Welcome to iGrow News, Your Source for the World of Indoor Vertical Farming
Bucolic Kailash, An Agritech Startup, Brings “Computerized Farms” From The Future!
At the futuristic and smart agritech start-up “Bucolic Kailash”, a mission is becoming more real every day; the vision that soon in the very near future, starting and running farms profitably, will be as easy as downloading an app
July 6, 2021
At the futuristic and smart agritech start-up “Bucolic Kailash”, a mission is becoming more real every day; the vision that soon in the very near future, starting and running farms profitably, will be as easy as downloading an app.
Bucolic Kailash researches, manufactures and markets user-friendly life-growing computers. These computers are meant to enable economic and nutritional autonomy for its users. For example, one of the patented life-growing computers at Bucolic testing labs grows as much as Rs. 25 lakh worth of healthy produce annually in just 100 sq ft space with operational expenses of under Rs. 50,000/month for the user. Systems like these can be started with as low as 3 sq ft of space and scaled up with time.
Bucolic Kailash’s Vertical Garden and Vertical Farm System series are made to deliver super intensive and sustainable cultivation that is 100% organic, without soil and achieves more than 90% of water and energy saving. The smart agritech company has developed and acquired multiple patents on products and technologies that have shown promising results in the scope of personal, organized, and organic aquaponics farms. Their hydroponics computers grow up to 84 plants, vegetables, and salads in 1 sq ft. Their mushroom farming computers grow 50 Kgs of mushrooms in 3 sq ft every 45 days. Their fish-farming computer designs yield up to 800 Kgs of shrimps in just 10 sq mt every 150 days. All of this is achieved with IT, IoT and their custom developed life-growing AI. The Systems are engineered by closely working with its early customers and focusing on ease of use, AI & IoT powered automation and distribution. Engineering, Manufacturing, and IT has been the most guiding product shaper for the company’s early success.
Bucolic Kailash has unlocked a huge market for vertical farming, fish farming and hydroponic personal gardens.Their use of technological intervention empowers people to cultivate and harvest every day and in the comfort of their own homes through most efficient and effective ways. The company’s new offering under Vertical Garden system series ‘Tree of Wisdom – Eleganté’ is by far the most groundbreaking vertical hydroponics system the world has ever seen before. The product complies with ISO 9001:2015 for best in grade Quality Management and has been tested to meet the required hydroponics system parameter controls, as well as the state-of-art features. Tree of Wisdom - Eleganté has been doing well since its launch on 11th May 2021 at amazon.in.
The Company was founded by Mr. Utkarsh Sinha in March 2020 and now the company is a community of 18 carefully selected and nurtured members. During our interview with the founder, we found him very engaged and excited about the road ahead. Utkarsh graduated in MCIT-Computing from The University of Melbourne and B. Tech from MIT, Manipal. According to him, having worked with Godrej's R&D, Honeywell Aero HTS, Fagerhult OR Tech teams in India and Australia, helped him manage the company’s departments, processes, and make shipments possible from concept-to-product, even during the pandemic. The company runs its fully functional aquaponic devices manufacturing facility in Manipal on lean manufacturing and quality control principles.
On further talking with the founder, we found that the company’s mission with its life-growing computers is to ultimately enable community empowerment and economic development. The company believes that such life-changing science and technology should be available as user-friendly products. In the founder’s words, “It was a contrasting journey that I took back home to India in 2019 while having employment opportunities from companies in Australia that made me reflect upon my priorities and self-actualization needs. I wish to make communities exchange value through healthy food and money that can make coexistence wholesome.” We believe that Bucolic Kailash is a futuristic company that understands the needs of today's communities and a fast-changing world. They develop and market environmentally friendly agritech computers. The company has raised partial seed-funding after a year of setting up its manufacturing factory and distribution channels and they plan to expand their life-growing computers reach to a wider niche and the tap global market in the next 6 months.
Visit www.bucolic.ltd for more inspiration and information
Building A Vertical Farm With Partners — An Ongoing Case In Switzerland
iFarm has recently announced a partnership with YASAI and Logiqs to create a new vertical farm in Switzerland. Working together, we aim to expand into new locations, highlight the growth potential of vertical farming in Europe and showcase the benefits of working with industry partners
iFarm has recently announced a partnership with YASAI and Logiqs to create a new vertical farm in Switzerland. Working together, we aim to expand into new locations, highlight the growth potential of vertical farming in Europe and showcase the benefits of working with industry partners.
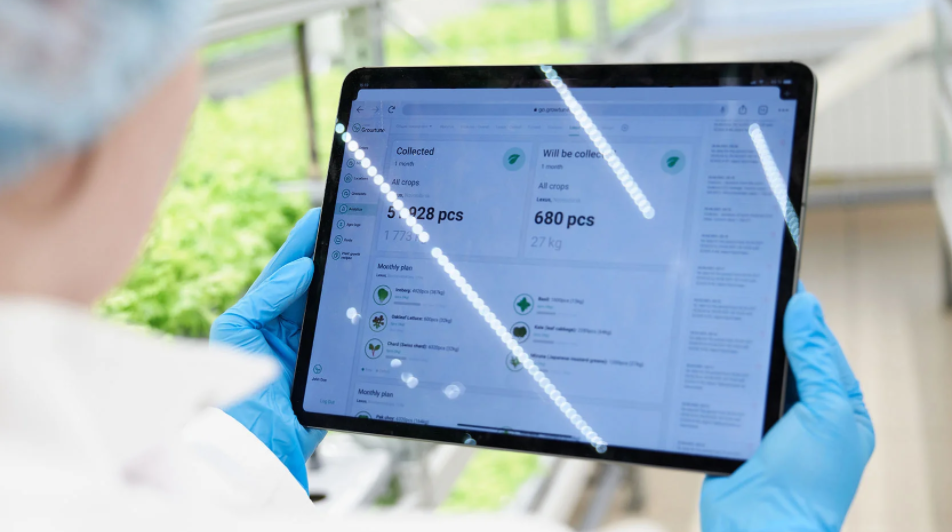
On 5 February 2021, iFarm (The Netherlands), YASAI AG (Switzerland) and Logiqs B.V. (The Netherlands) announced a strategic partnership with plans to launch Zurich’s first vertical farm. iFarm will supply the nutrient solution management system, specialist sensors, control systems and Growtune software platform and Logiqs will be supplying automated shelving systems at Yasai’s 673 sq. m plantation.
Now, we’re giving you behind-the-scenes access to the data and decisions that were the driving force behind the venture.
With contributions from Mark E. Zahran, Co-Founder, and CEO of YASAI, Gert-Jan van Staalduinen, CEO and Owner of Logiqs, and Kirill Zelenski, Managing Director of iFarm Europe, we’ll look at how and why this strategic partnership came about and what the future holds.
Read on to find out more about what goes into launching a successful vertical farm and how you can achieve the same goals.
Why Switzerland? Why Europe?
As you may already know, location is a critical factor when assessing the feasibility of a vertical farm. Locating a vertical farm in a densely populated urban area, with limited access to traditional farming facilities and rural land, ensures there is untapped demand for locally grown produce.
For Mark, being based in Switzerland made Zurich a natural choice for the first YASAI vertical farm. However, selecting the right location wasn’t merely a matter of convenience, as he emphasised:
The market is here. The market demands local produce, grown in a responsible and sustainable way, and, with the right technology, you can meet the demand and create a successful business.
Although the concept of vertical farming is becoming increasingly popular in Europe, there’s no doubt that the regional market lags behind its U.S. and Asian counterparts, but this needn’t be a deterrent for potential investors or farmers. In fact, the growth potential makes vertical farming in Europe a viable form of investment:
Vertical farming has grown more quickly in America and Asia but, I think, in the end, we will have a more sustainable model and acceleration is already taking place.
Gert, Logiqs
With demand for fresh, locally sourced produce creating a market for vertical farms and investors actively seeking out new ventures, it’s clear that Switzerland, and Europe as a whole, is a prime location for the partnership. By taking a strategic approach, other farmers, entrepreneurs and start-ups can use the same parameters to identify key locations for future vertical farms.
Do Local Trends Matter?
Local trends and current market conditions certainly play a role in identifying viable locations, and opportunities, for vertical farming. Whether you’re forming a partnership or starting your own venture, you’ll want to ensure that your vertical farm is situated in an area that prioritises what you can offer.
In Europe, for example, the current range of fresh produce available in the supermarkets is somewhat limited, despite the growing popularity of pesticide-free produce and plant-based foods. As awareness of environmental issues and climate change becomes more important to consumers, this is already being reflected in their decision-making and purchase behaviour.
The European Statistics Handbook reports that Nordic countries (Sweden, Finland and Denmark) are responsible for just 1.5% of Europe’s fresh produce, with the local climate being cited as the main obstacle to production. With climate-controlled production facilities, however, the potential of vertical farming in this region is clear and presents a worthwhile investment for entrepreneurs, farmers and investors.
Furthermore, the CBI estimates that Europe is responsible for 44% of worldwide fresh fruit and vegetable trade. Exporters to the region are encouraged to capitalise on the continent’s ‘off season' in order to maximise their profits. While traditional farming methods do, of course, result in off seasons, this no longer needs to be the case. The ability of vertical farmers to grow high-quality produce year-round using climate-controlled environments effectively eradicates off seasons and facilitates domestic fruit and vegetable production.
Based on these trends, it’s possible to predict that European consumers will respond positively to the presence of pesticide-free, locally grown, produce in shops and restaurants. For retailers and food or vegetables distributors, this makes partnering with vertical farmers a viable and exciting venture.
In relation to our current partnership, the fact that Switzerland imports 48% of its vegetables, reflects the Europe-wide food production trends and indicates that there is a growing market for fresh, local produce:
When fresh produce is imported, companies are more focused on transportability than flavour or quality. By shortening the supply chain and growing produce locally, we can deliver better tasting vegetables and higher quality produce.
Mark, YASAI
At the same time, a more health-conscious society is placing greater emphasis on food quality and diversity. The emerging, ‘pay the farmer, not the doctor' movement, is reframing the way we think about food as the foundation of our health, which will no doubt impact future consumer behaviour.
If you look at the last 200 years, the amount that people spend on medical care was increasing all the time and the amount they paid for food was decreasing, so now we are at a sweet spot where it could change again and people would eat more consciously and also get less sick, which leads to a healthier society.
Mark, YASAI
It’s evident, therefore, that local trends have been a key factor in identifying the right location for YASAI’s new vertical farm. By assessing potential locations from an economic perspective, analysing the domestic market and identifying current and emerging trends, it’s possible to determine where vertical farms can have the greatest success.
Finding the Right Partners
When you’re embarking on any venture, it’s important to work with the right partners. So, how did the alliance between YASAI, Logiqs and iFarm come about?
Already operational in Europe, Russia and the MENA, iFarm was approached by YASAI on the basis of our leading vertical farm solutions, collaborative approach to farming and reputation within the industry. Indeed, the success of the solutions was a factor in why YASAI were so keen to work with iFarm:
What we saw, in terms of hardware, is that there are very good logistics partners out there, such as Logiqs, and, in terms of software, iFarm’s solutions were already proven. Also, the range of plant growth recipes available via iFarm’s Growtune software was critical to our goal of increasing crop and food diversity.
Mark, YASAI
From our perspective, we were excited to work with both YASAI and Logiqs to create Zurich’s first vertical farm. Both the passion and expertise of the partners were clear from the outset with the potential for a long-lasting and successful relationship. Furthermore, our economic analysis of the region confirmed what a lucrative market Europe is for vertical farming and further cemented our commitment to expanding in the region.
Kirill, iFarm
However, identifying the right partners isn’t solely about finding organisations who can meet your needs or deliver the solutions you need to begin operating.
We’ve been delivering horticultural solutions for 45 years, so we have a lot of experience we can bring to a partnership, but, when it comes to complex innovation, it’s very important to have partners that are open and all focused on the same objective, instead of their own, individual success.
Gert, Logiqs
Creating the vertical farm in Niederhasli, Zurich, is a joint collaboration, with YASAI taking on the management, operations and branding, Logiqs providing automated hardware and iFarm delivering the nutrient solution management system, climate control equipment and the Growtune software platform. While each partner is bringing distinct, critical components to the table, it’s the values and objectives that form the union and facilitate a constructive and collaborative working partnership.
What we really liked about iFarm is its collaborative mindset. That’s how we want to accelerate, vertical farming — with collaboration.
Mark, YASAI
Whether you’re a farmer, retailer, food distributor, investor or entrepreneur, there are partnership opportunities available right now. However, it’s important to think about long-term goals and what success looks like when you’re deciding who to work with. By partnering with people and companies that share your values and ambitions, you can work together cohesively and increase your success.
Why is Vertical Farming Important?
Vertical farms may be a profitable investment, but they offer much more besides revenue and profit. In addition to being a prime investment in Europe, vertical farming can change the way we approach food production and provide better access to food, as well as reducing the environmental impact current production methods have.
At iFarm, the potential to spark worldwide change and benefit society has always been the driving force behind the operations, and we’re pleased to partner with organisations who share these values.
We have the ambition to accelerate access to ‘honest food'. People will learn about this partnership and will start to think about the way we produce foods and the potential vertical farming has to solve some of the acute global issues.
Gert, Logiqs
As we move towards a more circular economy, there’s a greater emphasis on the need to minimise waste and make better use of our resources. In comparison to traditional farming or greenhouses, vertical farming is more closely aligned to these objectives and will, therefore, be critical in shaping the future of food production.
If we want to create real circular food systems, we must think about how to integrate technology and not just build more efficient food factories.
Mark, YASAI
The trend towards sustainable, pesticide-free food production has gained traction in recent years, but it’s accelerated in recent months. As we continue to assess the impact of COVID-19 on the industry and society as a whole, it’s clear that the way we think about food, health and even retail is changing:
People started to rethink their diet habits, their way of life, and consider alternatives to the status quo.
Mark, YASAI
From a commercial perspective, the relative instability of large supply chains has been highlighted by COVID-19, which means businesses are now more wary of relying on complex chains and reluctant to put unnecessary distance between their own operations and their suppliers. As a result, the ability to grow produce in close proximity to retailers and distributors means vertical farms will play a key role in the evolution of the food production industry, in both the short and long-term.
With the potential to improve access to high quality produce, drastically reduce the environmental impact of food production, shorten supply chains and deliver better food diversity, vertical farming can provide solutions to so many of the issues we’re currently facing. From food scarcity in developing countries to volatility within the distribution industry, vertical farms can play a key role in transforming the way we grow, access and think about food.
What’s Next for iFarm, YASAI and Logiqs?
As YASAI’s Zurich vertical farm prepares to open in Niederhasli in autumn 2021, we’re already looking towards the future. We’ll be testing and perfecting our growing methods in Niederhasli, with a view to working together on an ambitious project to create another vertical farm that’s 10 times bigger. With plans already underway, the creation of Zurich’s first vertical farm could be the first step in our shared journey.
Is a Partnership Right for You?
Now you’ve got an insight into the rationale, decision-making and objectives behind our strategic alliance with YASAI and Logiqs, you may be wondering whether a partnership could offer the same growth potential to you.
By working with iFarm and other industry leaders, you can access the resources, services and expertise you need to create your own successful vertical farm. Whether you’re a traditional farmer who wants to incorporate new technology into your operations, a retailer that wants to access locally sourced produce or an investor looking for your next venture, a vertical farm partnership can deliver the practical, financial and sustainable rewards you’re looking for.
To learn more, take a look at how you can benefit from vertical farming:
1. Food, Fruit and Vegetable Distributors
For existing food, fruit and vegetable distributors, partnering with vertical farms and logistics companies offers clear benefits. With an abundance of crops being produced all year-round, distributors can expand their network and substantially increase their profitability.
As traditional farming delivers seasonal growth, distributors may be forced to work with numerous clients in order to trade throughout the year. Inevitably, this means changing distribution routes, switching equipment and altering the network to accommodate different types of produce.
In contrast, the year-round production at vertical farms enables distributors to minimise resource consumption, safeguard demand and use existing routes. As a result, food, fruit and vegetable distributors can maximise their own profitability by partnering with vertical farmers, investors, logistics providers, food retailers and entrepreneurs.
2. Food Retailers
Food retailers can benefit from vertical farm partnerships in a number of ways. For example, a food retailer can source fresh produce from their partners and increase the diversity of their stock. This enables retailers to enhance the quality and the flavour of their fresh produce, as well as meeting consumer demand for pesticide-free, locally-sourced food.
Critically, partnering with other organisations or investors to create a vertical farm also gives retailers the chance to shorten their supply chains. As we’ve seen over the past year, complex or lengthy supply chains are precarious, particularly when stock has a short lifespan, as is the case with fruits and vegetables. Supply chain delays and disruptions are now common, which leads to increased waste, additional expenditure and fewer products on the shelves.
As part of a vertical farm partnership, however, food retailers can produce their own stock, avoid the risk associated with lengthy supply chains and cater to a growing market. By doing so, retailers can reduce their expenditure, safeguard their supply chains and increase their profitability.
3. Investors
Investors, financial partners and private equity funds can capitalise on the evolving agro-tech industry by partnering with expanding vertical farms. As we can see with the YASAI vertical farm in Niederhasli, the initial production site is only a glimpse of what’s to come. With proven success at smaller sites, investors can get in at the ground level to fund expansion and reap the rewards.
The EU has already confirmed its plans to drastically reduce the use of pesticides in food production, with a 50% reduction estimated by 2030. This, combined with consumer demand for pesticide-free food, highlights a growing market. Furthermore, it’s a market that vertical farms can and will satisfy.
While the increasing market for pesticide-free produce is one reason why vertical farms present such a lucrative investment, there are many others. The relatively low start-up costs, in conjunction with low running costs, makes vertical farms a viable option for all types of investors.
Furthermore, many investors are actively seeking out ‘green investments'. From hedge funds to pension funds, an increasing number of people and companies are moving away from investing in products, firms or industries which are known to have a negative impact on the environment and searching for an alternative. Not only does a vertical farm partnership meet the criteria of a green investment and enhance the ‘green credentials' for all parties, it can also generate significant and sizable returns.
4. Distributors and Resellers of Agro-Technologies
For existing distributors and resellers of agro-technologies, the chance to form a partnership with vertical farmers, investors, retailers and entrepreneurs is undoubtedly compelling.
Instead of simply selling your tech innovations to farmers and companies, you’ll have the chance to create long-term professional relationships with people and organisations from your target audience. By doing so, you can increase customer lifecycle value and optimise your profitability.
However, the increased revenue isn’t the only benefit associated with a partnership. As we have seen with Logiqs' role within the iFarm and YASAI partnership, the chance to increase brand awareness within the industry and establish your firm as a market leader is valuable in itself.
As your role in ground-breaking partnerships becomes more widely-known, demand for your brand and your technologies is increased and further growth potential develops. From ad hoc sales to additional partnerships, distributors and resellers of agro-technologies can significantly increase their reach when they form partnerships with other people and organisations in the industry.
Additionally, being part of a partnership enables you to work closely with farmers and to gain an in-depth insight into the type of technology they require. In doing so, you will consistently enhance and evolve your technologies to deliver more efficient and more effective solutions. For agro-tech developers, the chance to shape the future of the industry makes a vertical farm partnership an opportunity that simply shouldn’t be missed.
To learn more or to explore upcoming partnership opportunities, contact iFarm today at +358 504 801 487 or email us at sales@ifarm.fi
Vertical Farming Startup Oishii Raises $50m In Series A Funding
“We aim to be the largest strawberry producer in the world, and this capital allows us to bring the best-tasting, healthiest berry to everyone.”
By Sian Yates
03/11/2021
Oishii, a vertical farming startup based in New Jersey, has raised $50 million during a Series A funding round led by Sparx Group’s Mirai Creation Fund II.
The funds will enable Oishii to open vertical strawberry farms in new markets, expand its flagship farm outside of Manhattan, and accelerate its investment in R&D.
“Our mission is to change the way we grow food. We set out to deliver exceptionally delicious and sustainable produce,” said Oishii CEO Hiroki Koga. “We started with the strawberry – a fruit that routinely tops the dirty dozen of most pesticide-riddled crops – as it has long been considered the ‘holy grail’ of vertical farming.”
“We aim to be the largest strawberry producer in the world, and this capital allows us to bring the best-tasting, healthiest berry to everyone. From there, we’ll quickly expand into new fruits and produce,” he added.
Oishii is already known for its innovative farming techniques that have enabled the company to “perfect the strawberry,” while its proprietary and first-of-its-kind pollination method is conducted naturally with bees.
The company’s vertical farms feature zero pesticides and produce ripe fruit all year round, using less water and land than traditional agricultural methods.
“Oishii is the farm of the future,” said Sparx Group president and Group CEO Shuhei Abe. “The cultivation and pollination techniques the company has developed set them well apart from the industry, positioning Oishii to quickly revolutionise agriculture as we know it.”
The company has raised a total of $55 million since its founding in 2016.
Study On Analytic Tools To Measure Future Plants Stress
The paper also assesses the future outlook, economic potential, and implementation strategies for the integration of these technologies in future farming practices.
New work from the Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology (SMART), MIT’s research enterprise in Singapore, and Temasek Life Sciences Laboratory (TLL) highlights the potential of recently developed analytical tools that can provide tissue-cell or organelle-specific information on living plants in real-time and can be used on any plant species.
In a perspective paper titled “Species-independent analytical tools for next-generation agriculture” published in the journal Nature Plants, researchers from the Disruptive and Sustainable Technologies for Agricultural Precision (DiSTAP) Interdisciplinary Research Group (IRG) within SMART review the development of two next-generation tools, engineered plant nanosensors and portable Raman spectroscopy, to detect biotic and abiotic stress, monitor plant hormonal signalling, and characterize soil, phytobiome, and crop health in a non- or minimally invasive manner. The researchers discuss how the tools bridge the gap between model plants in the laboratory and field application for agriculturally relevant plants. The paper also assesses the future outlook, economic potential, and implementation strategies for the integration of these technologies in future farming practices.
Crop loss
An estimated 11-30 per cent yield loss of five major crops of global importance (wheat, rice, maize, potato, and soybean) is caused by crop pathogens and insects, with the highest crop losses observed in regions already suffering from food insecurity. Against this backdrop, research into innovative technologies and tools is required for sustainable agricultural practices to meet the rising demand for food and food security — an issue that has drawn the attention of governments worldwide due to the Covid-19 pandemic.
Sensors
Plant nanosensors, developed at SMART DiSTAP, are nanoscale sensors, smaller than the width of a hair, that can be inserted into the tissues and cells of plants to understand complex signalling pathways. Portable Raman spectroscopy, also developed at SMART DiSTAP, encompases a laser-based device that measures molecular vibrations induced by laser excitation, providing highly specific Raman spectral signatures that provide a fingerprint of a plant’s health. These tools are able to monitor stress signals in short time-scales, ranging from seconds to minutes, which allows for early detection of stress signals in real-time.
“The use of plant nanosensors and Raman spectroscopy has the potential to advance our understanding of crop health, behavior, and dynamics in agricultural settings,” says Tedrick Thomas Salim Lew SM '18, PhD '20, the paper’s first author. “Plants are highly complex machines within a dynamic ecosystem, and a fundamental study of its internal workings and diverse microbial communities of its ecosystem is important to uncover meaningful information that will be helpful to farmers and enable sustainable farming practices. These next-generation tools can help answer a key challenge in plant biology, which is to bridge the knowledge gap between our understanding of model laboratory-grown plants and agriculturally-relevant crops cultivated in fields or production facilities.”
Early detection
Early plant stress detection is key to timely intervention and increasing the effectiveness of management decisions for specific types of stress conditions in plants. Tools capable of studying plant health and reporting stress events in real-time will benefit both plant biologists and farmers. Data obtained from these tools can be translated into useful information for farmers to make management decisions in real-time to prevent yield loss and reduced crop quality.
The species-independent tools also offer new plant science study opportunities for researchers. In contrast to conventional genetic engineering techniques that are only applicable to model plants in laboratory settings, the new tools apply to any plant species, which enables the study of agriculturally relevant crops previously understudied. Adopting these tools can enhance researchers’ basic understanding of plant science and potentially bridge the gap between model and non-model plants.
Technologies in agriculture
“The SMART DiSTAP interdisciplinary team facilitated the work for this paper and we have both experts in engineering new agriculture technologies and potential end-users of these technologies involved in the evaluation process,” says Professor Michael Strano, the paper’s co-corresponding author, DiSTAP co-lead principal investigator, and the Carbon P. Dubbs Professor of Chemical Engineering at MIT. “It has been the dream of an urban farmer to continually, at all times, engineer optimal growth conditions for plants with precise inputs and tightly controlled variables. These tools open the possibility of real-time feedback control schemes that will accelerate and improve plant growth, yield, nutrition, and culinary properties by providing optimal growth conditions for plants in the future of urban farming.”
“To facilitate widespread adoption of these technologies in agriculture, we have to validate their economic potential and reliability, ensuring that they remain cost-efficient and more effective than existing approaches,” the paper’s co-corresponding author, DiSTAP co-lead principal investigator, and deputy chair of TLL Professor Chua Nam Hai explains. “Plant nanosensors and Raman spectroscopy would allow farmers to adjust fertilizer and water usage, based on internal responses within the plant, to optimize growth, driving cost efficiencies in resource utilization. Optimal harvesting conditions may also translate into higher revenue from increased product quality that customers are willing to pay a premium for.”
Collaboration among engineers, plant biologists, and data scientists, and further testing of new tools under field conditions with critical evaluations of their technical robustness and economic potential will be important in ensuring sustainable implementation of technologies in tomorrow’s agriculture.
For more information:
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
www.mit.edu
A Fully Automated Three-Dimensional Vertical Farm Comes Into Operation
Eponic Agriculture Co. Ltd is a supplier of indoor farming equipment. Alice, the company's director, introduced the recently fully automated production system of a stereochemical vertical farm
Eponic Agriculture Co. Ltd is a supplier of indoor farming equipment. Alice, the company's director, introduced the recently fully automated production system of a stereochemical vertical farm.
"The current three-dimensional indoor farms on the market are based on semi-automated workflow, with some links requiring additional equipment configuration and no continuity in the whole planting system. In order to solve this problem, we developed and designed a complete automated planting system, including the processes from sowing to planting, full-spectrum planting light control, fertilization, harvesting, and cleaning. Which are all done by automated equipment. Whereas all procedures can be controlled by intelligent software with real-time monitoring, data collection, and many other functions."
Benefits of an automated farm
When talking about the advantages of the automated equipment, Alice said, "Take our recently built 20-layer vertical farm as an example. First of all, the mechanical sowing time is 10 times-30 times faster than manual sowing. And on top of that, the use of automated equipment can realize precise planting and efficient communication of multi-layer planting surfaces. The 20-layer vegetable trays are automatically transferred to the ground for uniform watering, harvesting, and cleaning. This greatly improves productivity.
Secondly, the use of lift trucks is required when handling high-level crops. There are certain safety hazards in using lift trucks in a small space. While operating the automated equipment, only a tablet computer is needed to control the whole planting process, which is much safer and more convenient."
Although automated vertical farm systems have many advantages, their application in China is not yet popular. "In terms of production design, we have gone through countless experiments to design the most suitable software program. As well as hardware equipment for practical planting applications. Luckily after a long period of research, we finally chose the most cost-effective and suitable materials. The R&D investment is large and time-consuming.”
From a cost point of view, according to Alice, a fully automatic system is 2-3 times higher in costs than the semi-automatic system which is currently used more often. Most traditional agricultural companies find it difficult to accept such high initial costs. Thirdly, the automated system requires high technical requirements for farm managers. Managers need to have an understanding of both planting technology and software. Alice adds: “It is for these three reasons that the application of fully automated stereoscopic systems is not very common in China and other countries."
Automated planting
"Although the application is not yet widespread, I think fully automated stereoscopic planting is a trend. Urbanization has led to a reduction in arable land and soil pollution has triggered problems with pests and pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables, and the development of three-dimensional agriculture is the only way to maximize and optimize output in a limited area. Currently, stereoscopic planting plants still require a lot of manual labor to operate. As labor costs rise and planting techniques require more precision, the use of automated equipment will be a future trend," Alice notes.
"Automated systems are a trend, not only in China but also globally. Urbanization has been moving forward, in the face of soil pollution, pesticides and pests, etc. The planting area is gradually reduced and three-dimensional agriculture must be developed in order to quantify planting. Three-dimensional agriculture can be located near the city, and reduce the transport distance, people can eat the freshest vegetables, to achieve local supply. Therefore it is necessary to promote automated, intelligent planting systems in order to achieve efficient planting and sustainable development." Alice said.
Industry experience
Eponic Agriculture Co. Ltd's head office, Dahua Intelligent Electronics, has a twenty-five-year history division. The team has been focusing on the development and production of intelligent control systems and industrial lighting. Alice said that based on years of technical foundation, we developed full-spectrum LED planting lights which have been approved and applied by the USDA. Over the years, we have received technical support and affirmation from several agricultural doctors from Europe and the United States, focusing on the development and production of automated stereoscopic planting equipment.
According to Alice, the company has laboratories and showrooms in the US, Australia and Africa. This year, the company is planning on opening new showrooms and laboratories in Europe. “We are expanding our global reach and continue to optimize our growing systems to be a better supplier of fully automated growing equipment."
For more information:
Eponic Agriculture Co. Ltd
Alice Ou, Director
aliceou@eponicagriculture.com
www.eponicagriculture.com
Author: Rebekka Boekhout
© VerticalFarmDaily.com
Little Leaf Farms Raises $90M to Grow Its Greenhouse Network
Massachusetts-based Little Leaf Farms has raised $90 million in a debt and equity financing round to expand its network of hydroponic greenhouses on the East Coast. The round was led by Equilibrium Capital as well as founding investors Bill Helman and Pilot House Associates. Bank of America also participated.
by Jennifer Marston
Image from: Little Leaf Farms
Massachusetts-based Little Leaf Farms has raised $90 million in a debt and equity financing round to expand its network of hydroponic greenhouses on the East Coast. The round was led by Equilibrium Capital as well as founding investors Bill Helman and Pilot House Associates. Bank of America also participated.
Little Leaf Farms says the capital is “earmarked” to build new greenhouse sites along the East Coast, where its lettuce is currently available in about 2,500 stores.
The company already operates one 10-acre greenhouse in Devins, Massachusetts. Its facility grows leafy greens using hydroponics and a mixture of sunlight supplemented by LED-powered grow lights. Rainwater captured from the facility’s roof provides most of the water used on the farm.
According to a press release, Little Leaf Farms has doubled its retail sales to $38 million since 2019. And last year, the company bought180 acres of land in Pennsylvania on which to build an additional facility. Still another greenhouse, slated for North Carolina, will serve the Southeast region of the U.S.
Little Leaf Farms joins the likes of Revol Greens, Gotham Greens, AppHarvest, and others in bringing local(ish) greens to a greater percentage of the population. These facilities generally pack and ship their greens on the day of or day after harvesting, and only supply retailers within a certain radius. Little Leaf Farms, for example, currently servers only parts of Massachusetts, Pennsylvania, New York, and New Jersey.
The list of regions the company serves will no doubt lengthen as the company builds up its greenhouse network in the coming months.
Agritech: Precision Farming With AI, IoT and 5G
For a company that grows and delivers vegetables, Boomgrow Productions Sdn Bhd’s office is nothing like a farm, or even a vertical farm. Where farms are bedecked with wheelbarrows, spades and hoes, Boomgrow’s floor plan is akin to a co-working space with a communal island table, several cubicles, comfortable armchairs, a cosy hanging rattan chair and a glass-walled conference room in the middle
Image from: Photo by Mohd Izwan Mohd Nazam/The Edge
For a company that grows and delivers vegetables, Boomgrow Productions Sdn Bhd’s office is nothing like a farm, or even a vertical farm.
Where farms are bedecked with wheelbarrows, spades and hoes, Boomgrow’s floor plan is akin to a co-working space with a communal island table, several cubicles, comfortable armchairs, a cosy hanging rattan chair and a glass-walled conference room in the middle.
At a corner, propped up along a walkway leading to a rectangular chamber fitted with grow lights, are rows of support stilts with hydroponic planters developed in-house and an agricultural technologist perched on a chair, perusing data. “This is where some of the R&D work happens,” says Jay Dasen, co-founder of the agritech start-up.
But there is a larger farm where most of the work behind this high-tech initiative is executed. Located a stone’s throw from the city centre in Ampang is a 40ft repurposed shipping container outfitted with perception technologies and artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities that mimic the ideal environment to produce more than 50,000kg of vegetables a year.
Stacked in vertical layers, Boomgrow’s vegetables are grown under artificial lights with Internet of Things (IoT) sensors to detect everything from leaf discolouration to nitrate composition. This is coupled with AI and machine learning algorithms.
Boomgrow is the country’s first 5G-connected vertical farm. With the low latency and larger bandwidth technology, the start-up is able to monitor production in real time as well as maintain key parameters, such as temperature and humidity, to ensure optimal growth conditions.
When Jay and her co-founders, K Muralidesan and Shan Palani, embarked on this initiative six years ago, Boomgrow was nowhere near what it is today.
The three founders got together hoping to do their part in building a more sustainable future. “I’ve spent years advising small and large companies on sustainability, environmental and social governance disclosures. I even embarked on a doctorate in sustainability disclosure and governance,” says Jay.
“But I felt a deep sense of disconnect because while I saw companies evolving in terms of policies, processes and procedures towards sustainability, the people in those organisations were not transforming. Sustainability is almost like this white noise in the background. We know it’s important and we know it needs to be done, but we don’t really know how to integrate it into our lives.
“That disconnect really troubled me. When we started Boomgrow, it wasn’t a linear journey. Boomgrow is something that came out of meaningful conversations and many years of research.”
Shan, on the other hand, was an architect who developed a taste for sustainable designs when he was designing modular structures with minimal impact on their surroundings between regular projects. “It was great doing that kind of work. But I was getting very dissatisfied because the projects were customer-driven, which meant I would end up having debates about trivial stuff such as the colour of wall tiles,” he says.
As for Murali, the impetus to start Boomgrow came from having lived overseas — while working in capital markets and financial services — where quality and nutritious produce was easily available.
Ultimately, they concluded that the best way to work towards their shared sustainability goals was to address the imminent problem of food shortage.
“By 2050, the world’s population is expected to grow to 9.7 billion people, two-thirds of whom will be in Asia-Pacific. Feeding all those people will definitely be a huge challenge,” says Jay.
“The current agricultural practice is not built for resilience, but efficiency. So, when you think of farming, you think of vast tracts of land located far away from where you live or shop.
“The only way we could reimagine or rethink that was to make sure the food is located closer to consumers, with a hyperlocal strategy that is traceable and transparent, and also free of pesticides.”
Having little experience in growing anything, it took them a while to figure out the best mechanism to achieve their goal. “After we started working on prototypes, we realised that the tropics are not designed for certain types of farming,” says Jay.
“And then, there is the problem of harmful chemicals and pesticides everywhere, which has become a necessity for farmers to protect their crops because of the unpredictable climate. We went through many iterations … when we started, we used to farm in little boxes, but that didn’t quite work out.”
They explored different methodologies, from hydroponics to aquaponics, and even started growing outdoors. But they lost a lot of crops when a heat wave struck.
That was when they started exploring more effective ways to farm. “How can we protect the farm from terrible torrential rains, plant 365 days a year and keep prices affordable? It took us five years to answer these questions,” says Jay.
Even though farmers all over the world currently produce more than enough food to feed everyone, 820 million people — roughly 11% of the global population — did not have enough to eat in 2018, according to the World Health Organization. Concurrently, food safety and quality concerns are rising, with more consumers opting for organically produced food as well as safe foods, out of fear of harmful synthetic fertilisers, pesticides, herbicides and fungicides.
According to ResearchAndMarkets.com, consumer demand for global organic fruit and vegetables was valued at US$19.16 billion in 2019 and is anticipated to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5% by 2026.
Meanwhile, the precision farming market was estimated to be US$7 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach US$12.8 billion by 2025, at a CAGR of 12.7% between 2020 and 2025, states MarketsandMarkets Research Pte Ltd.
Malaysia currently imports RM1 billion worth of leafy vegetables from countries such as Australia, China and Japan. Sourcing good and safe food from local suppliers not only benefits the country from a food security standpoint but also improves Malaysia’s competitive advantage, says Jay.
Unlike organic farming — which is still a soil-based method — tech-enabled precision farming has the advantage of catering for increasing demand and optimum crop production with the limited resources available. Moreover, changing weather patterns due to global warming encourage the adoption of advanced farming technologies to enhance farm productivity and crop yield.
Boomgrow’s model does not require the acres of land that traditional farms need, Jay emphasises. With indoor farms, the company promises a year-round harvest, undisturbed by climate and which uses 95% less water, land and fuel to operate.
Traditional farming is back-breaking labour. But with precision technology, farmers can spend less time on the farm and more on doing other things to develop their business, she says.
Boomgrow has secured more than RM300,000 in funding via technology and innovation grants from SME Corporation Malaysia, PlaTCOM Ventures and Malaysia Digital Economy Corporation, and is on track to build the country’s largest indoor farms.
Image from: Boomgrow
The company got its chance to showcase the strength of its smart technology when Telekom Malaysia Bhd (TM) approached it to be a part of the telco’s Smart Agriculture cluster in Langkawi last October.
“5G makes it faster for us to process the multiple data streams that we need because we collect data for machine learning, and then AI helps us to make decisions faster,” Jay explains.
“We manage the farm using machines to study inputs like water and electricity and even measure humidity. All the farm’s produce is lab-tested and we can keep our promise that there are no pesticides, herbicides or any preserving chemicals. We follow the food safety standards set by the EU, where nitrate accumulation in plant tissues is a big issue.”
With TM’s 5G technology and Boomgrow’s patent-pending technology, the latter is able to grow vegetables like the staple Asian greens and highland crops such as butterhead and romaine lettuce as well as kale and mint. While the company is able to grow more than 30 varieties of leafy greens, it has decided to stick to a selection of crops that is most in demand to reduce waste, says Jay.
As it stands, shipping containers are the best fit for the company’s current endeavour as containerised modular farms are the simplest means of bringing better food to local communities. However, it is also developing a blueprint to house farms in buildings, she says.
Since the showcase, Boomgrow has started to supply its crops to various hotels in Langkawi. It rolled out its e-commerce platform last year after the Movement Control Order was imposed.
“On our website, we promise to deliver the greens within six hours of harvest. But actually, you could get them way earlier. We harvest the morning after the orders come in and the vegetables are delivered on the same day,” says Jay.
Being mindful of Boomgrow’s carbon footprint, orders are organised and scheduled according to consumers’ localities, she points out. “We don’t want our delivery partners zipping everywhere, so we stagger the orders based on where consumers live.
“For example, all deliveries to Petaling Jaya happen on Thursdays, but the vegetables are harvested that morning. They are not harvested a week before, three days before or the night before. This is what it means to be hyperlocal. We want to deliver produce at its freshest and most nutritious state.”
Plans to expand regionally are also underway, once Boomgrow’s fundraising exercise is complete, says Jay. “Most probably, this will only happen when the Covid-19 pandemic ends.”
To gain the knowledge they have today, the team had to “unlearn” everything they knew and take up new skills to figure what would work best for their business, says Jay. “All this wouldn’t have been possible if we had not experimented with smart cameras to monitor the condition of our produce,” she laughs.
Vertical Farming ‘At a Crossroads’
Although growing crops all year round with Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) has been proposed as a method to localize food production and increase resilience against extreme climate events, the efficiency and limitations of this strategy need to be evaluated for each location
Building the right business model to balance resource usage with socio-economic conditions is crucial to capturing new markets, say speakers ahead of Agri-TechE event
Image from: Fruitnet
Although growing crops all year round with Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) has been proposed as a method to localize food production and increase resilience against extreme climate events, the efficiency and limitations of this strategy need to be evaluated for each location.
That is the conclusion of research by Luuk Graamans of Wageningen University & Research, a speaker at the upcoming Agri-TechE event on CEA, which takes place on 25 February.
His research shows that integration with urban energy infrastructure can make vertical farms more viable. Graamans’ research around the modelling of vertical farms shows that these systems are able to achieve higher resource use efficiencies, compared to more traditional food production, except when it comes to electricity.
Vertical farms, therefore, need to offer additional benefits to offset this increased energy use, Graamans said. One example his team has investigated is whether vertical farms could also provide heat.
“We investigated if vertical farms could provide not just food for people living in densely populated areas and also heat their homes using waste heat. We found that CEA can contribute to stabilizing the increasingly complex energy grid.”
Diversification
This balance between complex factors both within the growing environment and wider socio-economic conditions means that the rapidly growing CEA industry is beginning to diversify with different business models emerging.
Jack Farmer is CSO at vertical producer LettUs Grow, which recently launched its Drop & Grow growing units, offering a complete farming solution in a shipping container.
He believes everyone in the vertical farming space is going to hit a crossroads. “Vertical farming, with its focus on higher value and higher density crops, is effectively a subset of the broader horticultural sector,” he said.
"All the players in the vertical farming space are facing a choice – to scale vertically and try to capture as much value in that specific space, or to diversify and take their technology expertise broader.”
LettUs Grow is focussed on being the leading technology provider in containerised farming, and its smaller ‘Drop & Grow: 24’ container is mainly focussed on people entering the horticultural space.
Opportunities in retail
“This year is looking really exciting,” he said. “Supermarkets are investing to ensure a sustainable source of food production in the UK, which is what CEA provides. We’re also seeing a growth in ‘experiential’ food and retail and that’s also where we see our Drop & Grow container farm fitting in.”
Kate Hofman, CEO, GrowUp agrees. The company launched the UK’s first commercial-scale vertical farm in 2014.
“It will be really interesting to see how the foodservice world recovers after lockdown – the rough numbers are that supermarket trade was up at least 11 per cent in the last year – so retail still looks like a really good direction to go in.
“If we want to have an impact on the food system in the UK and change it for the better, we’re committed to partnering with those big retailers to help them deliver on their sustainability and values-driven goals.
“Our focus is very much as a salad grower that grows a fantastic product that everyone will want to buy. And we’re focussed on bringing down the cost of sustainable food, which means doing it at a big enough scale to gain the economies of production that are needed to be able to sell at everyday prices.”
Making the Numbers Add Up
The economics are an important part of the discussion. Recent investment in the sector has come from the Middle East, and other locations, where abundant solar power and scarce resources are driving interest in CEA. Graamans’ research has revealed a number of scenarios where CEA has a strong business case.
For the UK, CEA should be seen as a continuum from glasshouses to vertical farming, he believes. “Greenhouses can incorporate the technologies from vertical farms to increase climate control and to enhance their performance under specific climates."
It is this aspect that is grabbing the attention of conventional fresh produce growers in open field and covered crop production.
A Blended Approach
James Green, director of agriculture at G’s, thinks combining different growing methods is the way forward. “There’s a balance in all of these systems between energy costs for lighting, energy costs for cooling, costs of nutrient supply, and then transportation and the supply and demand. At the end of the day, sunshine is pretty cheap and it comes up every day.
“I think a blended approach, where you’re getting as much benefit as you can from nature but you’re supplementing it and controlling the growth conditions, is what we are aiming for, rather than the fully artificially lit ‘vertical farming’.”
Graamans, Farmer and Hofman will join a discussion with conventional vegetable producers, vertical farmers and technology providers at the Agri-TechE event ‘Controlled Environment Agriculture is growing up’ on 25 February 2021.
Nanobubble Tech Could Revolutionize Aquaculture & Aquaponics
“There is a pressing need to develop an alternative to the current highly energy-intensive conventional aeration,” said Khanal. “Nanobubble technology has a potential to revolutionize aquaculture and aquaponic systems, with higher productivity and resource recovery.” Khanal was initially awarded CTAHR’s Team Science grant, which was critically important to obtaining preliminary data for his grant proposal to NIFA
Image from: University of Hawai’i News
The burgeoning fields of aquaculture and aquaponics hold vast potential for growing food. Yet, the efficacy of these microbial-mediated processes is governed by the availability of dissolved oxygen in water. Generally, oxygen has poor solubility in water, which has a negative effect on fish growth and plant yields.
Almost $200,000 in new funding from the USDA-National Institute of Food and Agriculture’s (NIFA) Water Quantity and Quality Program may expand researchers’ understanding of how nanobubbles could improve aeration and oxygen supplies.
Under the grant, Samir Khanal of the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa’s College of Tropical Agriculture and Human Resources (CTAHR ) Department of Molecular Biosciences and Bioengineering, will apply the technology to these aqueous systems. His goal is to uncover new opportunities for improving fish and plant yields—with concomitant improvements in water quality.
Image from: University of Hawai’i News
“There is a pressing need to develop an alternative to the current highly energy-intensive conventional aeration,” said Khanal. “Nanobubble technology has a potential to revolutionize aquaculture and aquaponic systems, with higher productivity and resource recovery.”
Khanal was initially awarded CTAHR’s Team Science grant, which was critically important to obtaining preliminary data for his grant proposal to NIFA.
“Thanks to the CTAHR and NIFA grants, we hope our findings will benefit existing Hawaiʻi businesses, as well as a new generation of growers, across the state and beyond,” Khanal added.
Is AppHarvest the Future of Farming?
In this video from Motley Fool Live, recorded on Jan. 28, Industry Focus host Nick Sciple and Motley Fool contributor Lou Whiteman discuss AppHarvest, one such SPAC that is looking to disrupt the agriculture industry. Here are the details on what AppHarvest wants to do, and a look at whether the company represents the future of farming.
Special purpose acquisition companies, or SPACs, are red-hot right now, with investors clamoring to get into promising young companies.
In this video from Motley Fool Live, recorded on Jan. 28, Industry Focus host Nick Sciple and Motley Fool contributor Lou Whiteman discuss AppHarvest, one such SPAC that is looking to disrupt the agriculture industry. Here are the details on what AppHarvest wants to do, and a look at whether the company represents the future of farming.
Nick Sciple: One last company I wanted to talk about, Lou, and this is one I think it's -- you pay attention to, but not one I'm super excited to run in and buy. It was a company called AppHarvest. It's coming public via a [SPAC] this year. This vertical farming space. We talked about Gladstone Land buying traditional farmland. AppHarvest is taking a very different approach, trying to lean into some of the ESG-type movements.
Lou Whiteman: Yeah. Let's look at this. It probably wouldn't surprise you that the U.S. is the biggest global farm exporter as we said, but it might surprise you that the Netherlands, the tiny little country, is No. 2. The way they do that is tech: Greenhouse farm structure. AppHarvest has taken that model and brought it to the U.S. They have, I believe, three farms in Appalachia. The pitches can produce 30x the yields using 90% less water. Right now, it's mostly tomatoes and it is early-stage. I don't own this stock either. I love this idea. There's some reasons that I'm not buying in right now that we can get into. But this is fascinating to me. We talked about making the world a better place. This is the company that we need to be successful to make the world a better place. The warning on it is that it is a SPAC. So it's not public yet. Right now, I believe N-O-V-S. That deal should close soon. [Editor's note: The deal has since closed.] I'm not the only one excited about it. I tend not to like to buy IPOs and new companies anyway. I think the caution around buying into the excitement applies here. There is a Martha Stewart video on their website talking up the company, which I love Martha Stewart, but that's a hype level that makes me want to just watch and see what they produce. This is just three little farms in Appalachia right now and a great idea. This was all over my watchlist. I would imagine I would love to hold it at some point, but just be careful because this is, as we saw SPACs last year in other areas, people are very excited about this.
Sciple: Yeah. I think, like we've said, for a lot of these companies, the prospects are great. I think when you look at the reduced water usage, better, environmentally friendly, all those sorts of things. I like that they are in Appalachia. As someone who is from the South, I like it when more rural areas get some people actually investing money there. But again, there's a lot of execution between now and really getting to a place where this is the future of farming and they're going to reach scale and all those sorts of things. But this is a company I'm definitely going to have my radar on and pay attention to as they continue to report earnings. Because you can tell yourself a story about how this type of vertical farming, indoor farming disrupts this traditional model, can be more efficient, cleaner, etc. Something to continue paying attention to as we have more information, because this company, like you said, Lou, isn't all the way public yet. We still got to have this SPAC deal finalized and then we get all our fun SEC filings and quarterly calls and all those sorts of things. Once we have that, I will be very much looking forward to seeing what the company has to say.
Whiteman: Right. Just to finish up along too, the interesting thing here is that it is a proven concept because it has worked elsewhere. The downside of that is that it needed to work there. Netherlands just doesn't have -- and this is an expensive proposition to get started, to get going. There's potential there, but in a country blessed with almost seemingly unlimited farmland for now, for long term it makes sense. But in the short term, it could be a hard thing to really get up and running. I think you're right, just one to watch.
Advice For New Vertical Farmers: Grower Spotlight on Andrew Worrall
Andrew is LettUs Grow’s Farm Manager, he manages two of our sites across Bristol and has brought a wealth of knowledge into the company through his previous experience in indoor farming roles across the UK including at Grow Up, Raynor Foods & RootLabs. In this three part interview, we explore what it’s been like to move from animal husbandry to indoor farming, the lessons he’s learned along the way, what it’s like working at LettUs Grow and his advice for those new to indoor growing.
Last week we spoke about running a farm at LettUs Grow. What excites you about vertical farming?
It’s the future of the industry. Also, the amount of salad that these farms can produce for their local community. We want to be able to eat salad all year round and we import to make that happen. However, just a small farm can easily provide for its local community, very efficiently and all year round. The sustainability element is also exciting: with our salad there’s no food miles, it’s very minimalistic. You could use an electric van or bike to distribute this crop if you wanted to. It’s a step forward in terms of what we need to do to take care of our planet.
What do you think are the biggest downsides to vertical farming?
It’s still a new technology and it can be expensive. The biggest roadblock facing the industry is that we need more people and companies to collaborate together to make sure we can build these farms at a sensible rate, so we can provide farms to anyone. We want to be able to provide farms to people, communities and countries that don’t have a lot of money, so that they can provide affordable fresh produce to local people.
How has vertical farming impacted your life?
Massively! I wanted to find my passion, a job that I loved - that was very important to me. It’s satisfying to be in a position now where I’m very happy to be doing what I do and I look forward to going into work. I was happy to make the move from London to Bristol. I would have moved even further if it meant being able to continue working within this industry.
Image from: LettUs Grow
How do you see vertical farming playing a part in the future?
When indoor farming first came about, it had a reputation of being competition for outdoor farming, which just isn’t the case. There’s so much we can’t grow that outdoor farming can provide, such as cereal crops. I’m glad we’re at a stage where indoor and outdoor farms can start to work together to optimise both methods. With these new relationships, there should be a good increase in the amount of indoor farms you’ll be seeing. What LettUs Grow offers with DROP & GROW™ is an exciting project because that’s a 40ft shipping container which can be placed pretty much anywhere. It’s not that big - it could go in a car park or behind a restaurant, but actually provide quite a lot of salad to that area.
How much of our food should be grown this way?
Good question. If you had asked me a while back I would have just said salad, but now I’ve changed my mind. Indoor farming can have a massive impact on propagation, especially aeroponics, because of how we aerate and nourish our roots. We could start lettuce for greenhouse projects and we can also propagate tomatoes, strawberries and tree whips. Propagating trees in this way could potentially be hugely beneficial and it’s something we want to do more of.
We can also quickly grow large amounts of microgreens, baby leafs, herbs and we can grow fruiting crops like strawberries. We are slowly chipping away and it’s really exciting. I’m waiting to see if I can ever say I’ve grown or propagated every crop that can be grown in these farms!
What do you think are the biggest benefits of vertical farming?
How fast these crops can grow! The turnover can be as short as 5 days from seed, depending on the crop. Also how clean it can be - I’m very dedicated to making sure these farms are built to ensure they are easy to be maintained and clean. The most exciting part is the crop growth rate though - it’s incredible how fast our crop grows from seed to plate. In a very well maintained growing calendar, which Ostara® is great for supporting, you can optimise your beds so that the day you harvest can also be the day you germinate onto that same bed. Your farms can be forever providing salad at very fast rates.
Image from: LettUs Grow
What was the biggest change you encountered during your years indoor farming?
Moving from being a production grower to an R&D grower. It has been a great change! As a production grower I knew what I needed to know about growing the plant safely and getting it onto a plate so it was good for the consumer. Now I’m fully optimising, learning and understanding the plants completely, so that I can help the grower that I used to be. We spend a lot of time on crop recipes to make sure that whoever we sell our farms to can start up very quickly and they won’t have to spend months developing their crops. If they have the customers and clients behind them, they can buy DROP & GROW and start producing salad as soon as it's been commissioned.
What was the biggest change you encountered in the industry?
More and more people are speaking about what’s going on in the industry and getting involved. I get so many messages on LinkedIn with people who want to get into this career. It’s exciting to see that indoor growing is a career people can access now. When I was developing my skills I didn’t know I would end up in indoor farming. There are more opportunities than ever before. For example, our Crop Technician is doing a placement here for 2 years. The aim is that they can gain the skill sets and knowledge they need to then go off and do the same practice in any farm they want.
What advice do you have for people who are looking to start a career in growing?
Reach out to companies who are already out there. You could start off part-time or as an assistant. If you are patient and dedicated then it’s a journey I promise you won’t regret. It takes a lot of work, but the outcome is amazing - you’ll be learning so much about this new technology. You’ll also build great relationships: there are so many amazing people in this industry who are so interesting, with different backgrounds, who are willing to share their knowledge. You can always learn more and other people are a great source of that.
What about for those looking to start a vertical farming business?
Do your homework. There are people out there who you can reach out to and it’s very easy to get information. It’s very easy to get excited about the idea and jump straight into it, because it is exciting and can be very rewarding, but it’s really important to do it step by step. Know how to scale properly, learning the differences between a small and larger farm. Understand how many people you’ll need and the logistics. I’d also advise people to get some practical work experience before you buy. You want to start the company knowing the tricks of the trade.
Image from: LettUs Grow
LettUs Grow Blog: www.lettusgrow.com/blog/advice-for-vertical-farmers
2-Acre Vertical Farm Run By AI And Robots Out-Produces 720-Acre Flat Farm
A San Fransisco start-up is changing the vertical farming industry by utilizing robots to ensure optimal product quality
Plenty is an ag-tech startup in San Francisco, co-founded by Nate Storey, that is reinventing farms and farming. Storey, who is also the company’s chief science officer, says the future of farms is vertical and indoors because that way, the food can grow anywhere in the world, year-round; and the future of farms employ robots and AI to continually improve the quality of growth for fruits, vegetables, and herbs. Plenty does all these things and uses 95% less water and 99% less land because of it.
In recent years, farmers on flat farms have been using new tools for making farming better or easier. They’re using drones and robots to improve crop maintenance, while artificial intelligence is also on the rise, with over 1,600 startups and total investments reaching tens of billions of dollars. Plenty is one of those startups. However, flat farms still use a lot of water and land, while a Plenty vertical farm can produce the same quantity of fruits and vegetables as a 720-acre flat farm, but on only 2 acres!
Storey said:
“Vertical farming exists because we want to grow the world’s capacity for fresh fruits and vegetables, and we know it’s necessary.”
Plenty’s climate-controlled indoor farm has rows of plants growing vertically, hung from the ceiling. There are sun-mimicking LED lights shining on them, robots that move them around, and artificial intelligence (AI) managing all the variables of water, temperature, and light, and continually learning and optimizing how to grow bigger, faster, better crops. These futuristic features ensure every plant grows perfectly year-round. The conditions are so good that the farm produces 400 times more food per acre than an outdoor flat farm.
Storey said:
“400X greater yield per acre of ground is not just an incremental improvement, and using almost two orders of magnitude less water is also critical in a time of increasing environmental stress and climate uncertainty. All of these are truly game-changers, but they’re not the only goals.”
Another perk of vertical farming is locally produced food. The fruits and vegetables aren’t grown 1,000 miles away or more from a city; instead, at a warehouse nearby. Meaning, many transportation miles are eliminated, which is useful for reducing millions of tons of yearly CO2 emissions and prices for consumers. Imported fruits and vegetables are more expensive, so society’s most impoverished are at an extreme nutritional disadvantage. Vertical farms could solve this problem.
Storey said:
“Supply-chain breakdowns resulting from COVID-19 and natural disruptions like this year’s California wildfires demonstrate the need for a predictable and durable supply of products can only come from vertical farming.”
(Credit: Reuters)
Plenty’s farms grow non-GMO crops and don’t use herbicides or pesticides. They recycle all water used, even capturing the evaporated water in the air. The flagship farm in San Francisco is using 100% renewable energy too.
Furthermore, all the packaging is 100% recyclable, made of recycled plastic, and specially designed to keep the food fresh longer to reduce food waste.
Storey told Forbes:
“The future will be quite remarkable. And I think the size of the global fresh fruit and vegetable industry will be multiples of what it is today.”
Plenty has already received $400 million in investment capital from SoftBank, former Google chairman Eric Schmidt, and Amazon’s Jeff Bezos. It’s also struck a deal with Albertsons stores in California to supply 430 stores with fresh produce.
Ideally, the company will branch out, opening vertical farms across the country and beyond. There can never be too many places graced by better food growing with a less environmental cost.
Here’s a TechFirst podcast about the story behind Plenty:
Published by Dani Kliegerman for iGrow.News
Belgian Lettuce Grower De Glastuin Achieves Increased Production And Faster Growth Cycles Thanks To A Full LED Solution From Signify
Belgian farmers are using LED lights in an innovative way to enhance lettuce production
December 17, 2020
Eindhoven, the Netherlands – Since the introduction of Philips GreenPower LED Toplighting Compact from Signify (Euronext: LIGHT), the world leader in lighting, many vegetable, fruit and horticulture growers have made the choice to fully equip their greenhouses with LEDs. By combining this LED lighting with the GrowWise Control System, it is possible to both control and dim the light, giving growers a high degree of flexibility. This solution has now also found its way into lettuce growing; De Glastuin in Belgium opted for 100% LED grow lights from Signify.
Each type of lettuce requires a different amount of light. Heat is also a limiting factor when growing lettuce. As a result, in many periods it is not possible to illuminate the crops because too much heat accumulates in the greenhouse. Thanks to LED lighting, which emits less heat, it is possible to light the crop for longer hours, resulting in a increased production and faster growth cycles. The combination with the GrowWise Control System also allows the lighting to be dimmed. For example, to keep the light intensity the same on sunny days while maintaining light uniformity or to prevent climate fluctuations.
This summer, lettuce grower De Glastuin expanded its existing 1.75 hectare greenhouse with HPS lighting by 0.75 hectares. In this new part of the greenhouse, Philips GreenPower LED Toplighting Compact is installed together with the GrowWise Control System. The modules in the new part of the LED greenhouse have an output of 1800 µmol/s and require only 520 W (3.5 µmol/J). They provide a light level of 90 µmol/s/m². De Glastuin is pleased with the high quality and longer shelf life of the lettuce."With Toplighting Compact in combination with the GrowWise Control System, we can automatically adjust the amount of LED light to the amount of daylight at any given moment. As a result, there are fewer fluctuations in light intensity during the day. The lighting is much more efficient, dimmable and it offers us flexibility by allowing us to provide less light at any time," says Wouter de Bruyn, business manager at De Glastuin.
"De Glastuin's choice of Signify reinforces our conviction that we have chosen the right approach to make it easier for growers to switch to LED," says Udo van Slooten, Business Leader Horticulture LED Solutions at Signify.
The first Toplighting Compact was introduced in 2019 as a 1-on-1 replacement of HPS lighting to enable an easy transition to LED. The Toplighting Compact can be mounted on an existing HPS connection. This saves time and money during installation. In new greenhouses, installation is even easier thanks to easy-to-install brackets. The universal design of this system gives growers the possibility to fully equip their greenhouse with LED lights or to change their current set-up into a hybrid system with LED and HPS lighting. Signify's Compact range is also equipped with optics with normal and wide beam angles. The wide beam angle is ideal for growers looking for optimal light distribution or for lower greenhouses, for example. For crops where a greater distance between the plant and the grow light is possible, the normal beam is a better option.
More information about the Philips Horticulture LED solutions from Signify is available on the website.
For further information, please contact:
Global Marcom Manager Horticulture at Signify
Daniela Damoiseaux
Tel: +31 6 31 65 29 69
E-mail: daniela.damoiseaux@signify.com
About Signify
Signify (Euronext: LIGHT) is the global market leader in lighting for professionals and consumers and lighting for the Internet of Things. Our Philips products, Interact connected lighting systems and data-enabled services, deliver business value and transform life in homes, buildings, and public spaces. In 2019, we achieved sales of EUR 6.2 billion with approximately 37,000 employees in more than 70 countries. We unlock the extraordinary potential of light for better lives and a more sustainable world. We achieved CO2 neutrality by 2020 and have been on the Dow Jones Sustainability Index since our IPO in 2016. We were named Industry Leader in 2017, 2018 and 2019. Signify news can be found in the Newsroom, on Twitter, LinkedIn, and Instagram. Information for investors can be found on the Investor Relations page.
Hamill Has Moved Into Agritecture
Canadian farmers are relying on indoor farming than greenhouse farming for growing microgreens because of the electricity needed for lighting and also growing indoors eliminates many of the pest and disease problems of outdoor production”
When COVID-19 hit Canada in February 2020, the Hamill Group of Companies was in its early inception. “We weren’t quite sure how things were going to play out, but we knew that whatever challenges were, we could tackle them head on!” said CEO Bob Benner. As a leader in manufacturing services and having carved out a niche for microgreens harvesting equipment, Hamill quickly realized it would need to do more to support their growers.
The company took the step forward and moved to Agritecture. Vertical, hydroponic, and aquaponic farms are taking hold in many major cities throughout the world. With the help of enhanced indoor and vertical farming practices, the US growers have been able to produce microgreens on a large scale.
Canadian farmers are relying on indoor farming than greenhouse farming for growing microgreens because of the electricity needed for lighting and also growing indoors eliminates many of the pest and disease problems of outdoor production” [1].
One of the major crops that they grow are microgreens but these farming environments presented new challenges in and of themselves. As growers looked to establish their systems, they realized they needed the Hamill Group of Companies to propel them forward. This was due to Hamill's superior experience in 3D engineering, manufacturing, prototyping, electrical. For Hamill, they had to rapidly shift their focus from just harvesting equipment to innovating and designing farms, and full production facilities being an end-to-end provider.
Hamill’s ability to adapt and pivot meant that the Hamill Group of Companies could foster new partnerships throughout Canada and the US. They have undertaken projects such as with AquaGreens in Toronto, Intravision Group in Welland, as well as are in the preliminary stages of planning with InCity Farms in the United States.
For more information:
Hamill Agricultural Processing Solutions
contactus@hamillaps.com
www.hamillaps.com
Publication date: Thu 3 Dec 2020
VeggiTech Inspires People To Grow Crops Sustainably
VeggiTech is an agro-tech organization focused on disrupting the agriculture industry to create sustainable and eco-friendly farms
How VeggiTech Is Changing UAE's
Agriculture Sector With Innovative Farming-Tech
November 18, 2020
Hatim Morbiwala, Head of Learning and Development,VeggiTech, controls and monitors eco systems with VeggiTech IoTImage Credit: Supplied
VeggiTech is an agro-tech organization focused on disrupting the agriculture industry to create sustainable and eco-friendly farms. Its tech-enabled solutions are:
VeggiTech digital operating system (V-DOS)
This is a scalable, repeatable set of solutions that are focused on the controlled environment agriculture as well as farming as a service (FAAS) model for its customers and investors.
Grow operating system
VeggiTech deploys the latest technology in terms of grow lights that provide the right amount of spectrum of light frequency to a plant-based on its type and growth cycle. This light is tuned to the grow cycle and creates the optimum environment for it to grow, coupled with the right nutrition and water quality for the plants. Internet of Things (IoT)-based sensors manage the environment and are linked to the data models that track the yield per unit of input resource so that it continually improves the quality of yield per sqm of grow space.
Farm operating system
All of VeggiTech’s business activities are managed in an enterprise resource planning (ERP) solution that provides complete control of the unit economics while creating a unique QR code for every crop being grown on its farms.
Learning Hub
VeggiTech also manages its Learning Hub using a state-of-the-art learning management platform that has online and offline features to interact with the learners. This has proven to be a very useful tool during the Covid-19 times as it continues to enable the future leaders – students – with the knowledge to grow their own food.
New launches
“With our vision to create the next one billion farmers, we are delighted to announce the launch of two new products that have been conceived, designed, and developed in the UAE,” says Hatim Morbiwala, Head of Learning and Development at VeggiTech. “We have developed a mobile app – Grow App – that will enable everybody to grow their own food and they can interact with the VeggiTech agronomist in case they need support with their plants. The app also has the ability to diagnose issues with the plants and recommend solutions using a machine learning database.”
Grow Kit is another unique product, developed by VeggiTech. “This is a physical kit which will inspire everybody to start their journey of growing their own food. We believe this is a life skill and should be part of the curriculum of every citizen on the planet,” says Morbiwala.
For more information, visit Veggitech.com
Call 058 263 1317 and 06 881 1861
email: info@veggitech.com
New Digital Publication And Podcast Launched by Agritech Specialist, IGS
Covering the theme of global sustainable food security, the inaugural edition of Clima features interviews with Professor Colin Campbell, Chief Executive at the James Hutton Institute and Michael Dean, co-founder of specialist agrifood venture capital platform AgFunder
Edinburgh, Scotland – 12 June 2020 - Indoor agritech specialist IGS has today launched Clima, its new digital publication and accompanying podcast series. Through Clima, IGS will welcome industry-leading interviewees and share thought pieces on some of the most fundamental issues facing the world, including supply chains, agricultural innovation, and indoor growing.
Covering the theme of global sustainable food security, the inaugural edition of Clima features interviews with Professor Colin Campbell, Chief Executive at the James Hutton Institute and Michael Dean, co-founder of specialist agrifood venture capital platform AgFunder.
Professor Colin Campbell, who leads the world-renowned James Hutton Institute near Dundee, Scotland, explores what he believes are the greatest barriers to achieving a secure, sustainable food supply and the role science and technology have to play in attaining this goal. Continuing the theme, Michael Dean shares his thoughts on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and explores the future of food supply chains.
David Farquhar, Chief Executive of IGS, commented: “At IGS we are very aware just what a challenging time this is for our customers and partners, with many countries across the globe still considering the right strategies to alleviate COVID-19 restrictions. Clima was born from our desire to bring the industry together and drive collaboration, informed discussion, and debate which we hope will help to create a more sustainable and secure food eco-system for the future.
“We are very excited to launch Clima publicly and to have the opportunity to share the insights of two brilliant interviewees, both of whom are leading their fields. We hope that readers of Clima and those who listen to the podcast get as much out of it as we have in the process of producing this first edition.”
To subscribe to Clima and to access the first edition, please visit www.igsclima.io.
About IGS:
Founded in 2013, IGS brought together decades of farming and engineering experience to create an agritech business with a vision to revolutionize the indoor growing market. Its commitment to innovation has continued apace and it has evolved the applications of its technology beyond agriculture to create solutions for a wide variety of indoor environments that enhance life for people, plants, and animals.
IGS launched its first vertical farming demonstration facility in August 2018, based at the James Hutton Institute in Invergowrie.
For more information visit www.intelligentgrowthsolutions.com or connect with us on Twitter and LinkedIn.
VeggiTech Builds and Operates Digital Smart Farms For Customers
In conversation with Hemant Julka, Chief Operating Officer, VeggiTech
By GN Focus | May 28, 2020 | Gulf News
In conversation with Hemant Julka, Chief Operating Officer, VeggiTech
Could you tell us about VeggiTech and its operations in the UAE?
VeggiTech is an agro-tech organisation focused on disrupting the agriculture industry to create sustainable and eco-friendly farms. We focus on LED-assisted hydroponics for indoor vertical farms and protected hydroponics to farm sustainably even in the UAE’s challenging conditions, where soil, temperature and water are not conducive to traditional farming. Our farming landscape has grown to over 60 acres of protected hydroponic farms and more than 45,000 sq ft of indoor vertical farms, with a team of over 150 qualified agronomists, engineers and farmers.
How could you help traditional farms in the country incorporate hydroponic farming practices?
VeggiTech’s business model is to build and operate digital smart farms for our customers. We drive the transformation of farms with these innovative technologies in a cost-effective manner. The year 2019 saw more than 35 acres of traditional farms converted into protected hydroponics and the introduction of 45,000 sq ft of indoor vertical farms in Sharjah alone.
Given our expertise, we ensure the latest innovation in farming technology is delivered with optimal return on investment for our customers.
Could you talk about a couple of key projects that you have handled recently?
Some of our recent successes were the conversion of a traditional farms (640,000 sq ft) into modern protected hydroponic farms and the commissioning of the indoor vertical farm of 25,000 sq ft grow area. Our protected hydroponics technologies provide a harvest of 40-45kg per sq m per annum, while our indoor vertical farms provide a harvest of 85-90kg per sq m per annum using less than 5 percent of the water used in traditional farming.
What initiatives have you taken to create more awareness on hydroponics and other innovative farming technologies for a sustainable agricultural ecosystem in the UAE?
Education is key for long term sustainable impact. We work closely with the Ministry of Climate Change and Environment (MOCCAE). Our Chief Agronomy Officer, Bhaskar Rao, leads our Learning Hub platform that hosts the Urban Grower’s programme for students, parents and teachers. We have had more than 50 graduate participants from the programme.
Video: Interview with Christina Johnson from NASA Postdoctoral Program
Microgreens in Space
VIDEO: VeggiTech - Vegetation Technology Redefined
VeggiTech is an Agro technology start up with the sole aim of disrupting the agriculture industry
VeggiTech is an Agro technology start up with the sole aim of disrupting the agriculture industry. VeggiTech obsesses on addressing the key challenges of traditional farming – soil, temperature and water through its design of protected Hydroponics and Grow Lights assisted Hydroponics.
VeggiTech stands for Vegetation technology redefined and has currently chosen the harsh conditions of UAE to demonstrate these technologies in farms that are open for Investors, Students and Consumers to experience. The Leadership team firmly believes in moving beyond presentations and demonstrating technology that provides the Return on Investment in a live functional environment.
Lead Image Credit: Supplied
UAE Farm Tech To The Fore
New technologies are helping the country make more of its own produce
New technologies are helping the country make more of its own produce
Over a span of just six months, Covid-19 has not only changed the way we work, celebrate occasions and stay healthy but also forced countries to take a hard look at how they feed their residents. “I believe the current pandemic has provided us the opportunity to completely reimagine the global food system,” says Tony Hunter, a global food futurist.
Going urban
One of the factors pushing the global agri-tech agenda is the growth and increasing density of cities. “By 2050, more than two thirds of the world’s population is forecasted to live in cities,” explains Smitha Paresh, Executive Director of Greenoponics, a UAE-based retailer of commercial and consumer hydroponics systems, adding that urban agriculture will be crucial for feeding burgeoning urban populations.
“On a macro level, we will see a rise in urban farming, mostly using high-tech farming methods such as hydroponics, aeroponics or aquaponics.” Paresh cites Singapore’s conversion of car parks into urban farm centres as an example. “In the UAE, as per the national food security strategy for 2017-2021, we have already witnessed a huge increase in climate-controlled greenhouses all over the country.”
Arable environments
For Hunter, who spoke about potential silver linings of Covid-19 at a recent Gulfood webinar, new technologies present the best means of achieving domestic self-sufficiency. “They can release countries from the tyrannies of arable land and water stress.” He singles out algal products that rely on low rainfall and can use seawater; cultivated meat and biomass products; cell-based products such as milk proteins; and synthetic biology that can manufacture a range of food products.
Over the long term, Ravindra Shirotriya, CEO, VeggiTech, believes there are three critical areas for sustainable farming in the UAE. The first is precision agriculture, which focuses on growing conditions for plants using hyperbaric chambers and nanotechnology-based organic nutrition. Photo bio-reactors, meanwhile, can cultivate food-grade algae such as spirulina. Finally, Shirotriya cites smart farms, which work with smart cities to create harvest plans based on real-time data on food demand and consumption within communities. “This will address our current broken food ecosystem, where we waste 35 percent of food while 15 percent of the world population goes to sleep hungry.”
VeggiTech’s primary focus is on setting up LED-assisted hydroponics for indoor vertical farms and protected hydroponics for sustainable farming in the UAE.
In terms of crop production, Avinash Vora, Co-founder of Aranya Farms, says new technologies aim to boost yields, reduce waste and grow produce entirely. “Technology is being applied at every stage, whether for plant seeding, monitoring growth, managing water, energy conservation, harvesting and packaging. “We are making huge strides adapting all of them here in the UAE; the interest and investments in agriculture prove that.”
For Philippe Peguilhan, Country Manager of Carrefour UAE at Majid Al Futtaim Retail, the UAE had already been seeking self-reliance in food production, but coronavirus amped up its importance. “The disruption that Covid-19 caused to the supply chain highlighted the importance of local produce and presented an excellent opportunity for local farmers to grab a greater share of the market.” Majid Al Futtaim recently made headlines for opening the UAE’s third, and Dubai’s first, in-store hydroponics farm.
Hydroponic hope
Hydroponics is one agri-tech that’s attracting keen investor interest. “As an indicator, Madar Farms’ 7,000-sq-m factory will produce 365 tons of tomatoes a year, and about 14,000 tons of cherry vine tomatoes were consumed in the UAE in 2019,” says Hunter. “There’s therefore the market opportunity for 38 Madar farms in the UAE for tomatoes alone. Add in other nutrient-dense crops such as cucumbers, peppers and leafy greens. Depending upon their size, we could be looking at several hundred businesses.”
On an individual level, more people are leaning towards home farming, especially towards soil-less cultivation since it is simple and easy, according to Paresh. “It guarantees a certain amount of yield. Home farming will be on the rise, considering the disruption we may face in trying times like this.”
As with most technologies, Hunter says the biggest challenge of hydroponics is profitability. “Fortunately, the costs of technology inputs required to optimise hydroponic production efficiencies are falling rapidly. This drop, together with simultaneous increases in performance, is driving down the costs of hydroponics, making acceptable ROIs much easier to achieve.” He adds that economies of scale can help achieve good ROIs. “Currently most farms are in the 1-2 ton per day range but farms of 50 tons per day are being projected by as early as 2025.”
Sustainability challenges
“Challenges in building our own farm were access to sufficient and cost-effective electricity; renewable sources of water; and the availability of locally made raw materials, specifically growing media, nutrients and seeds. With seeds we are adapting — we have been growing our own seeds but having a library of seeds to choose from that are suitable for our climate and environment would be a huge boon to all farmers.”
— Avinash Vora, Co-founder of Aranya Farms
By Riaz Naqvi, Staff Writer | Gulf News | May 28, 2020