Welcome to iGrow News, Your Source for the World of Indoor Vertical Farming
Fluence by OSRAM Reveals Multiyear Global Research Results on Broad-Spectrum Lighting Strategies for Cannabis and Food Crops
Fluence by OSRAM (Fluence), a leading global provider of energy-efficient LED lighting solutions for commercial cannabis and food production, announced today the results from a series of multiyear global studies analyzing the effects of broad-spectrum white light on cannabis, Merlice tomatoes and bell peppers.
August 12, 2021
AUSTIN, Texas—Fluence by OSRAM (Fluence), a leading global provider of energy-efficient LED lighting solutions for commercial cannabis and food production, announced today the results from a series of multiyear global studies analyzing the effects of broad-spectrum white light on cannabis, Merlice tomatoes and bell peppers.
The studies found that while spectrum sensitivity is cultivar-dependent, broad-spectrum lighting strategies—which include green light and other wavelengths largely absent in narrow-band spectra—improved crop yield, morphology and overall performance in selected cultivars when compared to narrow-band spectra with high ratios of red and far-red wavelengths.
“The results from our global studies show how effective broad-spectrum white light can be in improving crop performance for many cultivators around the world,” said Dr. David Hawley, principal scientist at Fluence. “Broad-spectrum strategies are about balance and flexibility in the spectrum itself as well as the overall cultivation approach. While there are certain scenarios in which narrow-band spectra, or pink light, may make sense from an energy efficiency or crop production perspective, we’ve found that many cultivars simply perform better under broad spectra across the KPIs cultivators care about most: yield, morphology and overall quality. Our latest research empowers us with new insights to assess each grower’s objectives, weigh those objectives against a facility’s unique financial, environmental and energy parameters, and then ultimately derive a tailored solution for each cultivator.”
Merlice tomatoes
A collaborative study with Wageningen University and Research (WUR)—led by researchers Leo Marcelis and Ep Heuvelink—evaluated differences in yield, morphology, development and quality for Merlice tomatoes grown with the VYPR top light series under four light spectra: PhysioSpecTM BROAD R4, PhysioSpec TM BROAD R6, PhysioSpecTM BROAD R8 and PhysioSpecTM DUAL R9B. BROAD R4, R6 and R8 all contain significant fractions of green light and other photosynthetically active wavelengths, while DUAL R9B is a narrow-band spectrum that contains almost no green light.
As researchers increased the ratio of red light in the overall spectrum, they recorded a linear decrease in yield. Compared to spectra with higher blue, red and far-red wavelengths, Merlice grown under broader spectrum lights yielded increases in fruit weight as high as 13 percent. Other tomato cultivars grown under broad-spectrum saw yield increases up to 14 percent.
Cannabis
Fluence conducted individual studies with WUR and Texas Original Compassionate Cultivation (TOCC), respectively. In the TOCC study, researchers studied Type I, Type II and Type III cannabis response to broad-spectrum R4, R6 and R8 under high PPFD. In each case, broad-spectrum R4 generated the most dry weight per plant. In Type I cannabis, PhysioSpecTM BROAD R4 generated 17 percent higher yields than the next highest yielding spectral solution, R6. Cannabis grown under broad-spectrum R4 also significantly improved morphology compared to plants cultivated under R6 or R8. Plants grown under broad-spectrum R4 were free of photobleaching in their upper buds, a development that typically occurs in plants grown with a higher fraction of red light.
In the WUR study, researchers found that in some cultivars, monoterpene and cannabinoid content, including THC, CBD and CBG, is significantly inversely proportional to the fraction of red light in the production spectrum. With these cultivars, R4 induced a 20 percent increase in cannabinoid compounds compared to spectra with red light ratios as high as 90 percent or more.
“The results of the TOCC and WUR intensity and spectrum studies are important for cannabis cultivators for two reasons,” Dr. Hawley said. “First, there is rarely a scenario in which they should grow cannabis under low PPFD. Our research continues to emphasize how much more beneficial it is to grow cannabis under higher PPFDs. Second, watch your red light ratio. There are a couple very specific cultivars and production situations that could benefit from narrow-band or high red/far-red and blue wavelengths. But it can also have detrimental effects on cannabinoid content, terpene ratios, yield and morphology, and would raise the risk of significant photobleaching of the canopy. That’s why we generally recommend growing cannabis with broad-spectrum under high PPFD.”
Bell pepper
Fluence also conducted studies with bell peppers at the Harrow Research and Development Centre in Ontario, Canada led by Dr. Xiuming Hao and Dr. Jason Lanoue. The collaborative research on bell pepper found that fruit quality significantly increased in Gina and Eurix cultivars under broad-spectrum lighting. Peppers grown under broader spectrum light increased average fruit size by up to 15 percent compared to others with higher blue and red wavelengths. An increase in the dry matter content—which is largely associated with fruit quality—also increased with increasing green light. It was also found that broad-spectrum lighting strategies proved the consistency of week-to-week production by leveling out a traditionally flush-prone crop cycle.
“Time and time again, our research with leading institutions around the world is proving that there is no universal spectral strategy for cultivators,” said David Cohen, CEO at Fluence. “For many crops and cultivars, however, it’s also showing the holistic benefits of broad-spectrum white light not just for the crop, but for a cultivator’s entire operation. That’s why we at Fluence have a multilayered approach to how we work with our cultivators. We continue to invest heavily in industry-leading research around the world. We provide cultivators with boots-on-the-ground expertise and experience in the form of our horticulture services team, and we identify the right light fixture and spectral strategy to help cultivators achieve their most important goals.”
Fluence’s ongoing global research initiatives include additional studies on strawberry, lettuce and cucumber cultivation. To learn more about Fluence and discover its latest research results, visit www.fluence.science.
About Fluence by OSRAM
Fluence Bioengineering, Inc., a wholly-owned subsidiary of OSRAM, creates powerful and energy-efficient LED lighting solutions for commercial crop production and research applications. Fluence is a leading LED lighting supplier in the global cannabis market and is committed to enabling more efficient crop production with the world’s top vertical farms and greenhouse produce growers. Fluence global headquarters are based in Austin, Texas, with its EMEA headquarters in Rotterdam, Netherlands. For more information about Fluence, visit www.fluence.science.
"We’re Hoping For A More Domestic Type of Farming”
“Whilst living in a 9-square meter student residence, the idea of being able to use this really small space to sustain myself with well packed nutritious food was what sparked the idea of Vita” Walid Brahim, CEO with Élever Group explains.
By Jenneken Schouten
August 9, 2021
“Whilst living in a 9-square meter student residence, the idea of being able to use this really small space to sustain myself with well packed nutritious food was what sparked the idea of Vita” Walid Brahim, CEO with Élever Group explains.
A small personal farm for everyone, a revolutionary product that combines aesthetic looks and the implementation of the most advanced technologies to date. That is the idea behind Vita that Élever Group recently launched.
The main aim of creating Vita was to bring a new level of transparency to food production, powered by blockchain technology, permitting users to safely buy and sell their harvest within small-scale communities. “We noticed that France, despite being a nation known for its agricultural scene, has experienced somewhat of a downfall regarding the people’s confidence when buying or consuming the goods grown in their own country. With Vita, we aim to rebuild this confidence,” Walid explains.
Read the rest of the article here
Vertical Farming Startup Oishii Raises $50m In Series A Funding
“We aim to be the largest strawberry producer in the world, and this capital allows us to bring the best-tasting, healthiest berry to everyone.”
By Sian Yates
03/11/2021
Oishii, a vertical farming startup based in New Jersey, has raised $50 million during a Series A funding round led by Sparx Group’s Mirai Creation Fund II.
The funds will enable Oishii to open vertical strawberry farms in new markets, expand its flagship farm outside of Manhattan, and accelerate its investment in R&D.
“Our mission is to change the way we grow food. We set out to deliver exceptionally delicious and sustainable produce,” said Oishii CEO Hiroki Koga. “We started with the strawberry – a fruit that routinely tops the dirty dozen of most pesticide-riddled crops – as it has long been considered the ‘holy grail’ of vertical farming.”
“We aim to be the largest strawberry producer in the world, and this capital allows us to bring the best-tasting, healthiest berry to everyone. From there, we’ll quickly expand into new fruits and produce,” he added.
Oishii is already known for its innovative farming techniques that have enabled the company to “perfect the strawberry,” while its proprietary and first-of-its-kind pollination method is conducted naturally with bees.
The company’s vertical farms feature zero pesticides and produce ripe fruit all year round, using less water and land than traditional agricultural methods.
“Oishii is the farm of the future,” said Sparx Group president and Group CEO Shuhei Abe. “The cultivation and pollination techniques the company has developed set them well apart from the industry, positioning Oishii to quickly revolutionise agriculture as we know it.”
The company has raised a total of $55 million since its founding in 2016.
Improved Product Consistency
Introducing Travaglini FarmTech, a new business division that has been established by Travaglini S.p.a., the world leader in meat, cheese, and fish processing equipment. Travaglini FarmTech will deliver turnkey vertical farm solutions to food processors to help them improve product consistency and simplify their supply chain dynamics
12-03-2021 Philips Lighting
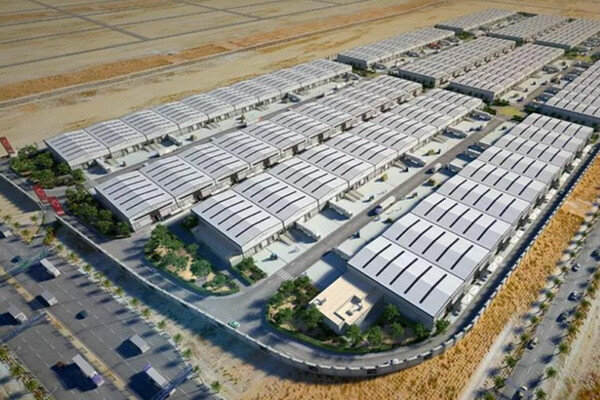
ITALY, Milan- Introducing Travaglini FarmTech, a new business division that has been established by Travaglini S.p.a., the world leader in meat, cheese, and fish processing equipment. Travaglini FarmTech will deliver turnkey vertical farm solutions to food processors to help them improve product consistency and simplify their supply chain dynamics.
“With vertical farming
we can grow and process consistent, high-quality produce in one location that can be close to retailers and consumers. We have full control over the entire process.”
- Luca Travaglini, leader Travaglini FarmTech
The challenge
Travaglini S.p.a. builds on 68 years of expertise in developing extremely accurate climate control, industrial automation, processing, and packaging equipment. The company is partnering with Philips Lighting, the world leader in lighting, to establish Italy’s first vertical farm research lab in Milan. This facility will be used to develop a state-of-the-art model for vertical farming growth strategies and technologies. The Italian vertical farm research lab will focus primarily on the production of leafy greens.
The right lighting
Vertical farming is a reply to the environmental problem that exists today in horticulture – how to provide fresh food to urban environments in a way that’s efficient and sustainable. “With vertical farming we are looking to answer many of the questions that the food industry is facing today and that will only become clearer and more pressing in the coming years,” said Travaglini. We can grow and process consistent, high-quality produce in one location in a vertical farm that can be close to retailers and consumers. Plus, we can fully control the entire supply chain, from seed to packaging.”
Luca Travaglini, leader of Travaglini FarmTech division said, “We chose to work with Philips Lighting because they have the strongest expertise in this field, and we trust them to help us expand our skillset and knowledge base over the long-term.
Photos Courtesy of Philips Lighting
Click here for more information.
Local Vertical Farm Startup Joins Growing Global Market
Ortaliza Urban Farms is a dream that has been sprouting for some time now.
What if there was a more sustainable way to provide fresh, truly local greens to our communities? And what if there was a way to do it while bringing diverse flavors to the table year-round?
It sounds like an ambitious goal. But it is one that Carina Biacchi and her partner, Alvaro Fernandes, are set to meet.
Ortaliza Urban Farms is a dream that has been sprouting for some time now.
Carina Biacchi is no stranger to business. With a bachelor’s and postgrads in business administration, she has worked in several different sectors, from NGOs to massive corporations. “I’ve mostly worked in sales and marketing” Carina states. “And I have entrepreneurship in my DNA. My parents were entrepreneurs long before I was born.”
And as formidable as Carina is, she is among good company. Alvaro Fernandes, her partner, is an Agronomist Engineer. “He’s a passionate specialist in controlled environment agriculture” Carina explains.
When the two met they quickly started dreaming about their own indoor farm. Years passed, and the two immigrated to Canada and started a family. But those entrepreneurial sparks continued to fly.
“It took us a while to build our lives in Canada,” Carina states. “But we continued to research the idea we had. We kept visiting other businesses in the industry and we even traveled to New York and other areas to see what they had to offer in terms of vertical farms.”
But what is vertical farming? Vertical farming is a growing worldwide phenomenon set to add significant value to the food system. Food security and sustainability continue to be some of the top concerns for city planners, and venture capital firms are investing big into vertical farm operations.
And what is an urban farm? Simply put, urban farming is growing food in urban areas. “We’re located right on Main Street,” Carina states. “In a commercial zoning area. That is pretty unique by itself, and the town of Kingsville has proven to be the perfect partner to help us launch our dream.”
A hyper-local farm-to-plate experience
And while Ortaliza is not the first micro green seller in the region, they are the first to create a storefront, creating an exciting farm-to-plate experience, loaded with flavor and freshness.
“We are truly local!” Carina stresses. “Sometimes, when you see that something is “local” on your grocery shelves, it’s actually from another part of the Province. That might be fine for large vegetables, but greens are special. Think of all the nutrients you would get from a full vegetable but concentrated to deliver all that deliciousness in every single bite. Microgreens require just-picked freshness, so we are super, hyper-local. We’re only growing and selling here in our County.”
This business model, Carina explains, also allows them to reduce food mileage and consequently, food waste. “Leafy greens in Canada can sometimes travel thousands of miles before reaching their destination” Carina reports. “And it can take up to two weeks for the produce to get there. We have a commitment to sustainability, and we will always be local, no matter where we spread our roots to in the future.”
One of Ortaliza’s business Advisors, Adam Castle of WEtech Alliance says the launch of this business in Kingsville represents a unique opportunity for the Startup. “Here we are in the very heart of greenhouse agriculture, not just for Canada but seconded only to Holland from a global perspective,” says Castle. “So you’re planting yourself in a community that lives and breathes agriculture, who knows the value of being able to see where your food comes from and how it’s grown, at a time when the average consumer is more engaged than ever in providing the freshest, most sustainably grown food they can for themselves and their family. I applaud Kingsville for making room at their table for new kinds of agriculture, and being a business-friendly partner that our clients can count on.
“…it certainly fits hand-in-hand with the innovation and the diversification that we’re trying to identify with.”
One enthusiastic supporter of this innovative new business is Nelson Santos, the Mayor of Kingsville and the Deputy Warden of Essex.
“This isn’t your typical business, but it certainly fits in with the entrepreneurial spirit that we have in our community,” Nelson explains. “And it certainly fits hand-in-hand with the innovation and the diversification that we’re trying to identify with. They are touching on all the different aspects of what the community is looking for. Their business is one that is certainly going to turn quite a few heads. It’s very exciting, both in regards to the food aspect and the extension of agriculture.”
Ortaliza is now taking pre-orders for their home delivery service at www.Ortaliza.ca, which promises to deliver a lot more than leafy goodness.
“We want to be more than a farm-to-table service,” says Carina. “We want our customers to think of us as their weekly dose of living, natural vitamins that add easy nutrition to just about every recipe they can think of!”
To learn more and become a friend of the farm, head to www.ortaliza.ca or find them on social media at @OrtalizaFarms
The Food Sustainability Dream
GCC countries are food-secure while not yet self-sufficient. Technology and policies seem to be areas that will help the region get self-sufficient, according to several experts from the region.
MITA SRINIVASAN
Food Security is everyone’s responsibility in the GCC. According to Satvik Jaitly, Consultant for Food & Nutrition at Frost & Sullivan in a special report to SME10x, the volatility in oil demand and trade disruptions due to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has raised concerns about the current status quo and the future outlook of food security in the GCC. No product or commodity carries the immediacy or political sensitivity of food.
Chandra Dake, Executive Chairman and Group CEO at Dake Group, agrees with Jaitly. “If the recent pandemic has shown us anything, it is that such dependencies are not as sustainable as previously presumed. As circumstances change so do requirements, and as populations rise, producers and exporters may prioritize internal markets, logistics could get disrupted and prices could fluctuate, anytime. Therefore, going forward, food security has to take a strong self-sufficiency focus.”
Dake feels that the region needs to acknowledge that conventional, intensive farming is not feasible in the Gulf. “We need cost-effective, eco-friendly and sustainable means to enhance domestic production, by addressing soil and climatic deterrents. In countries like the UAE, where hardly one per cent of the land area is considered arable, we have to enhance agricultural yield per square foot, besides increasing overall production.”
Technology, says Mohamed El Khateb, CPG Segment leader Middle East & Africa at Schneider Electric, is going to transform farming and provide the UAE with food security. In May 2020, the UAE harvested 1,700 kilograms of rice in the emirate of Sharjah. They did this through technology. And given that the UAE imports over 90 per cent of its food, like much of the rest of the Gulf, the country’s leaders want to address the issue of food security, of having access to more food staples locally rather than having to rely on imports.
In Dake’s opinion, a holistic approach involving favourable FDI policies, subsidies, strategic push for agritech, supporting talent etc is needed. Subsidies and grants can entice many entrepreneurs in the agricultural sector. The creation of such an ecosystem requires multi-stakeholder engagement and participation to drive micro sustainability and self-sufficiency. “However, since each economy in the GCC differs in size and capabilities, the transition will require extensive location-specific analysis, followed by strategy and effective on-ground implementation,” he added.
Schneider’s Khateb said, “Policies are one part of the solution. The other will be technology. The Gulf is primarily desert, lacking in water and arable land. Populations are growing, as is consumption. Many of the firms who have joined with the government to look into how to best grow food locally have one thing in common – they’re using agrotech, technology adapted to the agriculture sector, to find the best way to increase harvest yields.”
One area of promise is plant factories. These are facilities that don’t need access to natural sunlight. They use high-intensity lighting and vertical rows to fit as much produce into as small a space as possible, making them incredibly efficient. Plant farms require 95 per cent less water and 99 per cent less land than conventional farms. The farms are monitored by software and don’t use pesticides. Given that they require a smaller space than your traditional farm, plant farms can also be developed closer to or even in cities, cutting down on transportation to the retailer and consumer.
While there are major advantages to plant farming, they do need energy, lots of it. Lights need to be run for two-thirds of the day, and plant factories require heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) to regulate temperature. In fact, plant farms can consume more energy per square foot than a data center. Energy loads will vary based on the plant farm’s size and operations, but the power needs could vary from as little as 500 kilowatts to 15 megawatts.
“We believe that indoor agriculture is going to be one of the four major drivers of electricity consumption over the coming decade,” added Schneider’s Khateb. “What we are looking to do is develop innovative solutions to support this industry. One concept which is proving effective in the United States, which is pioneering plant farms, is the creation of on-site micro-grids.”
The thinking behind using microgrids is simple. Plant farms need power. And they’re often based in urban settings, where electrical distribution is constrained. By setting up a microgrid, which is basically a stand-alone set of energy sources and loads that can operate independently of the main energy network, plant farms can be energy self-reliant, operate at reduced costs, and rely on energy that’s clean.
Schneider is working with a number of plant farms in the US whose microgrids are powered by low-carbon energy through a mix of solar and natural gas. The company is looking at how it can develop feasible ways to have zero carbon microgrids and work through the constraint of space (plant farms are designed to be small, and the amount of surface area needed for solar panelling isn’t feasible in some cases). The energy requirements needed to power all of those lights and HVAC systems is sizable, and the cost of that energy can account for as much as 50 per cent of the operations at a plant factory based on studies in the US. Microgrids can give plant farm owners longer-term visibility over their costs (they’ll be able to calculate costs years in advance).
What’s most exciting for food security is that plant farms can produce significantly higher yields of crops throughout the year, thanks to the technology used to control the lighting, temperature, water and nutrients delivered to the plants. The flexibility of these setups is that the “daytime” for the plants can be in the middle of our night when electrical loads are lower. They can close the lights and simulate “night” for the plants during our daytime when the power loads are higher. In theory, a combination of power fed in from the grid can supplement a plant farm’s microgrid, allowing for even lower costs.
Khateb said, “Plant farms can help reduce the region’s food insecurity and tackle other big issues such as industrial agricultural pollution. Just as important right now, an effective food security response will create tens of thousands of jobs and result in economic gains worth billions of dollars for the country. Technology will both transform our farming for the better and create value for our society and the economy.”
Contrary to the connotation of a hi-tech solution, Dake Rechsand’s value proposition hinges on sustainability. The company’s products and solutions are employable by practitioners across the socio-economic spectrum, from individuals to institutions alike. Dake Rechsand has developed sand technology-based solutions for water-efficient desert farming, aimed at redefining the definition of "arable land", in the UAE and larger Gulf region.
Dake added, “Scarcity of water is a critical determinant of agricultural productivity. This is why Dake Rechsand has focused on innovations that harvest rain and reduce the water required to grow plants, as the path to achieving self-sufficiency in food production in the GCC. But creating these macro-outcomes requires both top-down initiatives from governments and bottom-up interest from individuals, communities, and corporates. So, we have positioned ourselves uniquely, between both ends of that spectrum, and tailored our offerings accordingly. We are actively onboarding sustainability advocates, administrations and farming communities, through awareness-based action and demonstrable positive impact. And the enthusiastic response our products has validated our strategy, for a self-sufficient and food secure GCC.”
The UAE has employed multiple strategies across the food value chain, focusing on enhancing domestic production, high-tech agriculture policies, research and development policies, import policies, foreign investment strategies, subsidization policies, stockpiling strategies, and food loss strategies, among others. These strategies contribute to addressing issues of food security self-sufficiency, trade, resilience, and sustainability in various degrees. These initiatives are gaining considerable traction due to enhanced public outreach campaigns and continued stakeholder engagements between the government and the private sector.
A New FEZ "Karakalpak-Agro" Established In Uzbekistan
“….increasing the production of agricultural products, expanding its deep processing and increasing exports, effectively using the production potential of the region…”
Tashkent, Uzbekistan (UzDaily.com) - The Cabinet of Ministers adopted a resolution”On measures to organize the activities of the free economic zone “Karakalpak-Agro”.
In accordance with the decree of the President “On measures for the comprehensive socio-economic development of the Republic of Karakalpakstan in 2020–2023” on an area of 875.4 hectares in Amu Darya, Buzatausky, Kegeili, Konlikul, Kushgirot, Muynak, Nukus , Takhiatash, Turtkul, Khodjeyli, Shumanai and Ellikala districts, the SEZ "Karakalpak-agro" was created.
The functions of managing the activities of the FEZ "Karakalpak-Agro" are assigned to the State Unitary Enterprise "Directorate of the free economic zone" Nukus ".
The main tasks and directions of the SEZ "Karakalpak-Agro":
- attracting direct foreign and domestic investments for organizing modern greenhouses on a cluster basis, including hydroponic ones, as well as organizing the production of structures, equipment and other components for the construction of modern energy-efficient greenhouses;
- increasing the production of agricultural products, expanding its deep processing and increasing exports, effectively using the production potential of the region;
- encouraging the organization of the complete process of agricultural production from seeds to delivery to the market;
- introduction of effective mechanisms for providing greenhouses with seeds and seedlings of high-yielding crops demanded by the market, by creating conditions for organizing nurseries, as well as seed production;
- formation of a modern infrastructure for the provision of logistics services, assistance to agricultural producers in organizing the export of their products;
- widespread introduction of modern resource-saving technologies, the use of alternative sources of thermal energy in the organization of greenhouses;
- creation of research and production centers to assess the compliance of products with international standards.
The Council of Ministers of Karakalpakstan, together with the Ministry of Investments and Foreign Trade, the Chamber of Commerce and Industry and commercial banks, was instructed to develop a targeted program of facilities for the production of structures for greenhouses on the territory of Karakalpak-Agro within two months, with the allocation of vacant non-agricultural land.
US-VIRGINIA: Arlington’s Only Commercial Farm To Expand, Double Production
Virginia Gov. Ralph Northam announced this afternoon that Fresh Impact Farms will be getting a $30,000 grant — half from the state, half from the county — that will help it double production and create six jobs.
Believe it or not, Arlington County has a working commercial farm.
The farm, which is located in a commercial building along Lee Highway, uses hydroponic technology to grow a variety of edible plants indoors. And it’s about to expand.
Virginia Gov. Ralph Northam announced this afternoon that Fresh Impact Farms will be getting a $30,000 grant — half from the state, half from the county — that will help it double production and create six jobs.
Fresh Impact, Arlington County’s only commercial farm, is banking on its restaurant customers ramping up purchases as vaccinated customers flock back to the indoor dining. It also launched a direct-to-consumer Community Supported Agriculture program last year.
County Board Chair Matt de Ferranti hailed the business and its expansion.
“Governor Northam’s award to Fresh Impact Farms, Arlington’s only commercial farm, is an innovative way to celebrate unique uses of technology to help a small business pivot during the pandemic,” de Ferranti said in a statement. “I am thrilled that Fresh Impact Farms is growing and looking to the future of a sustainable food supply.”
More on the company’s expansion, below, from a press release issued by the governor’s office.
Governor Ralph Northam today announced that Fresh Impact Farms will invest $137,500, create six new jobs, and more than double production at its Arlington County indoor facility. Operating since 2018 as Arlington’s only commercial farm, Fresh Impact Farms uses proprietary hydroponic technology to grow a variety of specialty herbs, leafy greens, and edible flowers for sale to customers in the Greater Washington, D.C. metro area.
Like many companies, Fresh Impact Farms has pivoted its business model amid the COVID-19 pandemic. Seizing the opportunity created by more people cooking at home, the company initiated a Community Supported Agriculture (CSA) program targeting area residents. The CSA program, which focuses on leafy greens and home kitchen-friendly herbs, has grown steadily since its establishment in April 2020 and now includes smaller wholesale clients. Now, with vaccinations underway and the restaurant industry poised to rebound, Fresh Impact Farms is expanding, which will allow the company to resume supplying their restaurant customers, while also meeting new demand through their CSA program.
“Agriculture continues to be a key driver of our economic recovery in both rural and urban areas of our Commonwealth,” said Governor Northam. “Innovative, dynamic businesses like Fresh Impact Farms are demonstrating how exciting new opportunities can grow out of pandemic-related challenges. I congratulate the company on their success and am thrilled to award the first-ever AFID grant to Arlington County to support this expansion.”
This expansion by Fresh Impact Farms will include a second grow room, larger production facility, and an educational hub where, post-pandemic, customers will be able to see how their food is harvested. Over the next three years, the company expects to grow an additional 10,500 pounds of Virginia-grown leafy greens, herbs, and edible flowers for restaurant and CSA customers.
“Agriculture is Virginia’s largest private sector industry and the Commonwealth continues to be on the forefront of emerging agriculture technologies,” said Secretary of Agriculture and Forestry Bettina Ring. “I am inspired by Fresh Impact Farms’ commitment to not only bringing fresh, local produce to Virginians, but also for its commitment to educate our community about how local food is grown.”
“2020 was undoubtedly one of the hardest years in recent memory for many people and businesses, but I’m heartened by the strength and flexibility the entire Fresh Impact Farms team has shown in our deep pivot to consumers and a CSA model to help us get to the point where we are ready to expand our business,” said Fresh Impact Farms Founder Ryan Pierce. “The support and generosity from the Commonwealth and Arlington County will be valuable as we expand our production and move towards a hybrid model of serving both the needs of restaurants and consumers. As the owner of a local food business, nothing gets me more excited than seeing the community come together in support of local food. The future is bright for urban agriculture and this grant will help us make an even greater impact in our community.”
The Commonwealth is partnering with Arlington County and the Arlington County Industrial Development Authority (IDA) on this project through the Governor’s Agriculture and Forestry Industries Development (AFID) Fund, which is administered by the Virginia Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services (VDACS). Governor Northam approved a $15,000 grant from the AFID Fund to secure the project for Virginia, which Arlington County will match with local funds.
“The Arlington County IDA’s match of the Governor’s AFID grant to Fresh Impact Farms represents an important investment in urban agriculture, sustainability, and technology,” said Arlington County IDA Chair Edwin Fountain. “This project will advance the County’s innovative and forward-thinking approach to developing new sectors of economic activity in Arlington.” […]
“Congratulations to Fresh Impact Farms,” said Senator Janet Howell. “This expansion not only supports our local economy, but also has a significant impact promoting healthy families and vibrant communities as a whole.”
“I am delighted Governor Northam has approved a grant from the AFID Fund to deliver this project for the Commonwealth and Arlington County,” said Delegate Richard Sullivan. “Fresh Impact Farms has been a pivotal resource for providing fresh food to the community. This expansion shows a commitment not only to homegrown produce, but to a healthier community and local economy in Arlington.”
"We’re Retrofitting With The Variables We Have In Place"
Planted Detroit introduces new 20.000 sq. ft. growing facility
“The Square Room is a big block of pink lights with eight levels, where all our growing is done. Everything after germination is done in the same room, both harvesting of our baby greens and microgreens. Because we’re almost done with our PARS (Planted Automated Racking System), which is the big automation,” says Megan Burritt, Managing partner at Planted Detroit.
From a mix-fused downtown neighborhood in Detroit, daily deliveries of ready-to-eat salads and fresh greens are transported to local retailers and restaurants. Planted Detroit makes a large contribution to the city’s share of fresh produce.
New facility
Planted Detroit has been in the middle of the construction of its new 20.000 sq. ft growing facility. The growing space has been a massive update to the company compared to its previous 6-level growing facility which was between 1500-2000 sq. ft. The same room was used for processing, packaging, harvesting, and so on. “It was rather crowded, says Megan, but the main goal was to keep everything tight for the construction to continue in the near surrounding. We’re very serious about biosecurity and we have a daily procedure for everyone who sets foot in our grow room to go through. Making sure our greens don’t come into contact with pathogens is our top priority.
The new growing room
The Square Room, one of our growing rooms, is highly automated, including an automatic harvester to ensure work-efficiency. Once everything is big enough to be transplanted out of their plug trays, PARS (Planted Automated Racking System) will be transplanted with gutters and then go into harvesting. On the other side of PARS, the gutters are taken down and harvested through Planted’s new automatic harvester.
Delivering directly to consumers
The company wants to reach a higher volume of customers as it’s aiming to obtain a consumer brand status. Next to that, the company is always on the lookout for finding more customers through other venues. “We want to go directly to consumers via our web-store to shorten food miles as much as possible, delivering the freshest and most delicious greens,” Megan says. In order to do that the company needed to have a bit more scale, trying to maximize the space they already had.
She adds: “Our farm maybe isn’t the square footage which we could have built from scratch, but we’re retrofitting with the variables we have in place. That is why we have done a combination of a microgreen vertical nursery and PARS for baby greens. Our direct customers wanted meal solutions and we’ve been able to deliver them that. We’ve been doing everything from seed to plate basically.”
Megan Burritt, Managing partner
New projects coming up
On the same campus, 10 meters away, a new farm will be constructed, under the company's office space. In this farm herbs and edible flowers will be grown in response to different customers' demands. Megan says that Planted Detroit’s wholesale customers got them to this point as they were very interested in herbs and edible flowers. “However we weren’t able to perfect these as well in the systems that our baby greens were in perfectly. That’s why we’ve been leaning into R&D lately because once finishing the construction of Farm 2 it will have excellent growing conditions that are better than they have been for those crops.”
Edible flowers are an interesting thing, says Megan, but the company has gotten so much interest in it. According to Megan there aren’t many farms in the US that are growing them. “They’re high priced at this point. It sort of sticks to our original innovation, namely what exists here in the food system and what does not. Where can we fill the ‘does not exist niche’ and satisfy the needs of our customers.”
The company is rolling out a subscription program sometime this year and figuring out where it fits into the fresh food subscription system and how they can partner with other parties in order to get produce closer to society. “It’s great to have this ag job, applied science to be able to do. In all the things we’ve been doing is hiring these Detroiters and showing that we can really create a really great culture of work. It’s really great to see we’re contributing to a better Detroit and a better tomorrow,” Megan states.
Team expansion
During 2020 most of the team stayed on by moving around working hours, so the farm could come back in full force. By the time all equipment was in place, 10 to 12 people were added to the team to have them fully trained before the system would be functioning. “It has been really wonderful to expand the team to see what our capacity is,” says Megan.
“Luckily we’ve been able to develop systems that have been resilient. We’ve seen so many different patterns in consumer behavior but they seem to have fallen in our favor. People are eating more at home, shopping for groceries more, and that triggered our pivot focusing on direct consumers. But now, it’s perfectly in line with our strategy on how we go to market. As long as we can supply our customer needs we’ll be on the right path. Nothing but bright hopes for the future right now,” Megan affirms.
For more information:
Planted Detroit
Megan Burritt, Managing partner
megan@planteddetroit.com
www.planteddetroit.com
Author: Rebekka Boekhout
© VerticalFarmDaily.com
Eastern Kentucky Company Growing Local Economy By Growing Vegetables Year-Round
AppHarvest has created 300 jobs in Appalachia, an area not really known for growing tomatoes.
by GIL MCCLANAHAN
MOREHEAD, Ky. (WCHS) — Imagine growing fresh local tomatoes in the dead of winter. A company in Eastern Kentucky is using high-tech agriculture to grow vegetables indoors.
To View The Video, Please Click Here.
AppHarvest checks tomatoes growing inside the company's 60-acre indoor greenhouse.
(AppHarvest ) Courtesy Photo
AppHarvest opened in Rowan County, Ky. last October. They are growing more than just vegetables. They are growing the economy in an area that sorely needs it.
What's growing inside AppHarvest's 2.8-million square foot facility is capable of producing more food with less resources.
"For our first harvest to be on a day where there was a snowy mountainside could not have been any more timely. The fact that we are able to grow a great juicy flavorful tomato in the middle of January and February is what we have been working to accomplish," AppHarvest Founder and CEO Jonathan Webb said.
Webb said five months after opening its Morehead indoor farm facility, the company shipped more than a million beefsteak tomatoes to several major supermarket chains, including Kroger, Walmart and Publix. Those large bushels and bushels of tomatoes are grown using using the latest technology, no pesticides and with recycled water in a controlled environment using 90% less water than water used in open-field agriculture.
"We're just trying to get that plant a consistent environment year round with the right amount of light and the right amount of humidity and the right temperature just to grow, and the vines of our crops the tomato plant end up being 45 feet and we grow them vertically so that is how we can get so much more production," Webb said.
One of the company's more well-known investors is Martha Stewart.
"I said Martha, can I get five minutes and I told her what we are doing. She was like, look we need good healthy fruits and vegetables available at an affordable price. I love the region you are working in," Webb said.
A couple of weeks later, Webb met with Stewart at her New York office, and she decided to become an investor in the company. Some local restaurants are looking forward to the day when they can buy their vegetables locally from AppHarvest. Tim Kochendoerfer, Operating Partner with Reno's Roadhouse in Morehead, buys his vegetables from a company in Louisville.
"It will be another selling point to show that we are a local restaurant," Kochendoerfer said.
Webb points out AppHarvest is not trying to replace traditional family farming. "Absolutely not. We want to work hard with local farmers," he said.
Webb said by partnering with local farmers, more local produce can get on grocery store shelves, because last year 4 billion pounds of tomatoes were imported from Mexico.
"What we are working to replace is the imports from Mexico where you got children working for $5 a day using illegal chemical pesticides in the produce is sitting on a truck for 2-3000 miles," Webb said.
AppHarvest has already started influencing the next generation of farmers by donating high tech container farms to local schools. Students learn to grow crops, not in the traditional way, but inside recycled shipping containers. The containers can produce what is typically grown on 4 acres of land. Rowan County Senior High School was the second school to receive one. It arrived last fall.
"We sell that lettuce to our food service department and it's served in all of our cafeterias in the district," said Brandy Carver, Principal at Rowan County Senior High School.
"When we talk about food insecurity and young people going home hungry, what better way can we solve these problems by putting technology in the classroom. let kids learn, then let the kids take the food home with them and get healthy food in the cafeterias," Webb said.
AppHarvest has created 300 jobs in Appalachia, an area not really known for growing tomatoes. Local leaders believe the company will attract more business to the area.
"I fully expect in time we'll see more and more activity along that line like we do in all sectors," said Jason Slone, Executive Director of the Morehead-Rowan County Chamber of Commerce.
"We will eventually be at the top 25 grocers. Name a grocer. We've been getting phone calls from all of them," Webb said.
AppHarvest has two more indoor farming facilities under construction in Madison County, Ky., with a goal of building 10 more facilities like the one in Rowan County by the year 2025.
To find out more about AppHarvest click here.
Fresh Impact Farms Awarded Arlington's First Agriculture Grant
Arlington County received its first-ever agriculture fund grant from the state, money that will go to county-based Fresh Impact Farms.
Operating since 2018, Fresh Impact Farms uses hydroponic technology to grow a variety of speciality herbs, leafy greens, and edible flowers indoors. (Mark Hand/Patch)
ARLINGTON, VA — Arlington County received its first-ever agriculture fund grant from the state, money that will go to Fresh Impact Farms, an Arlington-based company that plans to double production at its indoor growing facility.
Virginia Gov. Ralph Northam announced Monday that he had awarded an Agriculture and Forestry Industries Development, or AFID, Fund grant to Arlington totalling $15,000 to be given to Fresh Impact Farms. The company will receive a total of $30,000 from the government, with Arlington County matching the state grant with local funds.
"Agriculture continues to be a key driver of our economic recovery in both rural and urban areas of our commonwealth," Northam said Monday in a statement. "Innovative, dynamic businesses like Fresh Impact Farms are demonstrating how exciting new opportunities can grow out of pandemic-related challenges."
"I congratulate the company on their success and am thrilled to award the first-ever AFID grant to Arlington County to support this expansion," the governor said.
In recent decades, Arlington County has grown into one of the most densely populated counties in the nation. Up until World War II, Arlington still had plenty of farmland. But over the past 60-plus years, the only farming in the county has been of the backyard and patio variety or in the community gardens in the Four Mile Run area.
Operating since 2018, Fresh Impact Farms uses proprietary hydroponic technology to grow a variety of specialty herbs, leafy greens, and edible flowers indoors.
"Governor Northam's award to Fresh Impact Farms, Arlington's only commercial farm, is an innovative way to celebrate unique uses of technology to help a small business pivot during the pandemic," Arlington County Board of Supervisors Chairman Matt de Ferranti said. "I am thrilled that Fresh Impact Farms is growing and looking to the future of a sustainable food supply."
The company will invest a total of $137,500 as part of the expansion, which will include a second grow room, a larger production facility, and an educational hub where customers, after the pandemic, will be able to see how their food is harvested.
Fresh Impact Farms' community-supported agriculture or CSA, program focuses on leafy greens and home kitchen-friendly herbs and has grown them steadily since the program's creation last April. Along with residential customers, the company now has smaller wholesale clients in the Washington, D.C., area.
The future is bright for urban agriculture, said Ryan Pierce, founder of Fresh Impact Farms, located in the back of a Lee Highway strip mall. (Mark Hand/Patch)
After the start of the pandemic, Fresh Impact Farms decided to shift its business model to a CSA delivery service in order to continue generating revenue.
"Seizing the opportunity created by more people cooking at home, the company initiated a Community Supported Agriculture program targeting area residents," the governor's office said.
"Now, with vaccinations underway and the restaurant industry poised to rebound, Fresh Impact Farms is expanding, which will allow the company to resume supplying their restaurant customers, while also meeting new demand through their CSA program," the governor's office said.
Over the next three years, the company expects to grow an additional 10,500 pounds of Virginia-grown leafy greens, herbs, and edible flowers for restaurant and CSA customers.
The future is bright for urban agriculture, said Ryan Pierce, founder of Fresh Impact Farms, located in the back of a Lee Highway strip mall.
"The support and generosity from the Commonwealth and Arlington County will be valuable as we expand our production and move towards a hybrid model of serving both the needs of restaurants and consumers," Pierce said in a statement. "As the owner of a local food business, nothing gets me more excited than seeing the community come together in support of local food."
The funds from the Arlington County Industrial Development Authority, together with the state grant, represent "an important investment in urban agriculture, sustainability, and technology," Arlington County IDA Chair Edwin Fountain said in a statement. "This project will advance the County's innovative and forward-thinking approach to developing new sectors of economic activity in Arlington."
Plenty Ranked Number One on Prestigious FoodTech 500
Plenty came in first on the ranked list of 500 and out of a total of 2,000 nominees.
SOUTH SAN FRANCISCO, Calif.
Plenty, the flavor-first vertical farming company with a mission to improve the lives of people, plants, and the planet, today announced its #1 ranking on the esteemed Forward Fooding 2020 FoodTech 500.
Referred to as the “Fortune 500 list of agrifood companies,” the FoodTech 500 highlights global entrepreneurial talent at the intersection of food, technology and sustainability. Forward Fooding’s proprietary algorithms evaluate a business on its size, digital footprint and sustainability as measured against the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. Plenty came in first on the ranked list of 500 and out of a total of 2,000 nominees.
“It is an honor to be included on the FoodTech 500 and we are thrilled to be ranked first,” said Nate Storey, co-founder and CSO of Plenty. “The world is in need of an agricultural revolution, and there are many exciting areas where innovators are changing the future of food. At Plenty, we’re focused on using our proprietary, scalable vertical farming technology to deliver the freshest, most favorable produce year-round, while preserving our most precious resources.”
Plenty grows pesticide-free, non-GMO produce that tastes like it was fresh-picked from the garden because it was. The company ships from its farm to local stores every day. The farm’s controlled environment means the company can grow leafy greens year-round, regardless of the season. Plenty’s leafy greens are so clean, there is no need to wash because there is nothing to wash away - no bleaches, chemicals, soil or pesticides. The company wants the first person to touch their produce to be the consumer opening the package in their kitchen. Plenty plants are cultivated in an optimum growing environment, reaching peak flavors and nutrient value year-round, across every harvest.
The world is running out of usable land for growing crops and the global water supply is under severe threat of depletion. Plenty was founded on the need to create a more sustainable way to grow food using less land and water. Plenty yields hundreds of acres of crops in a building the size of a big box retailer, without cutting down a single tree, and using a fraction of the water required in the field. It’s San Francisco-based farm uses 100% renewable energy, and its greens are stored in 100% recyclable packaging and shipped locally to minimize the transportation footprint. Plenty’s data analytics and machine learning capabilities deliver 200 years’ worth of data each year, helping to quickly iterate and improve farm yield, quality and efficiency.
“The FoodTech 500 was created to shine a spotlight on the leading global innovators across the AgriFoodTech ecosystem, from farm to fork, who are making impactful solutions to better our food system,” said Alessio D’Antino, Forward Fooding founder and CEO. “This year’s list focused on understanding the driving factors behind the leading companies’ success and innovation, and we were thrilled to learn more about the top industry players, like Plenty, that are transforming our food system.”
The list represents 38 technology domains within the AgriFood space, including the broad categories of alternative proteins, farm management and precision farming, and vertical/indoor farming. The full ranking and more data about the 2020’s FoodTech 500 and its methodology can be found here.
About ForwardFooding
Forward Fooding is the world’s first collaborative platform for the food & beverage industry via FoodTech Data Intelligence and corporate-startup collaboration. Data services include The FoodTech Data Navigator data subscription service and facilitating corporate-startup collaboration through bespoke innovation programs and FoodTech consultancy.
To learn more visit: www.ForwardFooding.com
About Plenty
Plenty is an American farming technology company that frees agriculture from the constraints of land, weather, seasons, time, distance, pests, natural disasters, and climate. The company’s plant scientists, engineers, and farmers have developed its indoor vertical farming technology to grow nutrient-rich and pesticide-free plants with extraordinary flavor. The Plenty platform is designed to grow multiple crops in a building the size of a retail box store, yielding hundreds of acres using a fraction of the water and other precious resources. Plenty's flagship farm and headquarters are located in South San Francisco, and the company operates the largest of its kind Research and Development farm in Laramie, Wyoming. Plenty is currently building the world's highest-output, vertical, indoor farm in Compton, California.
View source version on businesswire.com:https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20210301005069/en/
CONTACT: Jane Gideon
KEYWORDS: CALIFORNIA UNITED STATES NORTH AMERICA
INDUSTRY KEYWORD: ENVIRONMENT TECHNOLOGY OTHER TECHNOLOGY FOOD/BEVERAGE AGRICULTURE SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT RETAIL NATURAL RESOURCES SCIENCE OTHER SCIENCE
SOURCE: Plenty
Copyright Business Wire 2021.
PUB: 03/01/2021
Kalera Acquires Customised Seed Developer Vindara For Vertical Farming
Following the acquisition, Vindara will become a fully-owned subsidiary of Kalera and will operate out of Kalera’s headquarters in Orlando, Florida.
US vertical farming company Kalera has announced the acquisition of Vindara, a S2G Ventures portfolio company which breeds plant varieties specifically designed for use in vertical indoor environments.
Founded in 2018, Vindara develops customised, non-GMO seeds for use in high-tech vertical indoor farm environments, as well as other controlled environmental agriculture farming methods.
Based in North Carolina, the company uses genomics, machine learning and computational biology along with traditional breeding methods to meet the market need for produce that is non-GMO, nutritious and high-yielding.
Following the acquisition, Vindara will become a fully-owned subsidiary of Kalera and will operate out of Kalera’s headquarters in Orlando, Florida.
Kalera says Vindara will significantly increase the output from its current and future facilities by reducing the plant grow cycle and providing higher yields.
According to the press release, Vindara’s breeding process shortens development time from the usual 5-7 years to just 12-18 months, resulting in increased output and optimising yield and profitability.
Together, the companies say they are better positioned to offer differentiated products – expanding beyond leafy greens to include high yield basil, spinach and strawberries – and have improved ability to optimise colour, texture, flavour and nutrient profile.
“While advances in technology such as lighting, robotics, sensors, and planting substrates are all improving grower economics, seeds developed specifically for indoor farming have been a ‘missing link’ to vertical farming achieving its full potential,” said Daniel Malechuk, CEO of Kalera.
“Together with Vindara, we are ushering in a new era of agricultural advancements that will increase production yields and produce unique crop varieties customised for the needs of our discerning customers around the globe,” he added.
The deal will see Jade Stinson continue in her existing role as co-founder and president of Vindara. “With Kalera’s commitment to R&D and improving the yield, variety and characteristics of its produce, we will be able to better leverage our ability to develop customised seeds for indoor growers faster than any other seed provider,” she said.
The transaction will reportedly enable Vindara to accelerate and expand its seed research and development programmes.
Bowery’s Founder, Irving Fain, On The Future of Vertical Farming
At one point in the not-so-distant past, vertical farming’s role in our future agricultural system was far from certain. Growing leafy greens in warehouse-like environments controlled by tech seemed like a compelling business, but one that had yet to prove itself either economically or as an important source of food for a growing world population
Image from: The Spoon
At one point in the not-so-distant past, vertical farming’s role in our future agricultural system was far from certain. Growing leafy greens in warehouse-like environments controlled by tech seemed like a compelling business, but one that had yet to prove itself either economically or as an important source of food for a growing world population.
That, at least, was a common sentiment Irving Fain, CEO and founder of Bowery, met with when he started his vertical farming company five years ago. “There was a bit of skepticism around it,” he told me over a call recently, suggesting that five years ago, there were a lot more “ifs” than “whens” in terms of vertical farming’s future.
Fain, Bowery, and the entire vertical farming industry get a much warmer reception nowadays. Investment dollars are pouring into the space. Around the world, companies, scientists, and food producers are using the method to not just supply upscale grocery stores with greens but experiment with breeds of produce, feed underserved populations, and grow food in non-arable regions. As Fain suggested when we spoke, the last 12 months seem to have turned those “ifs” into definite “whens.”
Bowery’s last 12 months also illustrate this change. Fain said that Bowery went from under 100 retail locations about a year ago to nearly 700 right now, and will be in more than 1,000 “in the coming months.” Its produce is in a number of food retailers around the Mid-Atlantic and Northeast, including Whole Foods Market, Giant Food, Stop & Shop, Walmart, and Weis Markets. And in 2020, the company experienced “more than 4x growth” with e-commerce partners.
While the pandemic is responsible for some of this popularity, Fain insists it is not the only reason for the eventful year. “It’s definitely bigger than the pandemic,” he said. “What you’re seeing is a food system that’s evolving and [people have a desire] to see transparency and traceability in the food system.” These, he says, are issues the traditional food supply chain isn’t really able to address right now, hence the opportunity for companies like Bowery, which effectively cut multiple steps out of the supply chain.
Bowery grows its greens (lettuces, herbs, and some custom blends) inside industrial spaces where crops are stacked vertically in trays and fed nutrients and water via a hydroponic system. Technology controls all elements of the farm, from the temperature inside to how much light each plants get. The company currently operates two farms, one in New Jersey and the other in Maryland. A third is planned for Pennsylvania.
Technology, in particular, is something Bowery has big plans for. On top of a retail expansion, Bowery also added some notable personnel to its staff, including Injong Rhee, formerly the Internet of Things VP at Google as well a chief technologist at Samsung. Having such technology chops onboard will be vital in order for Bowery to realize many of its ambitions around advanced automation, which has the potential to optimize many parts of the seed-to-store process for vertically grown greens.
For example, Bowery’s farms are equipped with sensors and cameras that are constantly collecting data — “billions” of points, according to the company — that can be used to not just observe the current state of plant health but also predict the most optimal growing conditions for each crop. Elements like temperature, humidity levels, nutrient levels, and light intensity can all be adjusted, via the BoweryOS software, to create those optimal conditions. The end result is more consistent crop production, better yields, more flavorful food, and, ideally, a better nutritional profile for the greens compared to what conventional produce offers.
The system can also, through automation and AI, detect problems with plants. In a recent interview with Venture Beat, Bowery Chief Science Officer Henry Sztul used the example of butterhead lettuce yellowing at the edges during growth. Bowery’s system is technologically advanced enough at this point that it is starting to understand the conditions that create those yellowing edges. That foreknowledge, in turn, will allow growers to adjust the crop “recipe” (see above mixture of lights, temperature, etc.) to avoid the problem.
It took Bowery years to get to this point in terms of what its technology is capable of doing. “The system [for] indoor farming that you choose has a direct impact on the crops you’ll be able to grow, on the margins you’ll be able to generate, and on the return profile of the business itself,” said Fain. “And so being incredibly intentional and thoughtful about what technology you use is something we spent a lot of time on because it has an extraordinarily important economic impact.”
On a less technically complex note, controlled ag from Bowery and others also goes some way towards reinventing the supply food chain. Rather than greens being harvested in, say, Mexico and shipped via a complex distribution process all the way to Baltimore, they are packaged up at the farm and distributed to nearby retailers, usually those within a day’s drive “It is much more sustainable. It is much more efficient, and it’s more reliable, and those things have been important to consumers long before COVID,” said Fain.
Bowery will continue to innovate on both the technology and supply side of its business, as well as with the food itself. The company just launched a new specialty product line that will experiment with different flavors of greens and change frequently.
In terms of tech, Bowery’s latest farm, currently being built in Bethlehem, Pennsylvania, will incorporate even more automation than the company’s two existing farms. That location is slated to open later in 2021. When it does, Bowery will be capable of serving nearly 50 million people within a 200-mile radius.
The company hopes to expand its geographic reach much wider some day, building farms near most major U.S. cities and beyond. Given the increased confidence in the vertical farming sector as a whole, now looks to be the optimal time to move towards those ambitions.
by Jennifer Marston, The Spoon
Bringing The Future To life In Abu Dhabi
A cluster of shipping containers in a city centre is about the last place you’d expect to find salad growing. Yet for the past year, vertical farming startup Madar Farms has been using this site in Masdar City, Abu Dhabi, to grow leafy green vegetables using 95 per cent less water than traditional agriculture
Amid the deserts of Abu Dhabi, a new wave of entrepreneurs and innovators are sowing the seeds of a more sustainable future.
Image from: Wired
A cluster of shipping containers in a city centre is about the last place you’d expect to find salad growing. Yet for the past year, vertical farming startup Madar Farms has been using this site in Masdar City, Abu Dhabi, to grow leafy green vegetables using 95 per cent less water than traditional agriculture.
Madar Farms is one of a number of agtech startups benefitting from a package of incentives from the Abu Dhabi Investment Office (ADIO) aimed at spurring the development of innovative solutions for sustainable desert farming. The partnership is part of ADIO’s $545 million Innovation Programme dedicated to supporting companies in high-growth areas.
“Abu Dhabi is pressing ahead with our mission to ‘turn the desert green’,” explained H.E. Dr. Tariq Bin Hendi, Director General of ADIO, in November 2020. “We have created an environment where innovative ideas can flourish and the companies we partnered with earlier this year are already propelling the growth of Abu Dhabi’s 24,000 farms.”
The pandemic has made food supply a critical concern across the entire world, combined with the effects of population growth and climate change, which are stretching the capacity of less efficient traditional farming methods. Abu Dhabi’s pioneering efforts to drive agricultural innovation have been gathering pace and look set to produce cutting-edge solutions addressing food security challenges.
Beyond work supporting the application of novel agricultural technologies, Abu Dhabi is also investing in foundational research and development to tackle this growing problem.
In December, the emirate’s recently created Advanced Technology Research Council [ATRC], responsible for defining Abu Dhabi’s R&D strategy and establishing the emirate and the wider UAE as a desired home for advanced technology talent, announced a four-year competition with a $15 million prize for food security research. Launched through ATRC’s project management arm, ASPIRE, in partnership with the XPRIZE Foundation, the award will support the development of environmentally-friendly protein alternatives with the aim to "feed the next billion".
Image from: Madar Farms
Global Challenges, Local Solutions
Food security is far from the only global challenge on the emirate’s R&D menu. In November 2020, the ATRC announced the launch of the Technology Innovation Institute (TII), created to support applied research on the key priorities of quantum research, autonomous robotics, cryptography, advanced materials, digital security, directed energy and secure systems.
“The technologies under development at TII are not randomly selected,” explains the centre’s secretary general Faisal Al Bannai. “This research will complement fields that are of national importance. Quantum technologies and cryptography are crucial for protecting critical infrastructure, for example, while directed energy research has use-cases in healthcare. But beyond this, the technologies and research of TII will have global impact.”
Future research directions will be developed by the ATRC’s ASPIRE pillar, in collaboration with stakeholders from across a diverse range of industry sectors.
“ASPIRE defines the problem, sets milestones, and monitors the progress of the projects,” Al Bannai says. “It will also make impactful decisions related to the selection of research partners and the allocation of funding, to ensure that their R&D priorities align with Abu Dhabi and the UAE's broader development goals.”
Image from: Agritecture
Nurturing Next-Generation Talent
To address these challenges, ATRC’s first initiative is a talent development programme, NexTech, which has begun the recruitment of 125 local researchers, who will work across 31 projects in collaboration with 23 world-leading research centres.
Alongside universities and research institutes from across the US, the UK, Europe and South America, these partners include Abu Dhabi’s own Khalifa University, and Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence, the world’s first graduate-level institute focused on artificial intelligence.
“Our aim is to up skill the researchers by allowing them to work across various disciplines in collaboration with world-renowned experts,” Al Bannai says.
Beyond academic collaborators, TII is also working with a number of industry partners, such as hyperloop technology company, Virgin Hyperloop. Such industry collaborations, Al Bannai points out, are essential to ensuring that TII research directly tackles relevant problems and has a smooth path to commercial impact in order to fuel job creation across the UAE.
“By engaging with top global talent, universities and research institutions and industry players, TII connects an intellectual community,” he says. “This reinforces Abu Dhabi and the UAE’s status as a global hub for innovation and contributes to the broader development of the knowledge-based economy.”
Democratic Mayoral Candidates Offer Ideas for Addressing Food Insecurity
Nine candidates vying for the Democratic nomination to become the next mayor of New York City gathered Tuesday morning in a virtual forum to discuss their visions for the city's food policy and serving the roughly 2 million New Yorkers who are food insecure
Image from: Ed Reed/Mayoral Photography Office
Nine candidates vying for the Democratic nomination to become the next mayor of New York City gathered Tuesday morning in a virtual forum to discuss their visions for the city's food policy and serving the roughly 2 million New Yorkers who are food insecure.
At the "Town Hall on the Future of Food in New York City" -- hosted by Hunter College in partnership with City Harvest, CUNY Urban Food Policy Institute, Food Bank for NYC, Hunger Free America, and other organizations, and moderated by NY1 anchor Errol Louis -- the candidates discussed the city's urgent need to manage rampant hunger during the pandemic and center it in the recovery effort. But the discussion also focused on the pre-existing problems of food insecurity, inequitable access to nutritious meals, and inefficiencies and lack of sustainability in the city's food use.
The participants, who were selected based on their polling and fundraising standings among a field of dozens of candidates, included Brooklyn Borough President Eric Adams, former federal housing secretary Shaun Donovan, former city sanitation commissioner and "covid food czar" Kathryn Garcia, former Citigroup executive Ray McGuire, former nonprofit executive Dianne Morales, former city veterans' services commissioner Loree Sutton, city Comptroller Scott Stringer, small business owner Joycelyn Taylor, and Maya Wiley, a civil rights attorney and former counsel to Mayor Bill de Blasio. Louis pushed them to focus on how they would bring anti-hunger initiatives to scale to address the food crisis compounded by the pandemic.
Programs to help feed New Yorkers have often missed the mark, failing to meet adequate health standards and leaving many New Yorkers out entirely. A 2017 study from the Robin Hood Poverty Tracker found 1 in 4 eligible food stamp, or SNAP, recipients -- 700,000 New York City residents -- were not enrolled in the program, less than the statewide participation rate of 93 percent the same year, according to the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities. In September, the Poverty Tracker reporter 1.7 million New Yorkers were getting food stamps, over 200,000 more than last February. During roughly the same period the percentage of food stamp recipients who also used a food pantry doubled, from 27 percent of enrollees to 60 percent.
Nearly all candidates agreed on the need to increase SNAP benefits, and improve enrollment in the program; expand community gardens and urban agriculture; and improve access to nutritious food throughout communities and in institutional settings like schools and food pantries. There was also broad consensus around creating a more unified food procurement and distribution system in New York City by strengthening the Mayor's Office of Food Policy. Multiple candidates highlighted the frequent lack of coordination among the myriad city agencies that provide food as part of their services.
"One of the reasons why I needed to step in is that the Mayor's Office of Food Policy is incredibly understaffed," said Garcia, who managed the city's emergency food response last summer before leaving the de Blasio administration last fall and launching her campaign to succeed him.
"[Food Policy Director] Kate McKenzie does an amazing job but she doesn't have procurement authority, she doesn't have logistical authority...one of the clear things is how we approach food is very siloed, very fragmented," Garcia said, noting the separate food procurement activities of the Department of Education, Department of Correction, and senior centers. Garcia says the city provided 1 million meals a day and shored up food pantries last summer under her leadership. (Shortly after the forum, Garcia released a multi-pronged platform to fight food insecurity with an emphasis on enrolling more New Yorkers in SNAP and expanding what the benefits would cover.)
Adams, who repeatedly discussed the need for nutritious food, criticized the nutritional value of many of the government-provided or -supported food services, including Garcia’s covid effort, and said increasing the size of the Mayor's Office of Food Policy would have a limited impact if the city did not also incorporate the new perspectives from food-access "visionaries."
"They don't share the values," Adams said of the city's food-oriented bureaucrats, historically. "I am amazed at the roadblocks, that organizations like Rockaway Youth Task Force are not able to scale," he said during a segment of the conversation on urban agriculture programs.
Some of the candidates saw the city's food dilemmas rooted in job scarcity and low wages and frequently discussed the importance of building food policy into the city's economic recovery.
"We solve none of this if we don't recognize that fundamentally what is broken and why 30% of our people were not eating through the month before covid is because the rent was too damn high and people were choosing to pay rent instead of buying groceries," Wiley said, adding, "at the end of the day it is about the city's ability to generate new jobs." Wiley has announced a plan as mayor to create 100,000 jobs through a $10 billion capital investment and cited it as an example of how she would leverage existing city resources to bring her approach to scale.
"Fundamentally, food insecurity is about income and it is about the fact that we do not intentionally ensure that our young people have pathways to careers and are prepared for the careers of the 21st Century," said Garcia.
The conversation of workforce development dovetailed with another on building an urban agrarian economy in New York to create good jobs and ensure both sustainable and equitable food access for city residents.
"We need to also think about aligning not just food policy, but the resilience office that exists right now to work more in tandem with each other because we know that food justice is also climate justice," said Morales, who was the executive director of Phipps Neighborhoods in the South Bronx, a social services provider. As mayor, Morales said she would invest $25 million to food innovation and sustainability programs in communities of color.
Multiple candidates, including Stringer, Donovan, and Adams wanted to see a greater emphasis on local and regional food procurement. "If I'm mayor, I really want to create a Mayor's Office of Food Markets because we've got to link farming with communities and for a farm-to-table policy that brings the purchasing power of this city regionally, upstate, downstate, and create those relationships," Stringer said. "Farmers markets should be everywhere."
Image from: Square Roots
"There is huge potential to grow, so to speak, the power of locally-grown produce," said Donovan, who was the city’s housing commissioner under Mayor Bloomberg before spending all eight years in the Obama presidential cabinet. "We need innovative approaches to ensure we are using every inch of available space that we can." Like other candidates, he expressed support for ideas like more community gardens and vertical agriculture. Donovan also repeatedly stressed the need to support struggling restaurants and incorporate them into the city's food programs as well as its economic recovery.
While supportive of partnerships with upstate and Long Island counties, Garcia took issue with the notion that New York could achieve a sustainable food market locally. "If we want fresh, healthy food day in and day out, we're not harvesting today in this region, we are going to have to bring it in," she said following Donovan's comments. "We need to make sure the systems go beyond just this region so that we can still be getting lettuce even though it's February."
"That should not hold us back from starting to have a robust agrarian economy in New York City," Adams countered, echoing Donovan's statements about the importance of life sciences in city schools and connecting lessons about food production to healthy eating.
When asked directly whether they would use the city's power of eminent domain to force the sale of private land for the city to use, most candidates raised their hands affirmatively. Adams expressed his dissent, noting that the many existing city resources that he said are being wasted or under-utilized should be tapped before forcing land sales. (Others also raised the importance of better using available land, with Stringer naming a report he issued as comptroller on the number of vacant city-owned lots that could be used to develop housing and noting that many lots could also be used for community gardens.)
McGuire, who recently stepped down from one of the biggest jobs on Wall Street to run for mayor, also criticized the mismanagement of city resources and cautioned on the costs to the city that eminent domain could pose. "It gets expensive so you have to figure out when you exercise eminent domain at market rates who is going to pay for it," he said.
Equity was an overriding theme in a number of areas of the food policy discussion, from eradicating food deserts to ensuring healthy options in schools and pantries.
"I think we do have a moral obligation to ensure that every resident of the city has those basic needs of food and housing," said Taylor, who created the nonprofit NYC WMBE Alliance, according to her website. "We have to make sure that when we look at the budget we look things that are 'nice to have' and things that are 'needs to have,' and if it means that we have to reallocate funds from the things that are nice to have to the needs, then that's what I would do."
"We need to stop leaving communities out of the co-creation process," said Morales, who stressed participation of food advocacy groups.
Wiley and Taylor also discussed the need for community participation in the form of locally-based food councils to inform nutrition, per Wiley, and more active mayoral outposts in each borough, per Taylor. Both also discussed the importance of collecting more targeted data to better determine the outcomes of food programs. Other candidates outlined plans or past work to incorporate cultural sensitivity into food access, including then-Manhattan Borough President Stringer's 2008 "Go Green East Harlem Cookbook" and Garcia's discussion of halal and kosher options in meal services, something others mentioned as well.
The candidates agreed that compounded structural problems of food deserts and the reliance of low-income communities on the city's various food programs exacerbate malnutrition and health outcomes, but not all offered the same solution.
"Today food deserts are such that many of our people don't have access to healthy food. They have access to those institutions that provide food that is pretty low on the nutrition scale," McGuire said. He laid out a more corporate-friendly view of the path forward, that involved rezoning to allow big supermarket chains, hiring gig workers to deliver meals to seniors, and bringing refrigeration resources to bodegas in order to better store fresh produce.
As is often the case, Morales was at the other end of the spectrum, saying she supports community land trusts to create both better access to fresh produce and greater "food sovereignty" in poor communities. Sutton said the solution was to leverage public-private partnerships.
"It's one thing to talk about all these ideas, but in the same breath to disdain, disparage and disrespect the top 1 percent of New Yorkers who bring in nearly 40 percent of our tax base or reject and shun real estate as one example, as a number of my fellow candidate have during this campaign," said Sutton, a former Army psychiatrist who led de Blasio's Department of Veterans' Services. "We are absolutely shutting down those pathways to partnership and prosperity."
Warehouse Becoming Vertical Farms — And They’re Feeding New Jersey
New Jersey's vertical farms are transforming agriculture by helping farmers meet growing food demand. New Jersey Agriculture Secretary Doug Fisher said that while conventional farming in outdoor fields remains critical, vertical farming has its advantages because of its efficiency and resistance to pests and thus less need for chemicals
Image from: New Jersey 101.5
New Jersey's vertical farms are transforming agriculture by helping farmers meet growing food demand.
New Jersey Agriculture Secretary Doug Fisher said that while conventional farming in outdoor fields remains critical, vertical farming has its advantages because of its efficiency and resistance to pests and thus less need for chemicals.
Vertical farming is the process of growing food vertically in stacked layers indoors under artificial light and temperature, mainly in buildings. These plants receive the same nutrients and all the elements needed to grow plants for food.
Vertical farms are also versatile. Plants may be growing in containers, in old warehouses, in shipping containers, in abandoned buildings.
"That's one of the great advantages — that we can put agriculture in the midst of many landscapes that have lost their vitality," said Fisher.
ResearchandMarkets.com says the U.S. vertical farming market is projected to reach values of around $3 billion by the year 2024.
The one drawback is that its operational and labor costs make it expensive to get up and running.
Image from: AeroFarms
In the past decade, however, vertical farming has become more popular, creating significant crop yields all over the state.
AeroFarms in Newark is the world's largest indoor vertical farm. The farm converted a 75-year-old 70,000-square-foot steel mill into a vertical farming operation. AeroFarms' key products include Dream Greens, its retail brand of baby and micro-greens, available year-round in several ShopRite supermarkets.
Kula Urban Farm in Asbury Park opened in 2014. Vacant lots are transformed into urban farms and there's a hydroponic greenhouse on site. That produce is sold to local restaurants.
Beyond Organic Growers in Freehold uses no pesticides and all seeds and nutrients are organic. There's a minimum of 12,000 plants growing on 144 vertical towers. On its website, it says the greenhouse utilizes a new growing technique called aeroponics, which involves vertical towers where the plant roots hang in the air while a nutrient solution is delivered with a fine mist. It also boasts that by using this method, plants can grow with less land and water while yielding up to 30% more three times faster than traditional soil farming.
Vertical farms in New Jersey help feed local communities. Many are in urban areas and are a form of urban farming.
Fisher predicts that vertical farms will be operational in stores and supermarkets around the state.
"It's continued to expand. There's going to be many, many ways and almost any area in the state has the opportunity to have a vertical farm," Fisher said.
London Food Bank Is Going Greener With Greenhouse
CTV's Nick Paparella check in on the progress as the food bank aims to grow some of its own fresh produce for use during the winter months.
Nick Paparella CTV News London Reporter
Inside the London Food Bank's greenhouse in London, Ont. on Friday, Jan. 29, 2021. (Nick Paparella / CTV News)
LONDON, ONT. -- The outdoors may be covered in a blanket of white in January, but at the London Food Bank these days everything seems to be coming up green.
After a year of planning and with donations from the community, the new greenhouse is bearing fruit - or in this case vegetables.
“This is what Londoners a few years ago wanted more than anything else, to donate funds towards fresh fruits, fresh produce and that's what they have done,” says Glen Pearson from the London Food Bank. “So we've just taken it to a different level so we can grow our own as well.”
The man with the green thumb here is horticulturalist Luis Reyes.
“A couple of weeks ago we received the heaters and since then you can see the growth in only a couple of weeks,” says Reyes.
Like many from the food bank, Reyes is passionate about helping those in need.
“I am a grower and that's what I like to do and now to do it directly to people makes me proud,” he says.
The greenhouse is expected to grow about 15,000 plants a year which amounts to about four tons of food.
“You're not going to get anything fresher than this in a supermarket,“ says Reyes. “So probably you're going to harvest today here and the people or clients are going to receive it tomorrow or the same day.”
In the winter months, they are growing cold-weather plants like lettuce, spinach and even kale, but once summer arrives they will switch to tomatoes, cucumbers and fruit-bearing plants.
Adds Pearson, “It just expands the nutrition we're able to give to other people.”
Resetting The Food System From Farm to Fork
Resetting the future of food is possible and with this aim, we will present in an international debate- concrete solutions to rethink our food systems from farm to fork
Barilla Foundation and Food Tank invite you to attend the online event “Resetting the Food System from Farm to Fork: Setting the Stage for the 2021 UN Food Systems Summit” to be held on December 1st, from 2.00 PM CET.
Resetting the future of food is possible and with this aim, we will present in an international debate- concrete solutions to rethink our food systems from farm to fork.
The event will begin by highlighting the critical role of farmers in feeding the world and managing natural resources, food business in progressing towards the 2030 Agenda, and chefs in re-designing food experiences.
Here are details of the first three conversations of the day, which will feature, among others, the likes of Edie Mukiibi, Vice President, Slow Food International; Massimo Bottura, Chef and Owner, Osteria Francescana; Jeffrey Sachs, Professor and Director of the Center for Sustainable Development, Columbia University; Director, U.N. Sustainable Development Solutions Network; Elly Schlein, Vice President, Emilia Romagna Region.
REGISTER FOR FREE NOW
The world needs urgent action on agriculture and food systems.
Let's make the future grow!
2030 is the deadline to achieve all 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The next decade is a chance to remake our future. Through the “Decade of Action”, we all have a part to play in the transition towards sustainable economic, social, and environmental development—with sustainable food systems at its heart.
In a rapidly changing world, food systems face substantial challenges, including the COVID-19 pandemic acting as a multiplier of food and nutrition insecurity. Globally, two billion people are malnourished. More than 700 million adults are obese while at least 820 million suffer from hunger—a statistic that will no doubt increase as a result of the pandemic. And some one-third of the global harvest is lost or waste. Biodiversity is declining, water and land are increasingly degraded, climate change is posing adverse impacts on agricultural production and livelihoods.
We must act now to address the impending global food emergency and avoid the worst impacts of the pandemic while seizing upon the opportunity of resetting food systems. Over the next 20 years, food systems will need to nourish 10 billion people while also protecting precious natural resources for future generations. The spread of COVID-19 has demonstrated the fragility of global food systems, but it also offers opportunities to transform the way we produce, distribute, and consume food.
Join the conversation
Distinguished speakers
Leading experts, world-renowned chefs, and international journalists will convene for this unique virtual event.
Lively discussions
Panels will cover diverse themes including the role of food as medicine, the new food economy, and the EU’s Farm to Fork strategy.
Trends spotlights
The latest food and agricultural technologies will be discussed, as well as how chefs are re-designing food experiences.
Concrete change
The event will generate recommendations that will help set the stage for the 2021 United Nations Food Systems Summit.
SPEAKERS
US Farming Is Tasteless, Toxic And Cruel
and its monstrous practices have no place here: Radio 4’s veteran food presenter Sheila Dillon decries ministers’ dangerous plans
By SHEILA DILLON FOR THE DAILY MAIL
19 September 2020
And its monstrous practices have no place here: Radio 4’s veteran food presenter Sheila Dillon decries ministers’ dangerous plans
British farming and food production are a remarkable success story. In recent years, this sector has been at the forefront of a revolution that’s transformed the quality of our food — and acted as a guardian of our countryside.
Through the vision and dedication of our farmers, Britain is increasingly a global leader in animal welfare, environmental protection, and high standards of produce. Now all these achievements are at mortal risk. As we prepare to leave the European Union at the end of this year, our impressive agricultural system could soon be wrecked by ruthless competition and a flood of cheap imports.
The most serious threat comes from the U.S., whose vast and unwieldy farming industry is far less regulated than ours.
In the name of efficiency, it has built a highly mechanised, intensive, and shockingly cruel approach which keeps animals in conditions so appalling it’s hard for us in the UK to grasp. Meanwhile, an arsenal of chemicals that are banned here are also deployed on these poor creatures.
It is not the sort of produce that should be allowed to swamp our own. When Brexit supporters spoke of ‘taking back control’, they did not envisage the destruction of British farming caused by mass-produced goods soaked in chlorine and cruelty.
In an attempt to prevent this grim eventuality, a last-ditch battle is under way at Westminster aiming to establish essential safeguards in post-Brexit Britain.
As the Agriculture Bill — which sets out a new domestic, post-Brexit alternative to the EU’s Common Agricultural Policy — makes its way through Parliament, MPs in the Commons and peers in the Lords have tried to impose amendments to keep Britain’s high standards of animal husbandry and environmental care. So far the Government has rejected all such proposals. Desperate to reach a trade deal, ministers seem unwilling to block the hugely influential U.S. food and agriculture lobby from gaining access to our market.
Their argument is that, in the brave new world of deregulation, consumers will enjoy more choice and, crucially, will have access to ‘cheap’ food. But cheapness will come at a huge cost to our health, our countryside, our rural economy, and our animals.
The reality is that choice will be restricted — because British farmers and producers will find it impossible to compete. From the supermarkets to takeaways, this ugly juggernaut of American food will sweep all before it.
The Agriculture Bill is about to go to the final stage of its passage through Parliament. There is one last chance for legislators to stop a free-for-all from which our agriculture would emerge the loser.
As someone who has covered the food industry for 20 years presenting The Food Programme on BBC Radio 4, I am deeply alarmed at the prospect of the advances British food has made in recent decades going into reverse.
Before COVID, British food was flourishing as never before. I think of the surge in high-quality bakeries, of our farmhouse cheeses beating rivals across the world — we produce more than France.
Even McDonald’s UK now uses free-range eggs and organic milk and recently won an RSPCA award for its animal welfare standards. I need hardly say it’s not how McDonald’s operates in the U.S.
It’s all part of Britain’s deep and enduring compassion for animals. We have 25 million free-range hens here, more than any other country — and more free-range pigs than anywhere in Europe.
In frequent talks with farmers, I have been struck by how they see themselves, not just as producers, but as custodians of the land, a vital role they fill with imaginativeness in an age of mounting concern about climate change.
The U.S. farming model is completely different. Its aim is not to work with nature but to dominate it. Industrialised and chemicalised, the entire system is a monument to the denial of biology.
I am not in any way anti-American — I’ve lived across that wonderful country in Indiana, California, Massachusetts, and New York. I’m married to an American: my son and his family live in Pennsylvania.
It’s precisely because I visit regularly, and have seen at first hand the harshness of U.S. food production, that I feel so strongly.
The ‘chlorinated chicken’ has rightly become a symbol of U.S. farming at its worst, but few ask why poultry has to be washed in chlorine before it can be sold. It is because the birds are kept in such over-crowded squalor and so pumped with chemicals during their brief, unfortunate lives.
The same applies throughout American industry. Even the British Government’s farming Secretary George Eustice has admitted U.S. animal welfare law is ‘woefully deficient’. Pigs are reared in grotesquely inhumane battery farms. More than 60 million are treated with the antibiotic Carbadox, which promotes growth and is rightly banned in the UK.
Similarly, U.S. cattle are fed steroid hormones to speed growth by 20 percent — the use of such chemicals has been illegal in Britain and the EU since 1989. And as the cattle are kept in vast confined feeding pens, they need regular antibiotics.
Incredibly, some staff processing carcasses at huge meatpacking plants wear nappies because they are not allowed time off to go to the lavatory. In arable production, pesticides are used on a scale far beyond anything in Britain. In recent decades, the U.S. has banned or controlled just 11 chemicals in food, cosmetics, and cleaning products — the EU has banned 1,300.
Polar opposites: Cows in a British field, and in beef pens in Texas
In U.S. farming there’s almost no effort to mitigate climate change yet here the National Farmers’ Union is committed to achieving zero carbon production by 2040. What will happen to that commitment if cheap U.S. food floods in?
The U.S. genetically modified crops to be resistant to Roundup weedkiller — but after weeds grew resistant to Roundup and flourished, one U.S. farmer told me proudly crops were now engineered to be resistant to the infamous Agent Orange, a defoliant used by the U.S. military to kill vegetation in the Vietnam War.
Environmental devastation and health problems — including disabilities to as many as a million people — were caused in Vietnam by Agent Orange. Is this a road we want to go down in Britain?
The so-called cheapness of American produce is a delusion. These farming methods carry a heavy price in quality and health. A battery chicken is tasteless compared to an organic one, just as factory-farmed salmon has nothing of the flavour of wild.
Cheap, low-quality foods have brought with them disturbing health problems including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.
The coronavirus crisis proved the need for resilient supply lines. But that cannot be achieved if we ruin our own domestic agricultural system and become reliant on imported food.
In World War II, when the survival of the nation was imperilled, the Government attached huge importance to domestic food output, reflected in the propaganda campaign ‘Dig for Victory’ and the Women’s Land Army. We need that collective spirit today.
It would be stupidity beyond measure to obliterate our farming industry for a short-term, unbalanced trade deal with the U.S.
A trade deal without agricultural safeguards would be a calamity for British farming and our prosperity. One in eight jobs in Britain is in food supply, while food exports brought in £9.6 billion to the economy. All that will be lost if cut-throat competition prevails.
And a vital part of our heritage will also be lost. From the robust imagery of John Bull as a yeoman squire to William Blake’s Jerusalem, with its evocation of our ‘green and pleasant land’, the countryside has always held a central place in our national soul. It must not be sacrificed on the altar of illusory cheapness or trans-Atlantic subservience.
Lead photo: It’s all part of Britain’s deep and enduring compassion for animals. We have 25 million free-range hens here, more than any other country — and more free-range pigs than anywhere in Europe
Sheila Dillon presents BBC Radio 4’s The Food Programme.