Welcome to iGrow News, Your Source for the World of Indoor Vertical Farming
Agtech Company AppHarvest Has Secured A $91m Financing Arrangement With Sustainably-Focused Investment Firm Equilibrium Capital To Fuel The Future Construction of 12 High-Tech Indoor Farms by 2025
Agtech company AppHarvest has secured a $91m financing arrangement with sustainably-focused investment firm Equilibrium Capital to fuel the future construction of 12 high-tech indoor farms by 2025.
By Mary Ellen Shoup
July 27, 2021
Agtech company AppHarvest has secured a $91m financing arrangement with sustainably-focused investment firm Equilibrium Capital to fuel the future construction of 12 high-tech indoor farms by 2025.
Read The Rest Here: HTTPS://WWW.FOODNAVIGATOR-USA.COM/ARTICLE/2021/07/27/APPHARVEST-SECURES-91M-FINANCING-TO-FUEL-2025-INDOOR-FARMING-AMBITIONS
Light Science Technologies Launches Sustainable nurturGROW LED Lighting Range
Leading UK AgTech company Light Science Technologies (LST) has launched nurturGROW to the market, its new sustainable grow lighting product range, offering an innovative, high-performance and cost-effective solution for indoor farming, covering greenhouses, vertical farming, polytunnels and medicinal plants.
July 21, 2021
90% recyclable and interchangeable design enables growers to simply upgrade and replace
Leading UK AgTech company Light Science Technologies (LST) has launched nurturGROW to the market, its new sustainable grow lighting product range, offering an innovative, high-performance and cost-effective solution for indoor farming, covering greenhouses, vertical farming, polytunnels and medicinal plants.
Created with four core component parts, the patent-pending nurturGROW range is made of high-quality, durable materials to give growers the ideal balance between strength and optimal performance. 90% of the components are recyclable, minimizing the amount of materials needed to drastically cut down on waste and reduce carbon footprint. Thanks to its sustainable, future-proof design, 85% of nurturGROW is also reusable, allowing growers to easily upgrade components, cost-effectively and with no downtime, making nurturGROW easy to maintain. Backed by a 25-year product lifecycle, it ensures indoor farmers maximize the use of every element over a longer lifespan to generate maximum yields and save them a third on future costs.
Built for scale and sustainability
Thanks to its modular structure, the nurturGROW range consists of more than 30 different options with variable lengths of up to 2.78m, making it the longest luminaire on the market. It provides the scale needed to commercialize the right recipe and cut down on waste with both energy and space. With a high efficacy of up to 3.0 umol/J and up to 30-degree variance, growers can choose from 1000s of different light recipes to improve plant performance, from one of the widest ranges of recipes available on the market.
What’s more, nurturGROW enables you to give back to the environment. As proud reforestation partners of One Tree Planted, they plant one tree for every LST product sold, as part of a mutual commitment to champion global reforestation efforts and raise awareness of the importance of ecosystem restoration.
In-house UK scientific and manufacturing expertise
nurturGROW features industry-leading, high performing LED lighting innovation by drawing on its own in-house manufacturing capabilities, assuring growers of nothing
less than high quality and high performance grow lighting. This is supported by a successful tried and tested approach in real environments to prove nurturGROW’s long-lasting lighting technology.
Backed by science, LST works with growers to create the perfect recipe for crop growth. Using light testing equipment and data gathered from LST’s purpose-built laboratory, its in-house team of scientists can help identify the right spectral waveforms and PPFD levels by recreating various environment scenarios in one of its accredited grow chambers.
Grow more, with less
Founded in 2019, LST’s approach from the beginning was to create a bespoke, fully integrated lighting solution that met key criteria for CEA farmers and growers: sustainability, cost-effectiveness, and high performance. Knowing that each growing environment has its own set of unique requirements, nurturGROW gives growers optimum control over their crops with the potential to deliver optimal yield and minimize both CAPEX and OPEX costs.
Craig Price, Operations Director at Light Science Technologies, said: “Being customer-focused by design means that as an experienced LED grow light partner, we understand every variable and can help indoor growers to design a sustainable solution that fits their unique growing parameters.
“This extends to adjusting the light recipe for growers, as nurturGROW will allow you to increase, decrease or change the recipe depending on preference, thanks to an interchangeable luminaire body.
“The unique aspect of our design also means that we have already allowed for future integration of sensor technologies, offering significant added value. By choosing to add in our new sensor technology, which is under development, indoor growers and farmers can look to control their environment in much more granular detail. This will enable them to reduce any sub-optimal performances, whether that be in any environmental controls or from the light itself.”
Building A Vertical Farm With Partners — An Ongoing Case In Switzerland
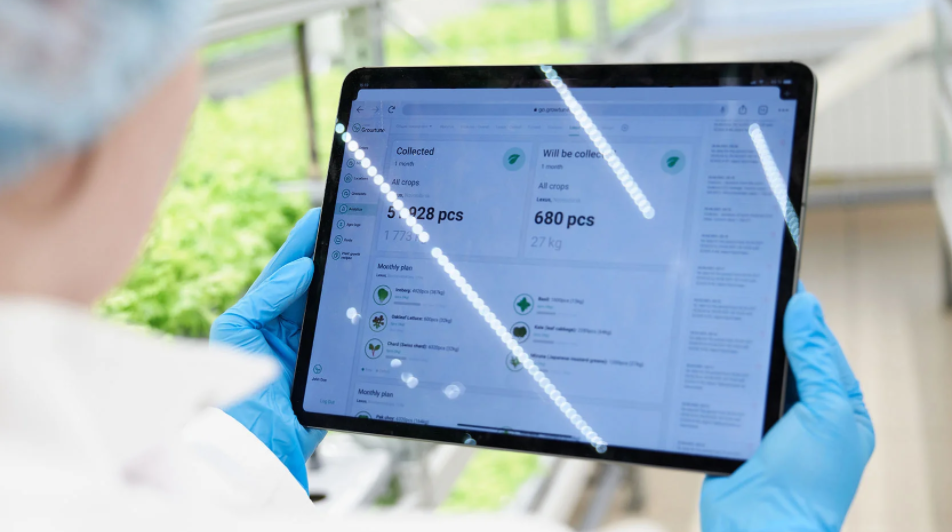
iFarm has recently announced a partnership with YASAI and Logiqs to create a new vertical farm in Switzerland. Working together, we aim to expand into new locations, highlight the growth potential of vertical farming in Europe and showcase the benefits of working with industry partners
iFarm has recently announced a partnership with YASAI and Logiqs to create a new vertical farm in Switzerland. Working together, we aim to expand into new locations, highlight the growth potential of vertical farming in Europe and showcase the benefits of working with industry partners.
On 5 February 2021, iFarm (The Netherlands), YASAI AG (Switzerland) and Logiqs B.V. (The Netherlands) announced a strategic partnership with plans to launch Zurich’s first vertical farm. iFarm will supply the nutrient solution management system, specialist sensors, control systems and Growtune software platform and Logiqs will be supplying automated shelving systems at Yasai’s 673 sq. m plantation.
Now, we’re giving you behind-the-scenes access to the data and decisions that were the driving force behind the venture.
With contributions from Mark E. Zahran, Co-Founder, and CEO of YASAI, Gert-Jan van Staalduinen, CEO and Owner of Logiqs, and Kirill Zelenski, Managing Director of iFarm Europe, we’ll look at how and why this strategic partnership came about and what the future holds.
Read on to find out more about what goes into launching a successful vertical farm and how you can achieve the same goals.
Why Switzerland? Why Europe?
As you may already know, location is a critical factor when assessing the feasibility of a vertical farm. Locating a vertical farm in a densely populated urban area, with limited access to traditional farming facilities and rural land, ensures there is untapped demand for locally grown produce.
For Mark, being based in Switzerland made Zurich a natural choice for the first YASAI vertical farm. However, selecting the right location wasn’t merely a matter of convenience, as he emphasised:
The market is here. The market demands local produce, grown in a responsible and sustainable way, and, with the right technology, you can meet the demand and create a successful business.
Although the concept of vertical farming is becoming increasingly popular in Europe, there’s no doubt that the regional market lags behind its U.S. and Asian counterparts, but this needn’t be a deterrent for potential investors or farmers. In fact, the growth potential makes vertical farming in Europe a viable form of investment:
Vertical farming has grown more quickly in America and Asia but, I think, in the end, we will have a more sustainable model and acceleration is already taking place.
Gert, Logiqs
With demand for fresh, locally sourced produce creating a market for vertical farms and investors actively seeking out new ventures, it’s clear that Switzerland, and Europe as a whole, is a prime location for the partnership. By taking a strategic approach, other farmers, entrepreneurs and start-ups can use the same parameters to identify key locations for future vertical farms.
Do Local Trends Matter?
Local trends and current market conditions certainly play a role in identifying viable locations, and opportunities, for vertical farming. Whether you’re forming a partnership or starting your own venture, you’ll want to ensure that your vertical farm is situated in an area that prioritises what you can offer.
In Europe, for example, the current range of fresh produce available in the supermarkets is somewhat limited, despite the growing popularity of pesticide-free produce and plant-based foods. As awareness of environmental issues and climate change becomes more important to consumers, this is already being reflected in their decision-making and purchase behaviour.
The European Statistics Handbook reports that Nordic countries (Sweden, Finland and Denmark) are responsible for just 1.5% of Europe’s fresh produce, with the local climate being cited as the main obstacle to production. With climate-controlled production facilities, however, the potential of vertical farming in this region is clear and presents a worthwhile investment for entrepreneurs, farmers and investors.
Furthermore, the CBI estimates that Europe is responsible for 44% of worldwide fresh fruit and vegetable trade. Exporters to the region are encouraged to capitalise on the continent’s ‘off season' in order to maximise their profits. While traditional farming methods do, of course, result in off seasons, this no longer needs to be the case. The ability of vertical farmers to grow high-quality produce year-round using climate-controlled environments effectively eradicates off seasons and facilitates domestic fruit and vegetable production.
Based on these trends, it’s possible to predict that European consumers will respond positively to the presence of pesticide-free, locally grown, produce in shops and restaurants. For retailers and food or vegetables distributors, this makes partnering with vertical farmers a viable and exciting venture.
In relation to our current partnership, the fact that Switzerland imports 48% of its vegetables, reflects the Europe-wide food production trends and indicates that there is a growing market for fresh, local produce:
When fresh produce is imported, companies are more focused on transportability than flavour or quality. By shortening the supply chain and growing produce locally, we can deliver better tasting vegetables and higher quality produce.
Mark, YASAI
At the same time, a more health-conscious society is placing greater emphasis on food quality and diversity. The emerging, ‘pay the farmer, not the doctor' movement, is reframing the way we think about food as the foundation of our health, which will no doubt impact future consumer behaviour.
If you look at the last 200 years, the amount that people spend on medical care was increasing all the time and the amount they paid for food was decreasing, so now we are at a sweet spot where it could change again and people would eat more consciously and also get less sick, which leads to a healthier society.
Mark, YASAI
It’s evident, therefore, that local trends have been a key factor in identifying the right location for YASAI’s new vertical farm. By assessing potential locations from an economic perspective, analysing the domestic market and identifying current and emerging trends, it’s possible to determine where vertical farms can have the greatest success.
Finding the Right Partners
When you’re embarking on any venture, it’s important to work with the right partners. So, how did the alliance between YASAI, Logiqs and iFarm come about?
Already operational in Europe, Russia and the MENA, iFarm was approached by YASAI on the basis of our leading vertical farm solutions, collaborative approach to farming and reputation within the industry. Indeed, the success of the solutions was a factor in why YASAI were so keen to work with iFarm:
What we saw, in terms of hardware, is that there are very good logistics partners out there, such as Logiqs, and, in terms of software, iFarm’s solutions were already proven. Also, the range of plant growth recipes available via iFarm’s Growtune software was critical to our goal of increasing crop and food diversity.
Mark, YASAI
From our perspective, we were excited to work with both YASAI and Logiqs to create Zurich’s first vertical farm. Both the passion and expertise of the partners were clear from the outset with the potential for a long-lasting and successful relationship. Furthermore, our economic analysis of the region confirmed what a lucrative market Europe is for vertical farming and further cemented our commitment to expanding in the region.
Kirill, iFarm
However, identifying the right partners isn’t solely about finding organisations who can meet your needs or deliver the solutions you need to begin operating.
We’ve been delivering horticultural solutions for 45 years, so we have a lot of experience we can bring to a partnership, but, when it comes to complex innovation, it’s very important to have partners that are open and all focused on the same objective, instead of their own, individual success.
Gert, Logiqs
Creating the vertical farm in Niederhasli, Zurich, is a joint collaboration, with YASAI taking on the management, operations and branding, Logiqs providing automated hardware and iFarm delivering the nutrient solution management system, climate control equipment and the Growtune software platform. While each partner is bringing distinct, critical components to the table, it’s the values and objectives that form the union and facilitate a constructive and collaborative working partnership.
What we really liked about iFarm is its collaborative mindset. That’s how we want to accelerate, vertical farming — with collaboration.
Mark, YASAI
Whether you’re a farmer, retailer, food distributor, investor or entrepreneur, there are partnership opportunities available right now. However, it’s important to think about long-term goals and what success looks like when you’re deciding who to work with. By partnering with people and companies that share your values and ambitions, you can work together cohesively and increase your success.
Why is Vertical Farming Important?
Vertical farms may be a profitable investment, but they offer much more besides revenue and profit. In addition to being a prime investment in Europe, vertical farming can change the way we approach food production and provide better access to food, as well as reducing the environmental impact current production methods have.
At iFarm, the potential to spark worldwide change and benefit society has always been the driving force behind the operations, and we’re pleased to partner with organisations who share these values.
We have the ambition to accelerate access to ‘honest food'. People will learn about this partnership and will start to think about the way we produce foods and the potential vertical farming has to solve some of the acute global issues.
Gert, Logiqs
As we move towards a more circular economy, there’s a greater emphasis on the need to minimise waste and make better use of our resources. In comparison to traditional farming or greenhouses, vertical farming is more closely aligned to these objectives and will, therefore, be critical in shaping the future of food production.
If we want to create real circular food systems, we must think about how to integrate technology and not just build more efficient food factories.
Mark, YASAI
The trend towards sustainable, pesticide-free food production has gained traction in recent years, but it’s accelerated in recent months. As we continue to assess the impact of COVID-19 on the industry and society as a whole, it’s clear that the way we think about food, health and even retail is changing:
People started to rethink their diet habits, their way of life, and consider alternatives to the status quo.
Mark, YASAI
From a commercial perspective, the relative instability of large supply chains has been highlighted by COVID-19, which means businesses are now more wary of relying on complex chains and reluctant to put unnecessary distance between their own operations and their suppliers. As a result, the ability to grow produce in close proximity to retailers and distributors means vertical farms will play a key role in the evolution of the food production industry, in both the short and long-term.
With the potential to improve access to high quality produce, drastically reduce the environmental impact of food production, shorten supply chains and deliver better food diversity, vertical farming can provide solutions to so many of the issues we’re currently facing. From food scarcity in developing countries to volatility within the distribution industry, vertical farms can play a key role in transforming the way we grow, access and think about food.
What’s Next for iFarm, YASAI and Logiqs?
As YASAI’s Zurich vertical farm prepares to open in Niederhasli in autumn 2021, we’re already looking towards the future. We’ll be testing and perfecting our growing methods in Niederhasli, with a view to working together on an ambitious project to create another vertical farm that’s 10 times bigger. With plans already underway, the creation of Zurich’s first vertical farm could be the first step in our shared journey.
Is a Partnership Right for You?
Now you’ve got an insight into the rationale, decision-making and objectives behind our strategic alliance with YASAI and Logiqs, you may be wondering whether a partnership could offer the same growth potential to you.
By working with iFarm and other industry leaders, you can access the resources, services and expertise you need to create your own successful vertical farm. Whether you’re a traditional farmer who wants to incorporate new technology into your operations, a retailer that wants to access locally sourced produce or an investor looking for your next venture, a vertical farm partnership can deliver the practical, financial and sustainable rewards you’re looking for.
To learn more, take a look at how you can benefit from vertical farming:
1. Food, Fruit and Vegetable Distributors
For existing food, fruit and vegetable distributors, partnering with vertical farms and logistics companies offers clear benefits. With an abundance of crops being produced all year-round, distributors can expand their network and substantially increase their profitability.
As traditional farming delivers seasonal growth, distributors may be forced to work with numerous clients in order to trade throughout the year. Inevitably, this means changing distribution routes, switching equipment and altering the network to accommodate different types of produce.
In contrast, the year-round production at vertical farms enables distributors to minimise resource consumption, safeguard demand and use existing routes. As a result, food, fruit and vegetable distributors can maximise their own profitability by partnering with vertical farmers, investors, logistics providers, food retailers and entrepreneurs.
2. Food Retailers
Food retailers can benefit from vertical farm partnerships in a number of ways. For example, a food retailer can source fresh produce from their partners and increase the diversity of their stock. This enables retailers to enhance the quality and the flavour of their fresh produce, as well as meeting consumer demand for pesticide-free, locally-sourced food.
Critically, partnering with other organisations or investors to create a vertical farm also gives retailers the chance to shorten their supply chains. As we’ve seen over the past year, complex or lengthy supply chains are precarious, particularly when stock has a short lifespan, as is the case with fruits and vegetables. Supply chain delays and disruptions are now common, which leads to increased waste, additional expenditure and fewer products on the shelves.
As part of a vertical farm partnership, however, food retailers can produce their own stock, avoid the risk associated with lengthy supply chains and cater to a growing market. By doing so, retailers can reduce their expenditure, safeguard their supply chains and increase their profitability.
3. Investors
Investors, financial partners and private equity funds can capitalise on the evolving agro-tech industry by partnering with expanding vertical farms. As we can see with the YASAI vertical farm in Niederhasli, the initial production site is only a glimpse of what’s to come. With proven success at smaller sites, investors can get in at the ground level to fund expansion and reap the rewards.
The EU has already confirmed its plans to drastically reduce the use of pesticides in food production, with a 50% reduction estimated by 2030. This, combined with consumer demand for pesticide-free food, highlights a growing market. Furthermore, it’s a market that vertical farms can and will satisfy.
While the increasing market for pesticide-free produce is one reason why vertical farms present such a lucrative investment, there are many others. The relatively low start-up costs, in conjunction with low running costs, makes vertical farms a viable option for all types of investors.
Furthermore, many investors are actively seeking out ‘green investments'. From hedge funds to pension funds, an increasing number of people and companies are moving away from investing in products, firms or industries which are known to have a negative impact on the environment and searching for an alternative. Not only does a vertical farm partnership meet the criteria of a green investment and enhance the ‘green credentials' for all parties, it can also generate significant and sizable returns.
4. Distributors and Resellers of Agro-Technologies
For existing distributors and resellers of agro-technologies, the chance to form a partnership with vertical farmers, investors, retailers and entrepreneurs is undoubtedly compelling.
Instead of simply selling your tech innovations to farmers and companies, you’ll have the chance to create long-term professional relationships with people and organisations from your target audience. By doing so, you can increase customer lifecycle value and optimise your profitability.
However, the increased revenue isn’t the only benefit associated with a partnership. As we have seen with Logiqs' role within the iFarm and YASAI partnership, the chance to increase brand awareness within the industry and establish your firm as a market leader is valuable in itself.
As your role in ground-breaking partnerships becomes more widely-known, demand for your brand and your technologies is increased and further growth potential develops. From ad hoc sales to additional partnerships, distributors and resellers of agro-technologies can significantly increase their reach when they form partnerships with other people and organisations in the industry.
Additionally, being part of a partnership enables you to work closely with farmers and to gain an in-depth insight into the type of technology they require. In doing so, you will consistently enhance and evolve your technologies to deliver more efficient and more effective solutions. For agro-tech developers, the chance to shape the future of the industry makes a vertical farm partnership an opportunity that simply shouldn’t be missed.
To learn more or to explore upcoming partnership opportunities, contact iFarm today at +358 504 801 487 or email us at sales@ifarm.fi
Vertical Farming Startup Oishii Raises $50m In Series A Funding
“We aim to be the largest strawberry producer in the world, and this capital allows us to bring the best-tasting, healthiest berry to everyone.”
By Sian Yates
03/11/2021
Oishii, a vertical farming startup based in New Jersey, has raised $50 million during a Series A funding round led by Sparx Group’s Mirai Creation Fund II.
The funds will enable Oishii to open vertical strawberry farms in new markets, expand its flagship farm outside of Manhattan, and accelerate its investment in R&D.
“Our mission is to change the way we grow food. We set out to deliver exceptionally delicious and sustainable produce,” said Oishii CEO Hiroki Koga. “We started with the strawberry – a fruit that routinely tops the dirty dozen of most pesticide-riddled crops – as it has long been considered the ‘holy grail’ of vertical farming.”
“We aim to be the largest strawberry producer in the world, and this capital allows us to bring the best-tasting, healthiest berry to everyone. From there, we’ll quickly expand into new fruits and produce,” he added.
Oishii is already known for its innovative farming techniques that have enabled the company to “perfect the strawberry,” while its proprietary and first-of-its-kind pollination method is conducted naturally with bees.
The company’s vertical farms feature zero pesticides and produce ripe fruit all year round, using less water and land than traditional agricultural methods.
“Oishii is the farm of the future,” said Sparx Group president and Group CEO Shuhei Abe. “The cultivation and pollination techniques the company has developed set them well apart from the industry, positioning Oishii to quickly revolutionise agriculture as we know it.”
The company has raised a total of $55 million since its founding in 2016.
VIDEO: Device Communicates With Plants Using Electric Signals
Researchers envision a future where farmers can take preventive steps to protect their crops, using the plant ‘communication’ device they have developed
24 March 2021
Researchers envision a future where farmers can take preventive steps to protect their crops, using the plant ‘communication’ device they have developed.
A team of scientists led by Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) has developed a device that can deliver electrical signals to and from plants, opening the door to new technologies that make use of plants.
The NTU team developed their plant ‘communication’ device by attaching a conformable electrode (a piece of conductive material) on the surface of a Venus flytrap plant using a soft and sticky adhesive known as hydrogel.
Pick up and transmit electric signals
With the electrode attached to the surface of the flytrap, researchers can achieve two things: pick up electrical signals to monitor how the plant responds to its environment, and transmit electrical signals to the plant, to cause it to close its leaves.
According to the scientists, the ability to measure the electrical signals of plants could create opportunities for a range of useful applications, such as plant-based robots that can help to pick up fragile objects or to help enhance food security by detecting diseases in crops early.
Text continues underneath the video
Monitor crop health
The research team envisions a future where farmers can take preventive steps to protect their crops, using the plant ‘communication’ device they have developed.
Lead author of the study, Chen Xiaodong, President’s Chair Professor in Materials Science and Engineering at NTU Singapore said: “Climate change is threatening food security around the world. By monitoring the plants’ electrical signals, we may be able to detect possible distress signals and abnormalities. When used for agriculture purpose, farmers may find out when a disease is in progress, even before full‑blown symptoms appear on the crops, such as yellowed leaves. This may provide us the opportunity to act quickly to maximise crop yield for the population.”
Smartphone
The device has a diameter of 3 mm and is harmless to the plant. The researchers say it does not affect the plant’s ability to perform photosynthesis while successfully detecting electrical signals from the plant. Using a smartphone to transmit electric pulses to the device at a specific frequency, the team elicited the Venus flytrap to close its leaves on demand, in 1.3 seconds.
The researchers have also attached the Venus flytrap to a robotic arm and, through the smartphone and the ‘communication’ device, stimulated its leaf to close and pick up a piece of wire half a millimetre in diameter.
Hydroponics Farming: Why Hydroponic Farms Are Trending In India?
As per reports, India’s hydroponics market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 13.53% between 2020 and 2027.
Hydroponics is slowly gaining popularity in India and attracting more and more farmers. Basically, hydroponics is a type of horticulture and a subset of hydroculture, which is a method of growing plants, usually crops, without soil, by using mineral nutrient solutions in an aqueous solvent.
Hydroponic farming can be done in a small space also like a balcony which is a soil-less, water-based farming process. Rather than using soil for plant nutrition, crops are fed nutrient-rich water, negating a lot of the baggage that comes with soil-based methods.
Hydroponics is the practice of growing plants in a nutrient-rich solution, skipping the soil. “It has been practised for centuries, so it is not a new technology," points out Akhila Vijayaraghavan, the founder-director of Coimbatore’s Parna Farms, adding the Hanging Gardens of Babylon are believed to have been hydroponically grown. “The Aztecs created vast hydroponic systems using rafts called chinampas," she says.
The film piqued Gopal’s interest, and he began reading about the method to grow plants without soil. “We started working with hydroponics as a project in 2012. At that time, we didn’t know much about the plight of farmers and how a technology like this could add value," said Gopal. The idea was to create awareness among the right audience and sell “through prototypes and hobby kits."
Urban farmers are taking to hydroponics, a water-smart solution to grow pesticide-free produce on rooftops and terraces. As per reports, India’s hydroponics market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 13.53% between 2020 and 2027.
What is Hydroponics
Hydroponics is a branch of hydroculture, in which plants are grown without soil by using water solvent which consists of minerals nutrient solution. Terrestrial plants may be grown with their roots only, roots are exposed to the nutritious liquid, or roots may be supported physically by a medium like gravel.
Plants are also grown through a process called photosynthesis, in which plants use sunlight and a chemical inside their leaves called chlorophyll to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen, as shown in reaction.
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6(Glucose)+ 6O2
The nutrients we use in hydroponic systems may come from different sources, such as fish excrement, duck manure, or chemical fertilisers.
1Advantages of Hydroponics
Plantation without soil
We can grow plants in places where the land is limited, doesn't exist, or is contaminated. In the early time period, Hydroponics was a successful technique used to supply fresh vegetables for troops in Wake Island. It has been considered as the future farming to grow foods for astronauts in space by NASA.
Better use of space and location
All those plants need are provided and maintained in a system, you can grow plants in a small apartment, bedrooms or kitchen as long as you have some spaces.
Roots of plants usually expand and spread out in search of foods, and oxygen in the soil but in the case of Hydroponics, roots are sunk in a tank full of oxygenated nutrient solution and are directly in contact with vital minerals. This means that you can grow your plants closer, and consequently huge space savings.
Climate control
Hydroponic growers can have total control over climate, temperature, humidity, light, the composition of the air. This means you can grow foods all year, regardless of the season. Farmers can produce foods at the right time to maximize their profits.
Water-saving
Plants grown by the process of hydroponically can use 10% of water, as compared to one grown on the field because water is recirculated, in this method. Plants will take up the water they need, while run-off water will be captured and return to the system. Water loss in this system will only occur in two forms - evaporation and leaks from the system.
Use of nutrients
You can have 100% control of the nutrients (foods) that plants need in this method. Before planting, growers can check what are plants requirement and what amounts of nutrients needed at particular stages and at what percentage they should be mixed with water.
Better growth rate
Do hydroponic plants grow faster than in soil? Yes, because you can set conditions favourable to the plant’s growth like temperature, lights, moisture, and especially nutrients. As plants are placed in favourable conditions, nutrients are provided in sufficient amounts and come into direct contacts with the root systems. Therefore, plants do not waste valuable energy in the search for diluted nutrients in the soil and put their complete focus on growth.
Little Leaf Farms Raises $90M to Grow Its Greenhouse Network
Massachusetts-based Little Leaf Farms has raised $90 million in a debt and equity financing round to expand its network of hydroponic greenhouses on the East Coast. The round was led by Equilibrium Capital as well as founding investors Bill Helman and Pilot House Associates. Bank of America also participated.
by Jennifer Marston
Image from: Little Leaf Farms
Massachusetts-based Little Leaf Farms has raised $90 million in a debt and equity financing round to expand its network of hydroponic greenhouses on the East Coast. The round was led by Equilibrium Capital as well as founding investors Bill Helman and Pilot House Associates. Bank of America also participated.
Little Leaf Farms says the capital is “earmarked” to build new greenhouse sites along the East Coast, where its lettuce is currently available in about 2,500 stores.
The company already operates one 10-acre greenhouse in Devins, Massachusetts. Its facility grows leafy greens using hydroponics and a mixture of sunlight supplemented by LED-powered grow lights. Rainwater captured from the facility’s roof provides most of the water used on the farm.
According to a press release, Little Leaf Farms has doubled its retail sales to $38 million since 2019. And last year, the company bought180 acres of land in Pennsylvania on which to build an additional facility. Still another greenhouse, slated for North Carolina, will serve the Southeast region of the U.S.
Little Leaf Farms joins the likes of Revol Greens, Gotham Greens, AppHarvest, and others in bringing local(ish) greens to a greater percentage of the population. These facilities generally pack and ship their greens on the day of or day after harvesting, and only supply retailers within a certain radius. Little Leaf Farms, for example, currently servers only parts of Massachusetts, Pennsylvania, New York, and New Jersey.
The list of regions the company serves will no doubt lengthen as the company builds up its greenhouse network in the coming months.
Vertical Farming ‘At a Crossroads’
Although growing crops all year round with Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) has been proposed as a method to localize food production and increase resilience against extreme climate events, the efficiency and limitations of this strategy need to be evaluated for each location
Building the right business model to balance resource usage with socio-economic conditions is crucial to capturing new markets, say speakers ahead of Agri-TechE event
Image from: Fruitnet
Although growing crops all year round with Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) has been proposed as a method to localize food production and increase resilience against extreme climate events, the efficiency and limitations of this strategy need to be evaluated for each location.
That is the conclusion of research by Luuk Graamans of Wageningen University & Research, a speaker at the upcoming Agri-TechE event on CEA, which takes place on 25 February.
His research shows that integration with urban energy infrastructure can make vertical farms more viable. Graamans’ research around the modelling of vertical farms shows that these systems are able to achieve higher resource use efficiencies, compared to more traditional food production, except when it comes to electricity.
Vertical farms, therefore, need to offer additional benefits to offset this increased energy use, Graamans said. One example his team has investigated is whether vertical farms could also provide heat.
“We investigated if vertical farms could provide not just food for people living in densely populated areas and also heat their homes using waste heat. We found that CEA can contribute to stabilizing the increasingly complex energy grid.”
Diversification
This balance between complex factors both within the growing environment and wider socio-economic conditions means that the rapidly growing CEA industry is beginning to diversify with different business models emerging.
Jack Farmer is CSO at vertical producer LettUs Grow, which recently launched its Drop & Grow growing units, offering a complete farming solution in a shipping container.
He believes everyone in the vertical farming space is going to hit a crossroads. “Vertical farming, with its focus on higher value and higher density crops, is effectively a subset of the broader horticultural sector,” he said.
"All the players in the vertical farming space are facing a choice – to scale vertically and try to capture as much value in that specific space, or to diversify and take their technology expertise broader.”
LettUs Grow is focussed on being the leading technology provider in containerised farming, and its smaller ‘Drop & Grow: 24’ container is mainly focussed on people entering the horticultural space.
Opportunities in retail
“This year is looking really exciting,” he said. “Supermarkets are investing to ensure a sustainable source of food production in the UK, which is what CEA provides. We’re also seeing a growth in ‘experiential’ food and retail and that’s also where we see our Drop & Grow container farm fitting in.”
Kate Hofman, CEO, GrowUp agrees. The company launched the UK’s first commercial-scale vertical farm in 2014.
“It will be really interesting to see how the foodservice world recovers after lockdown – the rough numbers are that supermarket trade was up at least 11 per cent in the last year – so retail still looks like a really good direction to go in.
“If we want to have an impact on the food system in the UK and change it for the better, we’re committed to partnering with those big retailers to help them deliver on their sustainability and values-driven goals.
“Our focus is very much as a salad grower that grows a fantastic product that everyone will want to buy. And we’re focussed on bringing down the cost of sustainable food, which means doing it at a big enough scale to gain the economies of production that are needed to be able to sell at everyday prices.”
Making the Numbers Add Up
The economics are an important part of the discussion. Recent investment in the sector has come from the Middle East, and other locations, where abundant solar power and scarce resources are driving interest in CEA. Graamans’ research has revealed a number of scenarios where CEA has a strong business case.
For the UK, CEA should be seen as a continuum from glasshouses to vertical farming, he believes. “Greenhouses can incorporate the technologies from vertical farms to increase climate control and to enhance their performance under specific climates."
It is this aspect that is grabbing the attention of conventional fresh produce growers in open field and covered crop production.
A Blended Approach
James Green, director of agriculture at G’s, thinks combining different growing methods is the way forward. “There’s a balance in all of these systems between energy costs for lighting, energy costs for cooling, costs of nutrient supply, and then transportation and the supply and demand. At the end of the day, sunshine is pretty cheap and it comes up every day.
“I think a blended approach, where you’re getting as much benefit as you can from nature but you’re supplementing it and controlling the growth conditions, is what we are aiming for, rather than the fully artificially lit ‘vertical farming’.”
Graamans, Farmer and Hofman will join a discussion with conventional vegetable producers, vertical farmers and technology providers at the Agri-TechE event ‘Controlled Environment Agriculture is growing up’ on 25 February 2021.
US - OHIO: Thinking And Growing Inside The Box
A brother-sister team has taken the mechanics of farming out of the field and into a freight container. “We are growing beautiful plants without the sun; there’s no soil, and so it’s all a closed-loop water system,” Britt Decker, co-owner of Fifth Season FARM, said
A brother-sister team has taken the mechanics of farming out of the field and into a freight container.
“We are growing beautiful plants without the sun; there’s no soil, and so it’s all a closed-loop water system,” Britt Decker, co-owner of Fifth Season FARM, said. “We use non-GMO seeds, completely free of herbicides and pesticides, so the product is really, really clean. In fact, we recommend people don’t even wash it, because there’s no reason to.”
Fifth Season FARM is unique in many ways; the 3-acre hydroponic farm is contained in a 320-square-foot freight container that sits along 120 S. Main St. in Piqua, with everything from varying varities of lettuce, to radishes, to kale and even flowers in a climate-controlled smart farm that allows Decker and his sister, Laura Jackson, to turn crops in a six- to eight-week cycle. The crops spend 18 hours in “daytime” every day, and the farm uses 90% less water than traditional farming.
“It’s tricky because we’re completely controlling the environment in here. It’s kind of a laboratory more than a farm,” Decker said. “I think there’s about 50 of them around the world right now. These are really international, and they’re perfect for places that are food deserts where they can’t grow food because of climate or other reasons. It gives them a way to grow food in the middle of nowhere.”
Image from: Sidney Daily News
Decker and Jackson, along with their brother Bill Decker, also do traditional farming and grow corn, wheat and soybeans, but Decker said they were looking for a new venture that would help lead them to a healthier lifestyle and learn something new.
“Just with the whole local food movement becoming more and more important and food traceability, we just thought it would be a great thing to bring to our community to help everyone have a healthier lifestyle,” Decker said. “People love food that’s grown right in their hometown and the shelf-life on it, when you get it home, is remarkable. It’ll keep for two weeks.”
Image from: AgFunder News
Currently, Decker and Jackson are growing a half-dozen variety of specialty lettuces that include arugula, butterhead and romaine, as well as specialty greens like kale and Swiss chard, and even radishes and flowers. They received their freight container at the end of July and set up their indoor farm over two weeks; while the farm has been in operation for less than six months, Decker says that they’re growing beautiful product.
They have also started growing micro-greens, said Decker. Micro-greens are immature plants which are 1 to 3 inches tall and are in a 5-inch by 5-inch container.
“People will use them as garnishments and in smoothies,” said Decker. “Since they are immature plants, they have an intense flavor.”
Decker said they are growing wheat germ, broccoli and spicy salad mixes.
They’ve also started moving forward with sales and marketing. Fifth Season FARM has partnered with the Miami County Locally Grown Virtual Market to sell their products to the community. They also take orders through their website, customers can opt to pick up their orders between 4 and 6 p.m. on Wednesdays, or Decker and Jackson will deliver products up to five miles from the farm. Decker said that Fifth Season FARM is also in discussions with three restaurants in the area about including their specialty greens on their menus.
Decker said they also plan to attend the Sidney Farmers Market when it opens for the spring/summer season.
“We’re really just getting going,” Decker said. “While we were learning to grow products, we didn’t want to overcommit to a restaurant or grocery store before we knew we could really grow beautiful product, so we’ve been donating product every week to the food pantry at the Presbyterian Church. It feels good to plant the seeds and watch them grow, and it feels good to make sure that people who aren’t getting the proper nutrition are getting some.”
Pontus Submits Building Permit Application for Surrey Aquaponics Facility
The Company has submitted a construction application to the City of Surrey for its 20,570 square foot aquaponics facility. The approval process is estimated to be completed within 6 weeks and is expected to be followed by the immediate commencement of construction of the Facility's leasehold improvements. Accordingly, the leasehold improvements are to consist of a complete retrofit of the Facility to establish Pontus' solar-powered, water recycling CEVASTM aquaponic system
VANCOUVER, BC, Feb. 3, 2021 /CNW/ - Pontus Protein Ltd. ("Pontus" or the "Company"), is pleased to announce it has made significant progress towards the development of its state of the art, integrated aquaponics facility located in Surrey, British Columbia, Canada (the "Facility").
Image from: CNW Group/Pontus Protein Ltd
The Company has submitted a construction application to the City of Surrey for its 20,570 square foot aquaponics facility. The approval process is estimated to be completed within 6 weeks and is expected to be followed by the immediate commencement of construction of the Facility's leasehold improvements. Accordingly, the leasehold improvements are to consist of a complete retrofit of the Facility to establish Pontus' solar-powered, water recycling CEVASTM aquaponic system.
The installation of all required equipment for the growth and production is forecasted to take between four and six months to complete. Upon completion, the Facility will be approximately 20 times the size of Pontus' prior prototype facility. The prototype facility has been used to test and develop the technology for the Company's proprietary growing process.
The Facility, as seen in the image above and video below, will utilize an array of additional technologies to create a clean and sustainable aquaponics ecosystem. Solar energy panels will be installed to capture renewable energy and power the closed-loop water system, which recycles up to 95% of all water inputs. The implementation of the Facility's unique, sustainable technology in conjunction with Pontus' proprietary CEVAS™ automated growth technology will allow the Company to emphasize biosecurity in its agricultural production processes, removing the need for additional chemicals, pesticides, and other non-native components.
Pontus CEO, Conner Yuen states: "Entering the construction application process is a major milestone for the Company as we move toward the commissioning of the Facility. Our aim is to create a state of the art process that will incorporate the latest in sustainable agriculture technology. The ability to implement this highly efficient technology solves many issues we see with current methods of food production such as land scarcity and low yields and contamination.
Pontus' biosecurity and renewable food sources are intended to create a proactive solution to these issues by reducing the potential for contamination and the need for pesticides. Pontus hopes the Facility will revolutionize how traditional agriculture is conducted and show the power of technological food advancements."
Plant-based Protein Powder Market
The Company's plant-based protein powder is a premium entry into the global protein and supplements market, which is currently valued at USD$15 Billion and is expected to grow to USD$20 Billion by 2025 according to Grand View Research. This growth is expected to be fuelled by many North Americans reducing or eliminating the regular consumption of animal products. The North American plant-based protein market is also anticipated to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 14% from 2019 through 2025.
About Pontus Protein Ltd
Pontus Protein Ltd. makes pure plant-based protein powder sourced from nutritious water lentils, farm-grown in Vancouver, BC, with development plans to expand to Surrey, B.C.. Not only does Pontus Protein Powder exceed certified organic standards, but it's also gluten-free, pure and allergen safe. It's jam-packed full of antioxidants, minerals, vitamins and ALL the essential amino acids.
This is not your average lentil, these are water lentils; a crop that can be harvested every 24 hours in an indoor aquaponic farm that uses 95% less water than traditional agriculture, using Pontus' proprietary Closed Environment Vertical Aquaponics System (or CEVAS™) aquaponic agritech technology. This is wonderful news for a planet populated with us hungry and health-conscious humans.
Nanobubble Tech Could Revolutionize Aquaculture & Aquaponics
“There is a pressing need to develop an alternative to the current highly energy-intensive conventional aeration,” said Khanal. “Nanobubble technology has a potential to revolutionize aquaculture and aquaponic systems, with higher productivity and resource recovery.” Khanal was initially awarded CTAHR’s Team Science grant, which was critically important to obtaining preliminary data for his grant proposal to NIFA
Image from: University of Hawai’i News
The burgeoning fields of aquaculture and aquaponics hold vast potential for growing food. Yet, the efficacy of these microbial-mediated processes is governed by the availability of dissolved oxygen in water. Generally, oxygen has poor solubility in water, which has a negative effect on fish growth and plant yields.
Almost $200,000 in new funding from the USDA-National Institute of Food and Agriculture’s (NIFA) Water Quantity and Quality Program may expand researchers’ understanding of how nanobubbles could improve aeration and oxygen supplies.
Under the grant, Samir Khanal of the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa’s College of Tropical Agriculture and Human Resources (CTAHR ) Department of Molecular Biosciences and Bioengineering, will apply the technology to these aqueous systems. His goal is to uncover new opportunities for improving fish and plant yields—with concomitant improvements in water quality.
Image from: University of Hawai’i News
“There is a pressing need to develop an alternative to the current highly energy-intensive conventional aeration,” said Khanal. “Nanobubble technology has a potential to revolutionize aquaculture and aquaponic systems, with higher productivity and resource recovery.”
Khanal was initially awarded CTAHR’s Team Science grant, which was critically important to obtaining preliminary data for his grant proposal to NIFA.
“Thanks to the CTAHR and NIFA grants, we hope our findings will benefit existing Hawaiʻi businesses, as well as a new generation of growers, across the state and beyond,” Khanal added.
Organic: The Battle for a Single Word
Throughout history, when we see great leaps forward in technology, there are always pushbacks from the old world who want to maintain the status-quo. This can be for a variety of reasons and come from a variety of people. Sometimes, the resistance comes from workers, an example of this would be the fierce opposition from workers who protested the mechanisation of their jobs brought about by the industrial revolution. They were often referred to as luddites because of the propensity to destroy the new machines that were taking their jobs
Throughout history, when we see great leaps forward in technology, there are always pushbacks from the old world who want to maintain the status-quo. This can be for a variety of reasons and come from a variety of people. Sometimes, the resistance comes from workers, an example of this would be the fierce opposition from workers who protested the mechanisation of their jobs brought about by the industrial revolution. They were often referred to as luddites because of the propensity to destroy the new machines that were taking their jobs.
On the other hand, there can be examples of when the resistance to innovations come from industry competitors who don’t want to lose the dominance they once had. An example of this can be seen through the fossil fuel industries continuous attempts to limit the growth of renewables by lobbying governments to pursue policies more favourable to them.
Today we are seeing resistance to a new green revolution through innovation in the vertical farming sector primarily from industry competitors or even protective policy makers. Politico recently reported on a story regarding a fight between a Danish vertical farming company, called Nordic Harvest, and the EU whereby the former was prohibited from labelling their crops as organically produced. The reason given for this was that EU regulation demanded that anything being described as organic had to be produced in soil. This seems to be the antithesis to their Farm to Fork strategy as it heavily handicaps innovative indoor vertical farming companies.
Image from: Nord Harvest
Now this may not seem much like a significant infringement on the indoor vertical farming sector, but what this does is make it more difficult for companies, such as Nordic Harvest, to indicate to consumers their green credentials. Moreover, under the EU’s Green Public Procurement rules, indoor vertical farming companies gain a smaller share in food market than it normally would have due to the ruling on the definition of organics. The unfortunate aspect of this is that words only mean what we define them as, so the personal opinions of the individuals who made this decision are going down this direction for reasons not non-partisan.
Now there may so semi-legitimate reasons to resist the rise of indoor vertical farming, but it is clear that this will be the future of farming and it must not be kneecapped by ill-intentioned actors. The limitations of the sector, such as intense energy use or limited crop varieties, can only be solved if there is financial and legislative support from the powers that be.
This is clear with the recent certification of Sky Greens in Singapore as organic whereby the central government has been forward thinking. Speaking of their decision, the chair of the Food Standards Committee stated:
“The certification may allow local urban farms to expand into markets outside of Singapore. Having a national organic certification will help local urban farms to be on equal footing with the US…”
The Food Standards Committee in Singapore defined organic differently from the EU affirming that as long as they avoid mineral fertilisers or other pesticides and herbicides, which indoor vertical farms operating on controlled environment agriculture adheres to. At full capacity, Sky Greens can produce up to half a tonne of salads daily without LEDs and using gravity to collect rainwater to avoid pests. An important point to note however is that the vast majority of Singapore is urbanised with no domestic traditional rural farming industry.
Image from: Sky Greens
Another problematic component of this EU ruling is that may prove controversial is its impact on trade. Any vertical farming company from a country not with the restrictive rules and the EU that wanted to export their food produced in a vertical farm, they would as need to abide by these rules. For example, with basil being one of the major herbs produced in vertical farms, we often see it being used in Pesto. Unfortunately, this would not be able to be marketed as organic. With the EU being the largest trading bloc in the entire world, this will affect the global fortunes of the sector. We are also seeing this happen in the US but due to many legal appeals and challenges, they have not currently implemented the same rules as the EU.
So, with all this in mind, it is important to be aware of the pushback that will inevitably happen due to a green revolution brought about by innovation in the indoor vertical farming sector. The debate surrounding the definition of the word organic is only the start. We already see concerted efforts to ban synthetic meat companies from using words such as hamburger, hot dog or steak. However, even with this uneven playing field, indoor vertical farming is on track to increase its market share significantly over the next decade and beyond while traditional farming methods are on the decline.
The Future of the Food Supply Chain Lives on a Rooftop in Montreal
The world’s biggest commercial rooftop greenhouse sits atop a former Sears warehouse in a semi-industrial northwestern quarter of Montreal. Early every morning, staff pick fresh vegetables, then bring them downstairs, where they get packed into heavy-duty plastic totes along with the rest of the day’s grocery orders.
Image from: Lufa Farms
The world’s biggest commercial rooftop greenhouse sits atop a former Sears warehouse in a semi-industrial northwestern quarter of Montreal. Early every morning, staff pick fresh vegetables, then bring them downstairs, where they get packed into heavy-duty plastic totes along with the rest of the day’s grocery orders.
Tablets loaded with custom pick-and-pack software tell them where to put what: This basket has lettuce, tomatoes, and cucumbers, plus some chicken, eggs, and milk. The next one has eggplant, cashew Parmesan, tomato sauce, fresh pasta, and vegan ground round crumble. Whatever Luca doesn’t grow in its four greenhouses comes from local farms and producers, mostly from within 100 miles.
This is a modern foodie’s dream: a tech-forward online shop full of locally grown, pesticide-free, ethically-sourced products at reasonable price points, delivered once a week to either your doorstep or a local pickup point in your neighborhood.
It’s stunning to think Lufa was founded by two people who’d never even grown a tomato before, let alone sold one. “We said, ‘Instead of learning how the food world works, let’s just come up with what we feel the food world should be,’” says Mohamed Hage, 39, who cofounded Lufa with Lauren Rathmell in 2009.
To them, it looked like this: rooftop greenhouses that bring agriculture into cities. No pesticides, herbicides, or fungicides. Composting their green waste. Selling direct-to-consumer the same day the food is harvested. Capturing and reusing rainwater. Reusable packaging.
That’s exactly what they now have—and they feed a portion of Montreal, the second-biggest city in Canada, with it.
Image from: Lufa Farms
Back in the warehouse, workers poke at their tablets, checking off items as they’re packed into the boxes.
Customers—Lufavores, as the company calls them—typically place their orders a few days before delivery through the online store, dubbed “the Marketplace,” which Lufa built from scratch in 2012. That’s how Lufa’s suppliers know how much product to provide: They get forecasts first, then final order numbers, through their Lufa software. Some items, like frozen meat, can be delivered to the warehouse once a week. Others, like bread, arrive fresh every day.
Artisanal Montreal bakery la Fabrique Arhoma started supplying Lufa with bread and pastries about six years ago, co-owner Ariane Beaumont tells Fortune. Today, they hand-make 6,000 individual items a day for Lufa. Beaumont said Lufa now accounts for between 30% to 40% of her commercial sales; since pandemic shutdowns, a lot of the product destined for restaurants got redirected to Lufa. “They’re an exceptional company. I don’t know how they do it,” Beaumont says. “And they pay the fastest, too.”
Technology is the underpinning of Lufa’s success, and the owners know it.
“We see ourselves as a technology company, in the sense that we solve with software,” Rathmell, 32, says. They didn’t really have any other choice. To fulfill that dream they had back in 2009—years before COVID-19 forced most grocery stores to enable online shopping—they had to do it themselves.
“Nothing off-the-shelf can be applied to what we do, because it’s so complex,” Rathmell notes. “We harvest food ourselves; we gather from farmers and food makers throughout the province; most of it’s arriving just in time throughout the night to be packed in baskets for that day, and every order is fully unique.”
Lufa now has a team of eight programmers working on software and systems that manage e-commerce, warehouse management, routing, customer relationships, supplier fulfillment, pick-and-pack, vendor payments, delivery ETAs, and more.
Those technologies were tested on that fateful Friday the 13th last March, when Quebec and Canada each announced their first waves of COVID-19 lockdowns. People panicked, rushing to the grocery store to stock up on flour and toilet paper.
Online, new sign-ups for Lufa’s weekly grocery baskets exploded, and existing subscribers began ordering more than they’d ever ordered before—all while Lufa’s pickup points were shutting down. “We essentially doubled overnight,” Rathmell recalls. Lufa was forced beyond its operational capacity, and the cracks started showing in the systems and software that had, until that point, done a fine job getting the company by.
Lufa temporarily closed the website and opened a wait list. The staff analyzed the pandemic’s trajectory and how they had to adapt at each step; reconfigured their warehouse floor to station workers further apart; then relaunched at the capacity they could handle, gradually scaling each week until they hit their usual stride. Today, they’re humming along at 25,000 baskets a week.
Leading with tech helped make them nimble and strategic during those hairy early pandemic days, said Hage and Rathmell. After some recalibrations and new developments, their software and processes can now handle more customers, vendors, and processes—critical elements as the company continues to scale its greenhouse operations. In August of 2020, Lufa opened its fourth greenhouse, doubling its square footage. The four greenhouses combined produce 57,000 pounds of food a week. A fifth is planned for this year.
“Our objective at Lufa is to get to the point where we’re feeding everyone in the city,” Hage says.
And after Montreal? They’re planning on a yet to be determined second site in the northeastern pocket of North America, ideally this year. “Our vision is to grow food closer to where people live, and grow it more sustainably,” Rathmell says.
Image from: Lufa Farms
Bringing high-yield crop production into cities is a smart answer to many modern challenges in environmental and human health.
Mark Lefsrud, an associate professor of agricultural and environmental sciences at McGill University, points out that embracing technologies like LEDs and automation to grow indoors and in urban greenhouses means shorter supply chains, better nutritional integrity, less food waste, and reduced vulnerability to climate swings. In cities fed primarily by low-carbon energy (hydroelectricity in Montreal’s case), indoor growing versus importation becomes even more of a no-brainer.
“I’ve been working in the controlled environment and greenhouse industry for 20-some years, and having a company like Lufa has brought a lot of attention to not just urban agriculture, but also the need for greenhouse production,” Lefsrud says, adding that Lufa’s success has prompted more government investment in the sector overall.
“The Quebec government now takes this as a serious venture system, which then means that the students that I’m training, and research we’re doing here at the university, now have employment and have the possibility of setting up their own system,” says the McGill professor.
That idea, of developing more vertically integrated food systems, is a passion of Hage’s—not only for the idea of cutting out production and transformation middlemen to improve profit margins, but also to improve quality, traceability, and ultimately the ethics of food production.
“You know, every time we talk to someone about it, we feel like it’s the ’80s, and we’re holding a big solar panel trying to convince the room that this is the future,” Hage says.
As the larger agricultural industry catches on to vertical integration, it seems Hage and Rathmell are no longer mad scientists with a crazy dream. Instead, they are the voice of reason—and a new generation of food.
As the larger agricultural industry catches on to vertical integration, it seems Hage and Rathmell are no longer mad scientists with a crazy dream. Instead, they are the voice of reason—and a new generation of food.
As the larger agricultural industry catches on to vertical integration, it seems Hage and Rathmell are no longer mad scientists with a crazy dream. Instead, they are the voice of reason—and a new generation of food.
Is AppHarvest the Future of Farming?
In this video from Motley Fool Live, recorded on Jan. 28, Industry Focus host Nick Sciple and Motley Fool contributor Lou Whiteman discuss AppHarvest, one such SPAC that is looking to disrupt the agriculture industry. Here are the details on what AppHarvest wants to do, and a look at whether the company represents the future of farming.
Special purpose acquisition companies, or SPACs, are red-hot right now, with investors clamoring to get into promising young companies.
In this video from Motley Fool Live, recorded on Jan. 28, Industry Focus host Nick Sciple and Motley Fool contributor Lou Whiteman discuss AppHarvest, one such SPAC that is looking to disrupt the agriculture industry. Here are the details on what AppHarvest wants to do, and a look at whether the company represents the future of farming.
Nick Sciple: One last company I wanted to talk about, Lou, and this is one I think it's -- you pay attention to, but not one I'm super excited to run in and buy. It was a company called AppHarvest. It's coming public via a [SPAC] this year. This vertical farming space. We talked about Gladstone Land buying traditional farmland. AppHarvest is taking a very different approach, trying to lean into some of the ESG-type movements.
Lou Whiteman: Yeah. Let's look at this. It probably wouldn't surprise you that the U.S. is the biggest global farm exporter as we said, but it might surprise you that the Netherlands, the tiny little country, is No. 2. The way they do that is tech: Greenhouse farm structure. AppHarvest has taken that model and brought it to the U.S. They have, I believe, three farms in Appalachia. The pitches can produce 30x the yields using 90% less water. Right now, it's mostly tomatoes and it is early-stage. I don't own this stock either. I love this idea. There's some reasons that I'm not buying in right now that we can get into. But this is fascinating to me. We talked about making the world a better place. This is the company that we need to be successful to make the world a better place. The warning on it is that it is a SPAC. So it's not public yet. Right now, I believe N-O-V-S. That deal should close soon. [Editor's note: The deal has since closed.] I'm not the only one excited about it. I tend not to like to buy IPOs and new companies anyway. I think the caution around buying into the excitement applies here. There is a Martha Stewart video on their website talking up the company, which I love Martha Stewart, but that's a hype level that makes me want to just watch and see what they produce. This is just three little farms in Appalachia right now and a great idea. This was all over my watchlist. I would imagine I would love to hold it at some point, but just be careful because this is, as we saw SPACs last year in other areas, people are very excited about this.
Sciple: Yeah. I think, like we've said, for a lot of these companies, the prospects are great. I think when you look at the reduced water usage, better, environmentally friendly, all those sorts of things. I like that they are in Appalachia. As someone who is from the South, I like it when more rural areas get some people actually investing money there. But again, there's a lot of execution between now and really getting to a place where this is the future of farming and they're going to reach scale and all those sorts of things. But this is a company I'm definitely going to have my radar on and pay attention to as they continue to report earnings. Because you can tell yourself a story about how this type of vertical farming, indoor farming disrupts this traditional model, can be more efficient, cleaner, etc. Something to continue paying attention to as we have more information, because this company, like you said, Lou, isn't all the way public yet. We still got to have this SPAC deal finalized and then we get all our fun SEC filings and quarterly calls and all those sorts of things. Once we have that, I will be very much looking forward to seeing what the company has to say.
Whiteman: Right. Just to finish up along too, the interesting thing here is that it is a proven concept because it has worked elsewhere. The downside of that is that it needed to work there. Netherlands just doesn't have -- and this is an expensive proposition to get started, to get going. There's potential there, but in a country blessed with almost seemingly unlimited farmland for now, for long term it makes sense. But in the short term, it could be a hard thing to really get up and running. I think you're right, just one to watch.
Advice For New Vertical Farmers: Grower Spotlight on Andrew Worrall
Andrew is LettUs Grow’s Farm Manager, he manages two of our sites across Bristol and has brought a wealth of knowledge into the company through his previous experience in indoor farming roles across the UK including at Grow Up, Raynor Foods & RootLabs. In this three part interview, we explore what it’s been like to move from animal husbandry to indoor farming, the lessons he’s learned along the way, what it’s like working at LettUs Grow and his advice for those new to indoor growing.
Last week we spoke about running a farm at LettUs Grow. What excites you about vertical farming?
It’s the future of the industry. Also, the amount of salad that these farms can produce for their local community. We want to be able to eat salad all year round and we import to make that happen. However, just a small farm can easily provide for its local community, very efficiently and all year round. The sustainability element is also exciting: with our salad there’s no food miles, it’s very minimalistic. You could use an electric van or bike to distribute this crop if you wanted to. It’s a step forward in terms of what we need to do to take care of our planet.
What do you think are the biggest downsides to vertical farming?
It’s still a new technology and it can be expensive. The biggest roadblock facing the industry is that we need more people and companies to collaborate together to make sure we can build these farms at a sensible rate, so we can provide farms to anyone. We want to be able to provide farms to people, communities and countries that don’t have a lot of money, so that they can provide affordable fresh produce to local people.
How has vertical farming impacted your life?
Massively! I wanted to find my passion, a job that I loved - that was very important to me. It’s satisfying to be in a position now where I’m very happy to be doing what I do and I look forward to going into work. I was happy to make the move from London to Bristol. I would have moved even further if it meant being able to continue working within this industry.
Image from: LettUs Grow
How do you see vertical farming playing a part in the future?
When indoor farming first came about, it had a reputation of being competition for outdoor farming, which just isn’t the case. There’s so much we can’t grow that outdoor farming can provide, such as cereal crops. I’m glad we’re at a stage where indoor and outdoor farms can start to work together to optimise both methods. With these new relationships, there should be a good increase in the amount of indoor farms you’ll be seeing. What LettUs Grow offers with DROP & GROW™ is an exciting project because that’s a 40ft shipping container which can be placed pretty much anywhere. It’s not that big - it could go in a car park or behind a restaurant, but actually provide quite a lot of salad to that area.
How much of our food should be grown this way?
Good question. If you had asked me a while back I would have just said salad, but now I’ve changed my mind. Indoor farming can have a massive impact on propagation, especially aeroponics, because of how we aerate and nourish our roots. We could start lettuce for greenhouse projects and we can also propagate tomatoes, strawberries and tree whips. Propagating trees in this way could potentially be hugely beneficial and it’s something we want to do more of.
We can also quickly grow large amounts of microgreens, baby leafs, herbs and we can grow fruiting crops like strawberries. We are slowly chipping away and it’s really exciting. I’m waiting to see if I can ever say I’ve grown or propagated every crop that can be grown in these farms!
What do you think are the biggest benefits of vertical farming?
How fast these crops can grow! The turnover can be as short as 5 days from seed, depending on the crop. Also how clean it can be - I’m very dedicated to making sure these farms are built to ensure they are easy to be maintained and clean. The most exciting part is the crop growth rate though - it’s incredible how fast our crop grows from seed to plate. In a very well maintained growing calendar, which Ostara® is great for supporting, you can optimise your beds so that the day you harvest can also be the day you germinate onto that same bed. Your farms can be forever providing salad at very fast rates.
Image from: LettUs Grow
What was the biggest change you encountered during your years indoor farming?
Moving from being a production grower to an R&D grower. It has been a great change! As a production grower I knew what I needed to know about growing the plant safely and getting it onto a plate so it was good for the consumer. Now I’m fully optimising, learning and understanding the plants completely, so that I can help the grower that I used to be. We spend a lot of time on crop recipes to make sure that whoever we sell our farms to can start up very quickly and they won’t have to spend months developing their crops. If they have the customers and clients behind them, they can buy DROP & GROW and start producing salad as soon as it's been commissioned.
What was the biggest change you encountered in the industry?
More and more people are speaking about what’s going on in the industry and getting involved. I get so many messages on LinkedIn with people who want to get into this career. It’s exciting to see that indoor growing is a career people can access now. When I was developing my skills I didn’t know I would end up in indoor farming. There are more opportunities than ever before. For example, our Crop Technician is doing a placement here for 2 years. The aim is that they can gain the skill sets and knowledge they need to then go off and do the same practice in any farm they want.
What advice do you have for people who are looking to start a career in growing?
Reach out to companies who are already out there. You could start off part-time or as an assistant. If you are patient and dedicated then it’s a journey I promise you won’t regret. It takes a lot of work, but the outcome is amazing - you’ll be learning so much about this new technology. You’ll also build great relationships: there are so many amazing people in this industry who are so interesting, with different backgrounds, who are willing to share their knowledge. You can always learn more and other people are a great source of that.
What about for those looking to start a vertical farming business?
Do your homework. There are people out there who you can reach out to and it’s very easy to get information. It’s very easy to get excited about the idea and jump straight into it, because it is exciting and can be very rewarding, but it’s really important to do it step by step. Know how to scale properly, learning the differences between a small and larger farm. Understand how many people you’ll need and the logistics. I’d also advise people to get some practical work experience before you buy. You want to start the company knowing the tricks of the trade.
Image from: LettUs Grow
LettUs Grow Blog: www.lettusgrow.com/blog/advice-for-vertical-farmers
Vertical Farms Grow Veggies On Site At Restaurants And Grocery Stores
The Vertical Field setup retains many of the advantages of hydroponic vertical farms, but instead of the plants growing in a nutrient-packed liquid medium, the container-based pods treat their crops to real soil, supplemented by a proprietary mix of minerals and nutrients
By Paul Ridden
The Vertical Field urban farm pod can be installed in parking lots or inside warehouses, with a modular design that can grow according to customer need Vertical Field
Last month we reported that a huge vertical farming operation near Copenhagen in Denmark recently completed its first harvest. That setup uses hydroponics, but the veggies grown in Vertical Field urban farming pods take root in real soil.
Traditional agricultural farming involves the use of a lot of land and resources to grow crops, and then even more resources to harvest and transport the goods – sometimes thousands of miles – to where consumers can get to them.
As well as requiring a fraction of the growing space, controlled-environment agriculture systems such as hydroponics operations can be much more efficient, are no longer bound by season or location, the growing to harvest cycle is reduced and crops could be produced all year, and as with the Copenhagen operation, they can be set up close to where the food is purchased or consumed.
The Vertical Field setup retains many of the advantages of hydroponic vertical farms, but instead of the plants growing in a nutrient-packed liquid medium, the container-based pods treat their crops to real soil, supplemented by a proprietary mix of minerals and nutrients. The company says that it opted for geoponic production "because we found that it has a far richer flavor, color, and quality."
Vertical Field's urban farms grow walls of veggies inside recycled shipping containers
Vertical Field
"Vertical Field offers a revolutionary way to eat the freshest greens and herbs, by producing soil-based indoor vertical farms grown at the very location where food is consumed," said the company's CEO, Guy Elitzur. "Not only do our products facilitate and promote sustainable life and make a positive impact on the environment, we offer an easy-to-use real alternative to traditional agriculture. Our urban farms give new meaning to the term ‘farm to table,’ because one can virtually pick their own greens and herbs at supermarkets, restaurants or other retail sites."
The recycled and repurposed 20- or 40-ft (6/12-ft) shipping containers used to host the farms can be installed within reach of consumers, such as in the parking lot of a restaurant or out back at the grocery store. Growers can also scale up operations to more than one pod per site if needed, and the external surfaces could be covered in a living wall of decorative plants to make them more appealing.
The vertical urban farms are claimed capable of supporting the production of a wide range of fruits and veggies – from leafy greens and herbs to strawberries and mushrooms, and more. And it's reported to use up to 90 percent less water than a traditional farming setup.
"Through internal experiments with our irrigation method using data from sensors and models we have understood that this is the level of water efficiency," Vertical Field's Noa Winston told New Atlas. "Thus we arrived at an optimal irrigation protocol tailored to the needs of the plant."
According to the company's website, though pesticide-free, the system is not yet considered organic (though Vertical Field is currently in the process of attaining organic certification for the urban farm unit from the USDA). The crops also grow in a bug-free environment.
"The container is kept bug-free because it is sealed off, automated, and we limit human entry to only essential people and essential work," Winston explained. "The container farm itself is not a street vendor or a point of sale, therefore unnecessary or frequent entry does not occur."
Installing a Vertical Field urban farm in a grocery store parking lot means that consumers can benefit from fresh veggies all year long Vertical Field
Unlike some high-tech farming solutions, staff won't need special training to work with the vertical farm as the automated growing process monitors, irrigates, and fertilizes the crops as they grow thanks to arrays of sensors that continually feed data on climate, soil condition, LED lighting and so on to management software. Each vertical farm unit has its own Wi-Fi comms technology installed to enable operators to tap into the system via a mobile app.
The company told us that, by way of example, one container pilot farm offered a growing space of 400 sq ft (37 sq m) and yielded around 200 lb (90 kg) of produce per month, harvested daily. Lighting remained on for 16 hours per day. We assume that the pods are completely powered from the grid at their respective locations, though the company says that it is looking at ways to make use of solar panels as well as making more efficient use of water.
Vertical Field has been around since 2006 and has built a number of living green walls around the world since then. The soil-based vertical farm initiative was started in 2019.
Recent installations include the first Vertical Field container farm in the US at a restaurant named Farmers & Chefs in Poughkeepsie, New York, which started producing its own crops of fresh greens in mid-April 2020. Last month, following a successful pilot, Israel's largest supermarket chain, Rami Levy, signed an agreement with the company to roll vertical farms into dozens of store locations over the course of the next five years.
"The Rami Levy chain understands the social responsibility that it has for customers as related to food security and supplying the highest quality products while maintaining low prices," said the chain's Yafit Attias Levy. "Our customers bought Vertical Field's produce during the pilot and returned to purchase more. Therefore, we have decided to expand the partnership with Vertical Field to additional branches of the supermarket, and to offer fresh, high-quality, and pesticide-free produce in a way that increases shelf-life for our customers."
The Vertical Field urban farm can produce crops year round, without the use of pesticides Vertical Field
And earlier this month, Moderntrendo SRO – one of the largest agricultural distributors in Ukraine – signed up for a pilot project that will start with supermarket chain Varus, and potentially expand to other chains.
"We are extremely excited about our partnership with Moderntrendo SRO which has led to the project with Varus and will lead to more projects in the near future with more chains in Ukraine," Vertical Field's Guy Elitzur said. "One of the realizations that have surfaced during the COVID-19 crisis is the need to develop solutions that allow urban residents access to healthy food, with minimal human handling and without depending on transportation and shipping from remote locations. We are delighted to be able to provide - and expand access to - healthy, and high-quality vegetables grown right outside the consumer's door."
As well as grocery outlets and restaurants, the company sees its container-based vertical farms also being installed in hotels, universities, hospitals, and so on, in the future. The video below has more.
Grow Vegetables On-Site with Vertical Field
Source: Vertical Field
A Whole Season of Hybrid Tomato Cultivation Den Berk Delice & Bryte Confirm: “LED Ensures Controllability”
A stronger plant, higher fruit weight, and more uniformity in growth; these are the results of a lit tomato crop when combining Philips GreenPower LED toplighting compact and HPS lighting in a hybrid lighting solution
September 9, 2020
A stronger plant, higher fruit weight, and more uniformity in growth; these are the results of a lit tomato crop when combining Philips GreenPower LED toplighting compact and HPS lighting in a hybrid lighting solution. The growers, the world-renowned tomato cultivators Bryte from the Netherlands and Den Berk Délice from Belgium share their experiences with hybrid lighting during the first cultivation season in this article. Both projects were installed at the end of 2019
Both entrepreneurs were very positive about their experiences after a year of tomato cultivation with hybrid grow light. The combination, which resulted in a more uniform fruit and crop growth and a more controllable greenhouse climate, asks for more. Cultivation with hybrid lighting, in which LED lighting is combined with HPS lighting, however, requires a different approach than cultivation with only HPS lighting. “The big advantage of LED lighting is that there is much less radiant heat from the light, which gives us more control over the climate in the greenhouse. Since light and temperature can be controlled more independently from each other with hybrid lighting, we have to change the way we approach the climate differently and that requires a new way of thinking, where the experience of the Signify plant specialists comes in handy, ”says Zwinkels.
Heat differences in the greenhouse
Where heat is mostly the deciding factor with traditional HPS illumination - but also plays a major role as an unavoidable by-product for cultivation control - this is no longer the case with hybrid illumination. LED leads to much less excess heat in the greenhouse, which makes it possible to control light and temperature separately. It is thus easier to control the growing conditions. For example, Den Berk Délice chooses to grow generatively up to 28° C in winter and from March more vegetatively to keep a strong crop. Lucas: "We noticed that we are much more in control with LED." The cultivation experts at both companies carefully thought about how they could anticipate on the changing temperature situation in the greenhouse. Erik: "With us, the position of the growth tube could be at the expense of the fruit weight. In our case, the best solution was to introduce extra heat from the bottom of the greenhouse. We also noticed that control errors were less likely to be made due to better control over the climate and that the climate became more constant. We saw positive crop development and were satisfied with the fruit weight and the crop growth."
Illuminate longer
“A big advantage of hybrid cultivation in comparison with HPS is the possibility to light the crop for a longer period of time", said Koen. “Especially in the winter months, a high crop yield is important to us; it is a period that we want to make the most of. We have seen that with hybrid cultivation you can illuminate earlier in the fall, but also until deeper in the spring, up to thirteen or fourteen hours a day. Of course, you have to keep looking at what extra lighting brings in terms of production and costs.”
Light advice
The plant experts of Signify are experts in using LED and know better than anyone else what LED lighting means for crop growing and climate. In the past growing season, they assisted the companies with light and climate advice. Both companies now have 180 µmol/s/m2 light, distributed across 90 µmol/s/m2 LED toplighting compact and 90 µmol/s/m2 HPS lighting. The Philips GreenPower LED toplighting compact was introduced to the market during the last growing season. "Signify talks a clear language", said Erik. "They are the right discussion partner for me, who regularly visits and discusses what we encounter in practice." Koen adds: “The specialists also have a large network. Via them, I managed to get into contact with other growers who also use LED. I look forward to the annual Tomato Community Event organized by Signify, where cultivators from around the world get together. This not only gives me the opportunity to share experiences with LED lighting, but also to expand my network that I can take advantage of in the future. We always see talking to like-minded people as very valuable.”
Does LED toplighting have a future?
Firstly, LED saves up to 60% on energy costs, but there is more. Erik: "As cultivator, I would like to bring the winter to the summer. LED lighting makes it possible to go to higher light levels and is the right way to do that. I prefer a hybrid solution with HPS, and then look at how we can regulate the heat in the greenhouse.” For Koen, the ideal cleaning conditions, where the modules do not have to be shielded, and the simple scaling options are reasons to choose a combination of HPS with LED toplighting compact luminaires. He refers to the plug-and-play ease of installation of the Philips GreenPower LED toplighting. Both consider future investments in a larger portion of LED in their greenhouses. They look forward to the development of LED in combination with higher light levels.
Create the correct balance to control your crops
Erik wondered if he, at his company, as he said, maybe loved the plants too much. In passing, he refers to the learning curve that you as a grower with LED go through. "You control it differently with hybrid lighting and that requires experience that you will gain through the years. You become wiser. Light and heat become more tangible and you are better able to control the right balance in your crop. I see it as an added value in which we can develop ourselves year after year, with better end results. Let the summer come during the winter!"
Erik and Mark Zwinkels are co-owners of Bryte; with 40 hectare - of which 60% is lit - one of the biggest players in the Dutch tomato cultivation. Koen Lauwerysen is one of the four business managers at Den Berk Délice, where Lucas Aertsen is the cultivation manager. With 60 hectares tomatoes - of which half is lit - their company is also one of the bigger ones in Belgium. Both share their experiences during the past cultivation season where they used the combination LED and HPS for the first time. Bryte installed it on eight hectares, and Den Berk Délice on ten.
For further information, please contact:
Global Marcom Manager Horticulture at Signify
Daniela Damoiseaux
Tel: +31 6 31 65 29 69
E-mail: daniela.damoiseaux@signify.com
Signify Global Media relations - Professional Lighting
Wendy Schellens
Tel: +31 6 51 863 401
Email: wendy.schellens@signify.com
About Signify
Signify (Euronext: LIGHT) is the world leader in lighting for professionals and consumers and lighting for the Internet of Things. Our Philips products, Interact connected lighting systems and data-enabled services, deliver business value, and transform life in homes, buildings, and public spaces. With 2019 sales of EUR 6.2 billion, we have approximately 36,000 employees and are present in over 70 countries. We unlock the extraordinary potential of light for brighter lives and a better world. We have been named Industry Leader in the Dow Jones Sustainability Index for three years in a row. News from Signify is located at the Newsroom, Twitter, LinkedIn, and Instagram. Information for investors can be found on the Investor Relations page.
VIDEO: 8 Startups That Are Revolutionizing AgTech
The growing interest in AgTech is reflected in venture capital investments for AgTech startups. According to Pitchbook, $6.7 billion was invested in AgTech startups in the last five years and $1.9 billion in the last year alone. These 8 AgTech startups are paving the way to revolutionize the future of the agriculture industry.
Agriculture is changing rapidly in the modern age. The global population is rising at an alarming rate and consumer preferences are shifting towards organic and sustainably produced goods. To keep up with these demands, the traditional agriculture industry must adopt new technologies to make farms more efficient and automate production.
The growing interest in AgTech is reflected in venture capital investments for AgTech startups. According to Pitchbook, $6.7 billion was invested in AgTech startups in the last five years and $1.9 billion in the last year alone. These 8 AgTech startups are paving the way to revolutionize the future of the agriculture industry.
1. Big Wheelbarrow
Big Wheelbarrow connects wholesale food buyers with local farmers. Big Wheelbarrow makes it faster and easier for buyers to work with small independent growers, regardless of size. Their technology empowers their customers to offer local products to their clients without the time and effort it used to require.
2. Vestaron
Vestaron Corporation develops and produces insecticides by employing peptides sourced from spiders in the United States. Its products are used in agricultural, animal health, and specialty non-crop applications, as well as in-household insects and commercial pest control applications.
3. Cainthus
Cainthus is developing the world’s most advanced technology for dairy farms today; technology that’s transformational for animals, farmers, and the production of food. Using computer vision and artificial intelligence to identify health, reproduction, and environmental changes early on, Cainthus translates visual information into actionable data.
4. Rex Animal Health
Rex Animal Health is on a mission to help livestock producers and farmers feed the world by increasing productivity and predicting, preventing, and precisely managing disease in the herd. They have a built up the largest database of clinical, health, performance, and genetic data on these livestock. Also, agribusinesses can use this data in order to understand their supply chain to identify the source of potential food borne illness, find the most efficient producers, set prices in commodities trading, and to understand and assess risk to increase transparency in the food supply chain.
5. Smallhold
Smallhold provides retailers and restaurants with contained-environment vertical farm units that produce large amounts of mushrooms, herbs, and leafy greens with minimal labor. Their current product offering is with on-site mushroom production and can produce up to 120 lbs/week in the space of a bookcase. The mushrooms are certified organic and are competitive with conventional ways of growing.
6. Babylon Micro-farms
Babylon Micro-farms provides an on-demand indoor farming service to make sustainable indoor farming more accessible than ever before. Their farms grow fresh produce 2x faster using 90% less water than conventional agriculture, without the use of pesticides or harmful chemicals. Their business model drastically reduces the upfront costs and expertise associated with indoor agriculture, powered by a patented IoT platform that remotely operates the ecosystem of farms.
7. Kiverdi
Kiverdi technology uses all-natural microbes to transform CO2 and other gases into high-valued nutrients, oils, and bio-based products. Kiverdi’s proprietary platform, which extends early NASA research, converts carbon dioxide from diverse industrial and agricultural sources into new materials using proprietary gas fermenting microbes.
8. Cambridge Crops
Cambridge Crops develops natural and edible coatings to extend the shelf life of a wide variety of perishable foods. Their coatings regulate the exchange of gases and slow down bacterial growth. These unique attributes allow for drastic improvements in shelf life for everything from avocados and spinach to meat and seafood. Cambridge Crops’ technology is easily integrated into existing packing and processing lines, minimizing the need for supply chain changes or expensive on-boarding. By increasing the window of peak freshness, Cambridge Crops allows food producers, food processors, and retailers to extend shelf lives, reach new markets, and reduce waste.
UAE, Israel Both Expect To Benefit From Agricultural Ties
The regional government in the capital, Abu Dhabi, announced in April that it was investing approximately $100 million in vertical farming
TARA KAVALER
08/23/2020
Emiratis will have access to Jewish state’s agritech while Israelis will gain financially
The United Arab Emirates, where less than 1% of the earth is arable, is set to reap major growth from its agricultural sector with the help of Israeli technology after the two countries normalize relations.
Israel, a world leader in agriculture under conditions with little water and high heat, will sell its expertise to farmers in the desert nation where the average temperature in August is 43°C (109°F) and the average annual temperature is 30°C (86°F). Israeli growers also plan to export food to the UAE, from where it may be re-exported to currently unreachable markets.
The UAE and other Gulf Cooperation Council countries have been trying to become more self-reliant in food, most of which they import. The UAE has already seen an explosion in agricultural growth, particularly in vertical farming and other next-generation planting techniques. It plans to start using hydroponics, soil-less crop cultivation, before the end of this year. The regional government in the capital, Abu Dhabi, announced in April that it was investing approximately $100 million in vertical farming.
“Any food production here requires a technological solution,” Nicholas Lodge, a UAE-based agricultural expert, told The Media Line.
“It doesn’t make sense to grow almost anything in terms of arable crops, except for higher-value crops like tomatoes that are grown in greenhouses, with the latest technology, like hydroponics, where minimal water is needed,” Lodge said.
Dr. Yaron Drori, an Israeli agronomist and co-owner of Etza Agriculture consultants, told The Media Line: “There are very sophisticated greenhouses all over the world, especially in northern Europe, but what is special about Israeli equipment is that we know how to deal with the excess of heat in the structures.”
“Most of the year in our greenhouses, we are trying to avoid overheating. This is the opposite of what you are trying to do in Europe, where you are trying to gain heat,” added Drori, whose company specializes in desert farming in southern Israel.
The greenhouses in Israel use shade nets that can be turned on automatically with a “smart” control system that monitors temperature, radiation, and humidity.
The system also activates cooling sprinklers, or a “curtain” of water, which brings outside air into the greenhouse to change the high temperatures and low humidity that make desert agriculture difficult.
The device also irrigates plants without wasting scarce resources. Saving water is one of the centerpieces of Israel’s “advanced innovation” in agritech, Drori said.
Associate Prof. Zvi Peleg of the Hebrew University in Jerusalem spoke to The Media Line about his work at the university’s Robert H. Smith Institute of Plant Sciences and Genetics in Agriculture to reduce the amount of water plants need.
“We are working now on how to improve water-use efficiency, meaning the plants will produce more biomass by using less water.”
“We are trying to change the plant … so it will be more suitable for the climate,” Peleg said. “We are changing the root system to become deeper … to get to the water more easily and reduce the size of the root architecture so it will not take so much water from the soil because it’s a very limited resource.”
He also explained some of Israel’s latest agricultural technology.
“By using sensors to check the water status in the soil and the plant, you improve productivity because you irrigate whenever the plants need water, not whenever you feel they need water,” Peleg said.
“We are also using thermal imaging to see if a plant needs water or nutrients. There are a lot of techniques now related to drones and different kinds of cameras to detect the plant’s growth, as well as diseases and other problems the plant has,” Peleg said. There is “a lot of technology that can benefit many regions, including the UAE.”
Meanwhile, the UAE is doing high tech agricultural research of its own. Dr. Mohammed Abdul Mushen Salem Alyafei, an associate professor at The College of Food and Agriculture at United Arab Emirates University, said studies are being done in the Emirates on an “open-top chamber,” which encircles a plant to examine the impact of carbon dioxide levels and an “aeroponic control unit.” Aeroponic devices grow plants in the air in a moist environment.
Israel’s successful efforts to make its own desert bloom have resulted in exports of its desert produce.
Some “60% of Israel’s [agricultural] exports, which include tomatoes and watermelon, come from the Arava [in the southeast], which is very similar to the UAE, with bad soil and poor [quality] and limited amounts of water,” Shafrir Godel, an agricultural business expert, told The Media Line.
“Everything is against the farmer, and yet it is the major export region for Israeli produce [sent] to Europe and America,” said Godel, founder and managing director of Israel-based AgriQuality, an international consulting company.
Long-distance exporting is very expensive, but Israel has figured how to do it profitably; this know-how could help the UAE.
“The chain from the seed to the supermarket shelf abroad is something that Israelis do well and cost-effectively: starting with the variety [of crop] to plant, the methods and technical solutions for growing, sorting, picking, the plastic you are using to extend shelf-life, and getting them to the right companies that have a hold on the main markets.”
Israeli growers are also looking for new markets.
“Over the years, Israeli farmers have grown with a capacity that is way beyond Israelis’ ability to eat. We need other markets. It is a new market, and it could be a transit station to places that we normally would not sell to,” Godel said.
The UAE is one of the world’s top three re-export hubs.
Agricultural expert Lodge noted that “the UAE has built a reputation as a transport hub serving many countries.” “It’s quite interesting what you might be able to do with that mix of location, technology, and capital for certain crops.”
Both countries’ agricultural businesspeople are excited about the potential for the new alliance.
“The UAE has a history of looking at where it can forge partnerships, where it can make investments where there’s a mutual benefit,” Lodge said. “Israel is an acknowledged leader in arid farming and the application of technology to make farming possible. I’m sure it’s one of the areas that could and should benefit both parties.”
Etza Agriculture’s Drori said: “If you bring the practical and academic knowledge and all the technology that we have to the UAE, we can all benefit from it, both the Emirati and the Israeli companies.”
“Israel gets business, so it benefits financially. But beyond that, it would be fascinating to work there. It’s a new place, you learn and see new things,” he said. “It’s a new world for us.”
Lead photo: Dr. Effi Tripler, a soil and water scientist, stands next to a solar-powered sensor that helps a drip-irrigation system know when and how much to water a crop of sorghum at the Central and Northern Arava R&D facility on May 21, 2015, in Hatzeva, Israel. The soil and water R&D facility tests and produces various crops in the dry, harsh climate of the Arava, near the Jordanian border. (Ann Hermes/The Christian Science Monitor via Getty Images)
TitletownTech VC Fund Invests in Appleton-Based Agtech Startup Fork Farms
The TitletownTech venture capital fund, a $25 million fund and venture studio led by the Green Bay Packers and Microsoft, is investing in a Wisconsin agriculture technology startup that makes hydroponic systems
TitletownTech is located within the 45-acre Titletown district and is devoted to tech startups, venture capital and offices for the leadership team that manages Titletown operations.
The TitletownTech venture capital fund, a $25 million fund and venture studio led by the Green Bay Packers and Microsoft, is investing in a Wisconsin agriculture technology startup that makes hydroponic systems.
Appleton-based Fork Farms' indoor vertical farming system, called the Flex Farm, was designed to eliminate food transportation costs, consume 97% less water than traditional agriculture practices, and be 40% more energy efficient compared to hydroponic systems currently in the market.
“Low accessibility of fresh food is a huge problem for many people, and Fork Farms is a great example of local entrepreneurs chasing a big opportunity to make positive change," said Craig Dickman, the managing director at TitletownTech, in a statement.
During the last 12 months, TitletownTech has invested in more than a dozen startups. Two of those startups have relocated their headquarters to Green Bay following the investment and including Fork Farm, 10 of TitletownTech’s investments are companies based in Wisconsin.
The fund, which is managed from the Packers' Titletown District in Green Bay, writes checks between $100,000 and $1 million.
“TitletownTech is an incredibly innovative model that will significantly bolster the local start-up economy," said Fork Farms founder Alex Tyink. "It provides an exemplary blueprint that should be followed by other organizations around the country. The depth of support is unprecedented and will provide Fork Farms significant acceleration and lift to our organization's mission of unleashing the power of fresh food production."
Lead Photo by Nick Williams
By Nick Williams, who is a reporter covering residential real estate, transportation and technology for the Milwaukee Business Journal
August 04, 2020