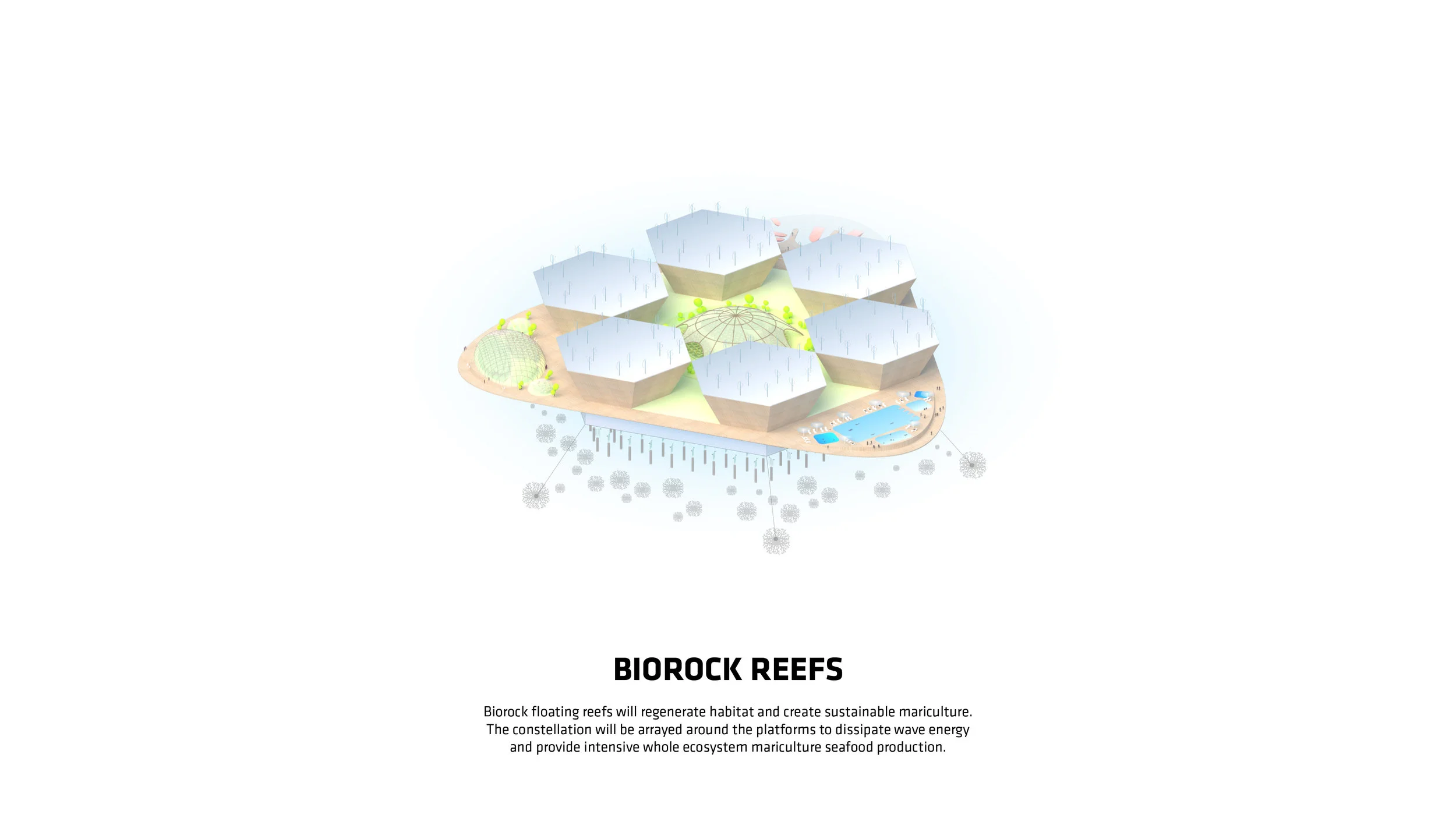
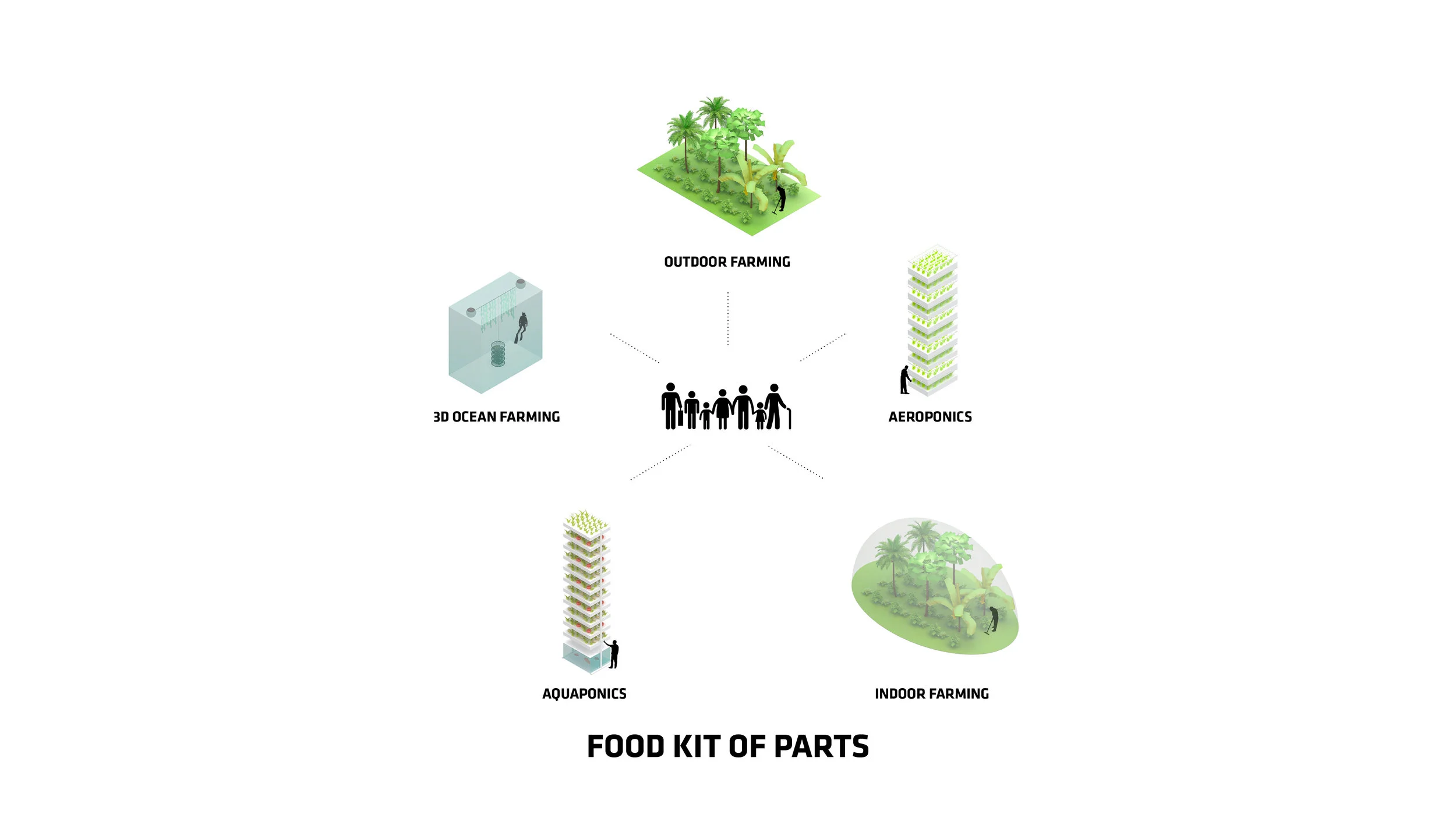
For Oceanix’s idea to work, all the food needed to feed every person living in the floating city would need to be grown there. What does that mean? There’s certainly no meat involved, mostly because beans are a far more efficient way of getting protein. Some crops would be grown outdoors–an estimated 32,000 square feet on each hexagon would be devoted to food cultivation. Much of that would be outdoors, since the sun uses the least amount of stored energy, and the crops would double as green space for residents.
But according to Clare Miflin, the cofounder of the Center for Zero Waste Design, a floating city would also need to experiment with other ways of growing food. One possibility: outdoor vertical farming for crops like lettuce. Then there’s hydroponics and aeroponics, the latter of which uses 10 times less water than traditional farming simply by spraying plant roots with mist. Aquaponics, in which plants grow hydroponically and are fertilized with fish waste, has a deep precedent–the Aztecs used aquaponic farming on their own floating agricultural islands many centuries ago.
With food comes food waste. Miflin wants to create a circular system where all food waste is turned into nutrients for the soil through composting. Food waste would go through a pneumatic system of pipes directly to an anaerobic digester to start the composting process. But there’s also the problem of packaging. Miflin believes that it would be crucial for the floating city to only use reusable food containers, with centrally located drop-off points for people to put their empty containers; from there, they could be cleaned centrally and reused.