Welcome to iGrow News, Your Source for the World of Indoor Vertical Farming
Vertical Farming and the Future of Automation in Agriculture
Vertical farming is by no means a new idea. However, recent supply chain disruptions coupled with the falling price of produce, is opening new doors for a farming method previously deemed unviable by many.
August 10, 2021
Vertical farming is by no means a new idea. However, recent supply chain disruptions coupled with the falling price of produce, is opening new doors for a farming method previously deemed unviable by many. Here, John Young, APAC country manager at automation parts supplier EU Automation, highlights the renewed interest in vertical farming among a new generation of farmers, and explores the advantages it offers in tackling some of the biggest challenges facing the sector.
Turn the clock back approximately 1000 years, and less than four per cent of the world's habitable land was used for farming — that is the equivalent of four million square kilometres. Today, farmland takes up more than half of the world's habitable land, which equates to a landmass larger than South America.
Our World in Data reports the alarming facts associated with industrialized livestock farming, involving climate change, extinction of species, widespread destruction of habitat, and 80 per cent of cropland grown to feed livestock. With the population of the Asia Pacific region expected to reach 5 billion by 2050, the responsibility to supply food to an ever-growing population is becoming difficult.
A new generation of farmers are rising to the sustainability challenge. This agricultural revolution presents the transition from traditional farming to futuristic high-tech artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics. Whether it's weed-killing robots, harvesting and picking robots, or autonomous tractors, the farming landscape is evolving. In this age of robotic farming, producers believe incorporating automation and data will enable farmers to produce more, while damaging the environment less.
One major process change that is currently on the rise is the shift to vertical farming. Currently, 16.55 million square feet (sq ft) of indoor farms operate across the globe. However, the State of Indoor Farming report suggests this figure will increase to 22 million sq ft by 2022. The demand is high, and the AI journey is only getting started.
Why are farmers suddenly interested in vertical farming?
Vertical farming is the practice of producing food in vertically stacked layers. The climate-controlled indoor farms contain rows of plants situated next to each other, growing vertically, and hanging from the ceiling. Robotics help manoeuvre the products around, and AI can monitor the different parameters that are required for the crops to grow, such as the levels of water, temperature, and light.
Indoor agriculture is at an exciting point in its development. Key technologies used in farming systems today range from perception technologies which use cameras and sensors to detect and monitor various factors of the lifecycle. AI processes the data from sensors and provides solutions, while automated and autonomous mechatronics that use robotics and automated machines collect products when ready to dispatch to the market and recover the crops from ailments during the growing cycle.
Right now, the focus is to take vertical farming to the next level by developing smart robots which can increase precision and productivity, while minimizing environmental impact and risk. Agriculture, one of humankind’s oldest inventions, is merging with the latest technology, and farmers will soon be looking to pair with a reliable automation parts supplier to make the step up to vertical farming.
Vertical farming offers a unique set of advantages. Farmers understand there are many urgent and practical reasons to grow upwards rather than outwards. This farming method has huge potential for sustainability and food security, while protecting the environment, economy, and ecosystems.
In addition, the inclusion of AI and robotics ensures high-quality growth of products all year round, while preserving water, nutrients, and land consumption by 95 per cent. The controlled process of indoor farming with the help of AI and robotics also protects crops against pest invasions, and ensures they are well insulated — this is an aspect field farming cannot guarantee since it requires amenable weather conditions and labour.
Vertical farms can operate anywhere with no geographical constraints and are not subject to the limitations presented in outdoor farming, such as extreme conditions. This not only protects the crops, but also provides a safer working environment for labourers. What’s more, labour costs can be significantly reduced due to the automated indoor growing systems; thus, there is no longer a need for manual labour all year long.
In addition, energy consumption can be drastically reduced in vertical farming by implementing LED lighting to mimic the sun as a light source. A minor change like this can limit heat waste while increasing energy efficiency and cutting energy costs. Not only can LED lighting be used as an alternative, but renewable energy generated from wind turbines can be paired with vertical farming to ensure 100 per cent of its energy is produced from renewable sources. It is a win-win situation.
How will it boost the economy?
This sector is expecting a huge boom in investment and interest and manufacturers, suppliers and retailers are therefore preparing for this shift through early adoption. In the past, vertical farming was viewed as theoretical, but now the vertical farming market in the APAC region is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 29 percent, rising from its current value of $0.78 billion to $2.77 billion by 2026. This is largely due to the advancement in technology such as sensors and smart energy systems that have improved the efficiency of growing products.
Although vertical farms will not replace traditional ways of farming, they hold great potential to revamp the future of agriculture in the APAC region by pushing towards a sustainable, environmentally conscious, tech savvy, economically rational, and health-sensitive world.
Source and Photo Courtesy of Agritech Tomorrow
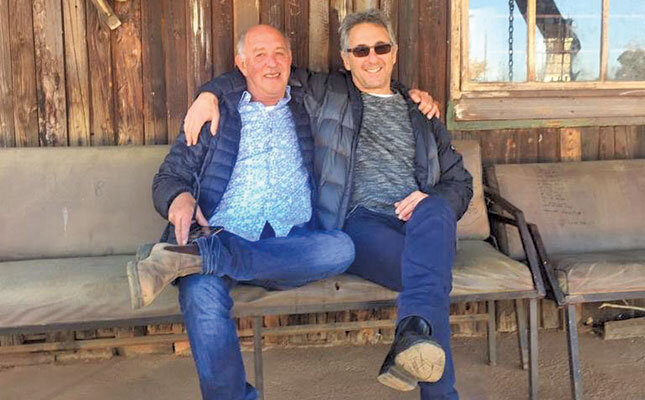
Lettuce: Meet The Salad Kings of SA
Back home in East London in 1978, he made the decision to become a farmer, an option that was met with criticism from family and peers who did not have farming backgrounds.
By Glenneis Kriel
August 6, 2021
Not knowing what to do after finishing his military service back in the 1970s, Michael Kaplan set off to work on a kibbutz in Israel, where he was exposed to banana, dairy and chicken production.
From there, he backpacked through Europe, and was particularly impressed by the new technologies that farmers in the Netherlands were using to protect their crops and improve production efficiencies.
Back home in East London in 1978, he made the decision to become a farmer, an option that was met with criticism from family and peers who did not have farming backgrounds.
“My mother, Ethel, was a doctor and my father, Lewis, a lawyer, so they thought I was completely bonkers when I told them I wanted to farm,” recalls Kaplan.
In pursuit of his dream, he wanted to study agriculture at the Elsenburg Agricultural
Training Institute in the Western Cape, but entries had already closed by the time he applied. So he began working at what was then the English Trust Company farm in Stellenbosch, thanks to an introduction from his childhood friend, Bruce Glazer, who already worked there.
Dew Crisp was co-founded by childhood friends Michael Kaplan (left) and Bruce Glazer.
“It really was a case of being in the right place at the right time, as the English Trust Company was one of the first to introduce farming tunnels in South Africa.
“They produced tomatoes using the nutrient film technique [NFT] and experimented with the gravel flow technique [GFT] to grow butter lettuce and celery,” says Kaplan.
These hydroponic techniques, he explains, are similar in that both entail the circulation of a nutrient solution in a closed system. The difference is that with GFT, gravel is used as a growth medium, whereas, with NFT, plants are suspended and their roots exposed.
Early days
Kaplan worked at the English Trust Company for two years. He then learnt that the Joburg Market sold up to three times more vegetables than its Cape Town equivalent.
Deciding it was time to spread his wings, he drove up to Johannesburg, where he began looking for a business partner and land on which to grow his own produce.
“My mother lent me R10 000, which I used to rent land near Heidelberg [about 50km south-east of Johannesburg] and produce celery under 2 000m² of nets using GFT,” says Kaplan.
In 1981, Heidelberg was hit by a severe snowstorm. It destroyed almost all of Kaplan’s infrastructure, but he managed to save most of the crop and used the income from the sale to rebuild his operation.
“I kept costs low by doing almost everything myself, and using the income to grow the operation, reaching 8 000m² by the third year of production,” recalls Kaplan.
In his fourth year of operation, he started looking for land closer to the Joburg Market and with more favourable production conditions.
“These are actually two of the most important prerequisites for farming success; you need to be close to the market, and farm in a region where the climatic and production conditions are suited to the crop you want to grow. I learnt the hard way that the Highveld is unsuited to salad production in winter,” he says.
Financing
With a clearer idea of what he required, Kaplan bought land near Nooitgedacht and applied to the Land Bank for a loan.
Being unfamiliar with hydroponic production, the bank declined his application, but Kaplan managed to secure a loan from First National Bank at an interest rate of 26%. Fortunately, the market was far less competitive and demanding in those days, which enabled him to repay the loan quickly.
“It would be almost impossible to accomplish the same today; land, labour, infrastructure and production costs are exorbitant. And you buy everything in dollars and euros but get paid in rands,” he says.
Costs are driven up even further by international production standards and auditing programmes such as GlobalGAP and HACCP, which are required to supply most markets today, while market access is complicated by retailers and big buyers demanding huge supply volumes all year round.
An impressive growth path
In the intervening years, Glazer had studied agriculture at Elsenburg and thereafter also worked on a kibbutz in Israel. On his return in 1984 he bought a farm near Kaplan’s, and two years later the two decided to amalgamate their businesses to create better economies of scale.
The new company was called Dew Crisp. To add value to their produce, they sold ready-to-eat lettuce in pillow packs, a market they dominated for over six years.
Since then, Dew Crisp has grown into one of the largest value-added salad suppliers in South Africa, expanding their geographical footprint over time to lengthen their production season and mitigate climate and production risks.
Today, they have 10ha under production in Muldersdrift, 200ha near Bapsfontein and 140ha near Philippi, as well as processing plants in the West and East Rand of Gauteng and in Franschhoek in the Western Cape.
Dew Crisp also sources produce from between 15 and 20 selected farmers across geographically diverse regions, some of whom have been supplying the business for over 25 years.
The company’s empowerment arm, Rural Farms, supports and sources produce from five previously disadvantaged smallholder farmers.
In 2009, Agri-Vie, the Africa Food & Agribusiness Investment Fund, bought a 49% share in Dew Crisp, which enabled Kaplan and Glazer to grow the business and place greater emphasis on financial administration and corporate governance.
“We realised that it wasn’t enough to simply follow the market; we had to create our own destiny by becoming market leaders.
“To achieve this, we needed to be innovative and have a really good understanding of consumer trends. We’ve introduced many firsts on the market,” says Kaplan.
Glazer and Kaplan have also drastically diversified their market risks by supplying all the major retailers, various prepared-meal manufacturers such as the Rhodes Food Group, and food service companies such as KFC, McDonald’s, Nando’s and Burger King.
Production
Dew Crisp’s produce is grown under nets, in plastic tunnels and in open fields.
“Tomatoes, English cucumbers and peppers don’t like water or cold [air] on their leaves, so we generally produce them under plastic,” says Kaplan.
Shade nets are used in the production of salad vegetables, as these are sensitive to sunlight, heat and wind. The nets also protect against hail and bird damage while reducing the impact of rain by breaking up the droplets. In addition, they help to absorb heat and keep the production area cool.
Open-field production is highly seasonal and limited to hardier vegetables such as sweetcorn, onions and cabbage.
Most of the produce is grown in hydroponic systems, where the plants are supplied with nutrients via a nutrient solution. In most cases, Dew Crisp uses closed hydroponics (recycled water).
“Closed hydroponics is used for salad production in GFT, whereas open hydroponics is used in the production of tomatoes and cucumbers, as they are really sensitive to diseases that might spread with the water. For this reason, each of these plants has access to its own dripper,” explains Kaplan.
Sawdust and coco peat are used as growth mediums in the open hydroponic systems.
“Some farmers sterilise these mediums to reuse them, but I prefer using them only once to prevent disease outbreaks. We do, however, reuse the gravel in the open gravel system, after cleaning it with a chlorine solution at the end of each production cycle.”
In the same way, the crops that are planted in the soil are rotated to prevent a build-up of diseases.
Water quality largely determines the success of a hydroponic system, so a farmer should not even think of using it if the irrigation water is of poor quality or has high levels of chlorine or sodium. Water can be pretreated to rectify mineral imbalances, but this drives up costs. Water should, in any case, be filtered before use.
Dew Crisp has worked with scientists for years to refine its plant feeding programmes based on the nutritional requirements of various crops during different development phases.
“The trick is to supply exactly what the plant needs. An undersupply leads to plant deficiencies, while an oversupply is wasteful and might result in damage to the system and plants. To prevent this, we constantly monitor the recycled solution, plant growth and climatic conditions, and tweak the nutritional programme accordingly,” says Kaplan.
Achieving this with open-field crops is even more challenging due to soil differences. Soil, nonetheless, has a higher buffering capacity and is thus more forgiving.
The farm does not employ any climate-control technology because of its high capital and running costs. Instead, tunnel windows are opened and closed to augment ventilation and reduce the interior temperature.
Even without climate-control technology, production is energy-intensive, as the water has to be recycled continuously. Back-up generators are a necessity, as most of the salads will die within hours if water flow is interrupted.
Advice
Farming, and especially farming under protection, has become highly specialised over the years, with low profit margins leaving little room for error.
“In the past, when a buyer ordered a hundred frilly lettuces, we could plant 150 and it didn’t really have an impact on the bottom line. These days, production costs are so high that we plant to order and programme,” says Kaplan.
The shift has also made it increasingly important for farmers to make use of consultants to fill their knowledge gaps.
“If you want to be successful today, you need to surround yourself with people who are better skilled than you are in their respective jobs.”
Email Michael Kaplan at mkaplan@dewcrisp.com.
Lead Photo: Shade nets are used in the production of salad vegetables, as these are sensitive to sunlight, heat and wind. Photo: Dew Crisp
Exeter Town Council Considers Turning Schartner Farm Into Massive High-Tech Agricultural Project
On Wednesday, the Exeter Town Council will hold a public hearing on a proposal for a zoning change that will allow for the development of a high-tech farm, with huge parking areas for trucks, a building the size of the Warwick Mall, and a 13 acre solar farm.
By Frank Prosnitz
August 8, 2021
On a crisp October morning, leaves turning the color of the rainbow and pumpkin patches filled with pumpkins awaiting children to turn them into Jack-O-Lanterns, thousands of parents, children, and grandparents would flock to Schartner Farm in Exeter.
They’d likely find the home-cut French Fry stand, and inside freshly baked pies, homemade jams and newly picked apples of every variety, fresh vegetables and fruits, and an array of Mums.
But that was all a few years ago, before the 150-acre farm closed when a fire partially destroyed its main building in 2015, leaving fields that once produced corn and strawberries, pumpkins, and large variety of vegetables, to go fallow. The farm was founded more than a century ago, in 1902.
Farm buildings were left behind decaying, greenhouses in disrepair, and nearby residents fearful that the land would become a strip mall, the likes of which are found only in Rhode Island’s more urban areas.
On Wednesday, the Exeter Town Council will hold a public hearing on a proposal for a zoning change that will allow for the development of a high-tech farm, with huge parking areas for trucks, a building the size of the Warwick Mall, and a 13 acre solar farm.
Some in the community are fearful the council will approve the zone change and a project that will forever change the character of the land, and possibly the community. Others see it as providing a needed food source, making the property productive again.
The zone change, proposed by Richard Schartner of RI Grows, would establish a Controlled Environmental Agricultural Overlay District that, according to the town’s public hearing notice “would contain eligibility and process standards for establishing Controlled Environmental Agriculture (“CEA”) facilities which provide a controlled environment for year-round production of food and plants using a combination of engineering, plant science, and computer managed greenhouse control technologies to optimize plant growing systems, plant quality and production efficiency. The “CEA” facilities would also include onsite solar power as a ‘by-right’ accessory use to the primary CEA agricultural facility.”
In other words, high-tech greenhouse that are driven by technology, a building that would reportedly be 35 feet high and cover 20 acres, powered by solar energy.
The council’s public hearing is being held at the Metcalf School and begins at 6:30 p.m. on Wednesday.
In June, Rhode Island Grows broke ground for a 25-acre indoor tomato farm on Schartner Farm. At the time it was reported, the farm would have hydroponics technology, powered by solar energy, using recycled rainwater.
According to the RI Department of Environmental Management, the tomato farm facility would cost $57 million and take eight months to build, produce 14 million pounds of tomatoes, and employ 80 people. DEM said it is only the first phase of the $800 million project that will eventually add 10 greenhouses over the next decade.
“As industrial agricultural in other areas of the country and central America have squeezed out local farms, this self-sufficient facility will enable the Schartner family to continue their century of farming in Rhode Island with another 100 years,” the DEM said in a statement.
Opponents of the proposed zone that would permit the new high-tech farming, are concerned that the process is more manufacturing than farming and “since a CEA (Controlled Environmental Agriculture) does not need farmland, should a huge CEA be located on a farm when preserving what’s left of Rhode Island’s farms is critical?” wrote Megan Cotter of the Exeter Democratic Town Committee.
“The project would negatively impact the scenic beauty of Route 2 and disrupt the quality of life for all in the vicinity,” she wrote. Cotter emphasised she’s not opposed to high-tech farming but feels it’s more appropriate in industrialized locations.
Another Exeter resident, Asa Davis, who owns more than 100-acres in town, is a strong proponent of the project.
“If you really want to preserve things like natural resources for future generations, you don’t use them,” Davis wrote. “Traditional agriculture can wear land out, and uses a lot of water, fertilizer and pesticides. The 1930’s Dust Bowl in the Midwest was man-made, not a natural occurrence. If we want to preserve water and farming resources for future generations, CEA looks like a good solution. The greenhouse is big, but it’s got a dirt floor. If it doesn’t work out, it wouldn’t be hard to remove it and revert to traditional farming – nowhere near the cost or effort of removing a shopping mall.”
Lead Photo: On Wednesday, the Exeter Town Council will hold a public hearing on a proposal for a zoning change that will allow for the development of a high-tech farm, with huge parking areas for trucks, a building the size of the Warwick Mall, and a 13 acre solar farm.
Sustainability, Global Trade, Climate Change – WIA Summit Covers THE Industry Topics
At its 10th anniversary event this fall, the Women in Agribusiness Summit (WIA) will continue the tradition it is known for – providing key ag industry business knowledge to help women excel in the sector.
August 3, 2021
Kelly Lockwood Primus, Opening Speaker
BOSTON - At its 10th anniversary event this fall, the Women in Agribusiness Summit (WIA) will continue the tradition it is known for – providing key ag industry business knowledge to help women excel in the sector. This in-person conference – to be held September 21-23 at the Hyatt Regency Minneapolis – features a robust agenda, expert speakers, plenty of networking and a special off-site reception.
Opening speaker Kelly Lockwood Primus, CEO of Leading NOW, will start the business discussion with The Career Advice You Probably Didn’t Get. This presentation will include Leading NOW’s research on women’s leadership, what's missing from conventional career advice and the barriers women face in achieving executive positions.
“Through our research, we have identified traits for success in leadership. These include integrity, transparency, confidence and more, but most importantly, women need to focus on what we call The Missing 33%™,” said Lockwood Primus, who is an advisor to global organizations seeking to change mindsets, behaviors and cultures. “This is the business acumen that sets them apart, and we will discuss this in detail at the Women in Agribusiness Summit this fall.”
Others who will share the stage with Lockwood Primus include Scott Sigman, principal advisor at EASE, who will focus on connecting the dots in global trade and examining alternative transport paths; Shawn Jarosz, CEO of TradeMoves, who will speak to why international trade matters to food & ag; and Beth Sauerhaft of American Farmland Trust, who will moderate a panel of esteemed experts in a discussion on sustainability and climate change.
Interspersed with this critical industry content will be the annual highlights that the WIA community has grown to expect and anticipate: Ag Innovation Hour, Executive Profiles and the Female Producer Panel. Through these, attendees will hear from soybean and egg farmers, and a specialty meats producer. They also will gain valuable career insights from accomplished female executives and be enlightened about the latest agtech innovations that are disrupting the sector.
Other sessions at the 10th annual Women in Agribusiness Summit include:
• The Fragile Ecosystem: Our Decisions Impact the World
• Understanding the Plant-Based Consumer
• Transforming the Workplace
• The Future of North American Agriculture
• Grain Industry Overview
Women in Agribusiness initiatives have fostered a year-round community of engaged executives, leaders and professional women. Learn more and register at womeninag.com , and visit us on Twitter, Facebook, and LinkedIn.
AppHarvest Taps Amazon Veteran Mark Keller To Operationalize AI-Informed Farm Operating System
AgTech leader AppHarvest, a public benefit company and certified B Corporation focused on farming more sustainably using 90% less water than open-field agriculture and only recycled rainwater, has named Amazon veteran Mark Keller as its SVP, Software Applications Platform.
July 26, 2021
Keller joins the AppHarvest technology group as SVP, Software Applications Platform, with a proven track record of building AWS services and high-performing teams
AgTech leader AppHarvest (NASDAQ: APPH, APPHW), a public benefit company and certified B Corporation focused on farming more sustainably using 90% less water than open-field agriculture and only recycled rainwater, has named Amazon veteran Mark Keller as its SVP, Software Applications Platform. Keller joins the AppHarvest technology group as it works to operationalize its Project TalOS platform to make fresh fruit and vegetable production as reliable as consumer goods manufacturing.
To create the Farm of the Future, AppHarvest is investing in robotics, artificial intelligence, tele-operation, and proprietary seed genetics. With robots roving through the facility alongside the company’s human labor force, interacting with and caring for the crops, the company will be collecting data continuously on plant production to feed into AI and then using software to align facility operations with sales and logistics.
“We are massively expanding our team to build out our digital operating model for farming, which has AI at its core that can manage a global network of facilities and effortlessly execute complex supply chain strategies intelligently and autonomously,” said Josh Lessing, AppHarvest chief technology officer. “Adding an industry veteran like Mark will be a true game-changer for this growth phase of our business, and his strong, people-centric leadership skills will be a key enabler for the AppHarvest technology group.”
Keller has a proven record spanning more than 25 years of turning ideas into full-featured technology solutions, such as launching Amazon’s first four large-scale Kiva robotics sortable warehouses and the PrimeNow Warehouse Management Software used to run the company’s one-hour fulfillment centers.
“The Holy Grail in agriculture is predicting and managing yield and quality,” said AppHarvest founder and CEO Jonathan Webb. “Having Mark join will accelerate our efforts as we train our intelligent robot, Virgo, to harvest multiple crops—ranging from tomatoes and cucumbers to more delicate fruits such as strawberries—as we move toward more AI-informed growing. These insights collected and analyzed, then fed into AI, will be the true game-changer for us since every piece of fruit is an outcome that resulted from the many variables in the growing process.”
“Two of the most pressing global concerns are water scarcity and creating resilient food supply, and AppHarvest is solving for both,” said Keller. “As a father of four, I want to leave a strong legacy for my children and leverage technology for good. The foundation AppHarvest is building will give controlled environment agriculture the opportunity to restructure the food landscape to mirror the hyper-efficient e-commerce landscape.”
Keller is a Hispanic Gulf-War veteran who brings a unique perspective to employee engagement programs being an early driver of the Amazon Warriors veterans employee group and having participated in the Latinos @ Amazon employee group. Keller also was an early adopter of the Military Apprentice Software Development Engineer program to improve diversity hiring in technology, which he expects to continue at AppHarvest.
About AppHarvest
AppHarvest is an applied technology company in Appalachia developing and operating some of the world’s largest high-tech indoor farms, designed to grow non-GMO, chemical pesticide-free produce, using up to 90 percent less water than open-field agriculture and only recycled rainwater while producing yields up to 30 times that of traditional agriculture on the same amount of land without agricultural runoff. The company combines conventional agricultural techniques with cutting-edge technology including artificial intelligence and robotics to improve access for all to nutritious food, farming more sustainably, building a domestic food supply, and increasing investment in Appalachia. The company’s 60-acre Morehead, Ky. facility is among the largest indoor farms in the U.S. For more information, visit https://www.appharvest.com/.
Center To Announce First Winners of Its “Best In Class” Awards
The Center of Excellence for Indoor Agriculture, a U.S. based company that supports the growth and development of the vertical and indoor farming industry, will announce the first winners of its Center of Excellence “Best in Class”TM Awards for indoor farm manufacturers at a virtual event scheduled for August 4th with Indoor Ag-Con.
By July 23, 2021
The Center of Excellence for Indoor Agriculture, a U.S. based company that supports the growth and development of the vertical and indoor farming industry, will announce the first winners of its Center of Excellence “Best in Class” TM Awards for indoor farm manufacturers at a virtual event scheduled for August 4th with Indoor Ag-Con. The goal of the “Best in Class” Awards is to recognize operational excellence in the indoor agriculture industry through an analysis of KPI’s on indoor farm operations and the supporting equipment.
The announcement will take place in the context of a virtual panel discussion on the importance of metrics to indoor farm sustainability and future investment in indoor agriculture. Finalists and industry thought leaders will sit on the panel. Those interested may register for the event at: indoor.ag/webinar.
The winners will be announced virtually in two categories: commercial indoor production systems and indoor farm lighting fixtures. Indoor production systems are turnkey systems that are optimized for the production of leafy greens and other vegetables in indoor vertical farm facilities. The top systems use the least amounts of water, energy, labor, and other resources to produce the greatest yield. The top lighting fixtures are energy-efficient, affordable, and yield-optimizing.
“We are really excited to recognize excellence among the Agtech manufacturers supporting the indoor and vertical farming industry. Our finalists offer solutions that help indoor farms achieve operational efficiency and sustainability. We believe the awards can help spur innovation in this space,” stated Eric W. Stein, Ph.D., founder and Executive Director of the Center of Excellence.
The winning products were selected through a process that includes being nominated and then evaluated according to technical and operational merits in several categories. The Center performs a quality check on the data before being input into a proprietary weighted multi-criteria model. Products are also evaluated based on interviews and an analysis of online data.
More Info: More detailed information on the Center’s awards can be found at https://indooragcenter.org/awards. Growers and manufacturers are invited to become nominated and begin the application process. Winners receive several benefits including industry recognition, social media exposure as well as participation in future panel discussions and conferences.
About the Center
The Center of Excellence for Indoor Agriculture provides insights about the economics of indoor farming based on a careful analysis of industry data and from thought leaders in industry and academia. As the first U.S.-based Center of Excellence dedicated to indoor farming, it promotes best practices, benchmarking, networking, knowledge development, and research. Its annual Best in Class Indoor Farming Awards (TM) recognizes top indoor growers and manufacturers. The Center is located in the Philadelphia metro region.
About Indoor Ag-Con
Indoor Ag-Con is an organization that hosts premier events centered around building the indoor agriculture community. They unite growers and engineers alike to create a prime networking opportunity through discussions, workshops, and exhibits enhancing the participants’ knowledge of growing crops in indoor systems.
Media Contact Information
Center of Excellence for Indoor Agriculture
indooragcenter.org
team@indooragcenter.org
Drought Signals Need For Sustainable Agriculture
As Winnipeggers funnel into air-conditioned buildings to stave off record-breaking heatwaves, Manitoba’s farmers are facing a much deeper crisis.
By Lucas Edmond
July 20, 2021
As Winnipeggers funnel into air-conditioned buildings to stave off record-breaking heatwaves, Manitoba’s farmers are facing a much deeper crisis.
For avid small talkers who love to discuss the weather, the low river and empty floodways during flood season were the first indications that Manitoba was going to have a summer of extreme conditions. Then the aphids appeared — a small insect that thrives in hot, dry weather — lathering Winnipeg’s canopy with sticky gunk. Finally, reality of the drought’s devastation struck when the West Coast of North America erupted in flames following a heatwave that stretched across several borders earlier this summer.
On July 5, just days after the heatwave, St. Laurent, Man. declared an agricultural state of disaster as potential crop yields continued to dwindle in the face of high aridity and soil exhaustion. Armstrong, Man. was the second rural municipality to declare a state of agricultural disaster on July 9, but it is likely not the last.
As Manitoba’s farmers fight to stay afloat with the support of only 40 per cent of Manitoba’s natural rainfall, a grasshopper infestation — produced by the dry conditions — has begun eating away at the limited vegetables, grains and oats farmers have managed to grow.
Due to the heat and the grasshoppers, a significant portion of crops that are often recycled as feed for cattle have been lost. Many farmers are being forced to cut their losses and sell their herds. Some have decided to prematurely cut their crops to bundle their feed in order to keep their livestock through the winter — forcing them to lose large portions of their annual incomes.
The ecological disaster and its consequential financial impact has stimulated discussions with the provincial government about financial aid to keep the province’s large agricultural sector healthy. However, subsidies for lost incomes should go a step further.
Although droughts have been prevalent across North America throughout the 21st century, this year is shaping up to be the driest in the last century. Record-breaking heat and inconsistent rain due to global warming — compounded by exhaustive industrial agriculture — are destroying the soils, stripping them of nutrients at a rate incomparable to any other period in modern history. Humanity and our methods of production, accumulation and distribution has spurned a new geological epoch now visibly discernable in the stratigraphic record. If the weather continues to become increasingly unpredictable due to our ecological impacts, then something must be done to create a more sustainable and predictable agricultural sector.
The provincial government should take time to consider the benefits of establishing a fund dedicated to farmers who want to transition their efforts away from the unsustainable methods of industrial monoculture cropping that have proven to be unstable during this perilous drought. Although much more expensive and labour intensive, permaculture cropping adopts a land management system dedicated to farming based on a balanced ecosystem that can thrive through tough environmental conditions without the assistance of expensive and detrimental inputs of herbicide, pesticide and artificial fertilizer.
In other words, instead of planting one cash crop that is easy to harvest but tough on the environment, the agricultural sector should look toward planting crops and vegetation that mutually complement each other in their ecological contexts.
Monoculture industrial farmers typically try to avoid using pesticides due to their damaging effects on the ecosystems that surround their plots. However, if the dry conditions and the infestations persist, many farmers — without the capacity to produce natural solutions to the crisis — may have to bite the bullet to protect their livelihood in the short term.
As many biologists from around the world have concluded, killing back pests with artificial products stunts local ecology and the environment’s natural ability to balance itself. Using pesticides kills off vital food sources for various predators, thus unintentionally killing various other species and reproducing the conditions for much worse infestations in the future. Destroying biodiversity is exactly what farmers need to avoid during these periods of agricultural crisis.
By adapting to living with pests and drought, farmers will be investing in the longevity of their yields while simultaneously reducing their industrial emissions. Transitioning into a labour-intensive permaculture system will be a crucial step in making the future of the planet green, but the transition must start with incentives and funding from federal and provincial coffers.
Fundamentally, it is up to farmers to make their decisions in conjunction with government bodies. However, the world is not fixing itself, and sustainable agriculture is a good first step at mitigating the public calamities that lie ahead.
Lead Photo: Climate challenges lie ahead, but governments can reduce risks by investing in food
USA - VIRGINIA - Urban Farm In Newport News Aims To Reduce Food Insecurity. It’s Not A ‘Handout,’ It’s A ‘Hand Up.’
Graham was gardening on a recent Saturday morning in a farm run by Hampton Roads Urban Agriculture, which wants to create a healthy, sustainable food system in the neighborhood. The farm is a partnership between the church and the Newport News-based nonprofit, which is working to reduce food insecurity through farming and educational programming.
By Sonia Rao
July 20, 2021
NEWPORT NEWS — Judge Graham knelt over a row of bare soil and the occasional yellow marigold, planting seeds. In a little over a month, he hopes, the bed near Zion Baptist Church will be bursting with ripe tomatoes. The tomatoes, and the rest of the food Graham and other volunteers are growing, will go to the surrounding community.
Graham was gardening on a recent Saturday morning in a farm run by Hampton Roads Urban Agriculture, which wants to create a healthy, sustainable food system in the neighborhood. The farm is a partnership between the church and the Newport News-based nonprofit, which is working to reduce food insecurity through farming and educational programming.
On Aug. 14, the farm will open its first farmers market, which will take EBT and SNAP payments.
“The ones that can afford to pay, fine, but I’m not gonna turn anybody away,” said Graham, who helped start the group. “Anybody that shows up is gonna go home with some groceries.”
The area around Zion Baptist is a food desert, said Renee Foster, founder of Hampton Roads Urban Agriculture. It has only one grocery store, a Piggly Wiggly, and many residents are low-income and don’t have transportation to drive elsewhere.
The garden has been around for four years and Hampton Roads Urban Agriculture has managed it for two. All of its workers are volunteers, including high school students, veterans and service members. This year, the farm is expected to grow about 3,500 pounds of produce. Graham and Foster also deliver food to older adults who can’t come out because of health concerns or a lack of transportation.
Graham said the farm is also a teaching garden, so he treats it as a place for visitors and volunteers to get hands-on experience.
On June 25, a group from the Coast Guard came to volunteer. This was the first time Petty Officer 2nd Class Stacey Maine gardened. But by the end of the hour, she was explaining how to weed and cut asparagus.
Coast Guard Petty Officer 2nd Class Stacey Maine weeds a vegetable bed in the urban garden near the intersection of Jefferson Avenue and 21st Street in Newport News. (Kaitlin McKeown/Virginia Media)
Some people drive from Norfolk, Chesapeake or Virginia Beach to volunteer.
On the left of the 34-by-100-foot garden is an orchard of peach, plum, apple, fig, pear, cherry and nectarine trees. Next to the orchard are rows of tomatoes, butternut squash, strawberries, asparagus and radishes, and a garden of herbs with basil, sage, lemongrass and stevia. At the back is a collection of chili, tabasco, habanero and ghost peppers. A sign says “Judge’s ’HOT Pepper Zone’ ” with an image of a skull and crossbones to warn children away. Children, Graham said, often mistake the peppers for strawberries.
Interspersed between the crops are bright pink, purple, red and yellow flowers. They bring in pollinators like bees and hummingbirds, Graham said.
The farm also has more than eight types of sweet potatoes, all donated by Clifton Slade, who owns Slade Farms in Surry. Slade donated 270 slips of sweet potatoes. Other donors include The Virginia Small Farm Resource Center, Tidewater Community College’s horticultural program and the Hampton Roads Agricultural Research and Extension Center. The farm gets the rest of its supplies from Norfolk Feed and Seed or Slade Farms. Everything the garden grows is organic, Graham said.
Foster said she’s excited to start hosting more events now that more people are vaccinated and pandemic restrictions have been lifted. The farm has been having movie nights when children can come to have fun and learn about the garden.
She hopes the market will turn enough of a profit so that she can put more food back into the ground. She’s also raising $10,000 to start a “Drones in Agriculture” program to introduce children to careers in agriculture, science, technology, engineering and math. Children will learn how to code and fly drones, which will be used for agriculture scanning — mapping out the layout of the garden and recording plant health.
Foster hopes eventually to raise enough money to hire a part-time farm manager and create more urban farms across Hampton Roads. She and the other board members of her group work full-time jobs, so managing even one is difficult.
“It takes many, many hands,” she said.
At the end of the day, the goal is to empower food-insecure communities to create and maintain access to healthy food.
“We don’t want to give them a handout,” Graham said. “We want to give them a hand up.”
Lead Photo: Volunteers weed a vegetable bed in a garden on Friday, June 25, 2021, near the intersection of Jefferson Avenue and 21st Street in Newport News, Va. The garden is a partnership between Hampton Roads Urban Agriculture and Zion Baptist Church. (Kaitlin McKeown/Virginia Media)
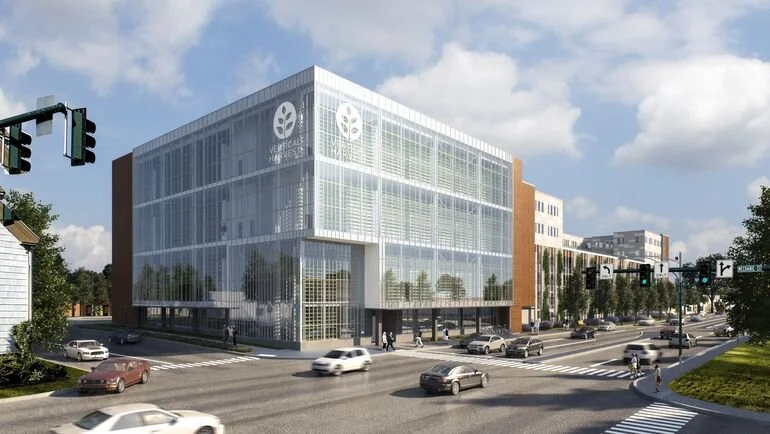
Vertical Harvest, MedRhythms Get FAME Financing to Advance Growth Plans
The Finance Authority of Maine has approved a total of nearly $50 million in financing for two startups — Vertical Harvest L3C, which plans to launch a hydroponic greenhouse in Westbrook, and a Portland provider of "digital therapeutics," MedRhythms Inc.
By Catie Joyce-Bulay
July 19, 2021
The Finance Authority of Maine has approved a total of nearly $50 million in financing for two startups — Vertical Harvest L3C, which plans to launch a hydroponic greenhouse in Westbrook, and a Portland provider of "digital therapeutics," MedRhythms Inc.
Vertical Harvest will receive $45 million in conduit bond financing. The company plans to produce over 1 million pounds of produce annually, and FAME's funds will be used to finance a portion of the construction costs to build 70,000-square-foot Westbrook farming facility. The project ultimately is expected to create approximately 50 full- and part-time jobs, many of which are expected to be performed by individuals with disabilities.
The project is part of a larger master-planned development that is expected to include affordable housing and parking in downtown Westbrook. Because the project will treat wastewater as an exempt facility, all or a portion of the bonds will be eligible for tax-exempt treatment under federal tax law.
“We appreciate FAME’s support for the agricultural component of this project,” said Greg Day, president of TDB LLC, developer of the project. “This master-planned program establishes a compelling business model for food production in an urban core that our firm is expanding to other communities throughout New England and the nation.”
Vertical Harvest plans to break ground on the facility in the fall. It's expected to be Maine’s first vertical farm, and the country’s second. The company’s first location in Jackson Hole, Wyo., was the first of its kind and has been operating for five years.
MedRhythms, Inc. will receive tax credit certificates related to approximately $2.8 million in investments through the Maine New Markets Capital Investment Program to help with the costs of a commercialization strategy of its device and software for stroke rehabilitation. The certificates authorize the issuance by the state of approximately $1.1 million in tax credits through the program.
“We are pleased to support MedRhythms’ plans to advance their digital therapeutic for stroke rehabilitation, as well as additional research and development,” said David Daigler, chair of the FAME board. “Digital therapeutics are a cutting-edge field that can help to improve the everyday lives of Mainers and other patients who will benefit from the company’s technology.”
MedRhythms uses sensors, music, and software to build solutions that measure and improve walking. The company, which currently employs 18 individuals, with 13 full-time employees in Maine, hopes to triple its workforce in the next few years.
“Digital therapeutics are the future of health care, and we appreciate the support of FAME,” said Brian Harris, CEO and founder of MedRhythms.
FAME uses tax-exempt private activity bonds, or “conduit bonds,” which are authorized by the Internal Revenue Code in order to stimulate economic development in certain targeted industries. The projects financed in recent years range from nonprofit health and higher education projects to solid waste improvements, public infrastructure and manufacturing.
Lead Photo: A 300,000-square-foot Westbrook building, shown in this rendering, is expected to house the Vertical Harvest indoor farm, as well as apartments, parking and commercial space.
An Affordable Solution To Monitor And Optimize Food Production
Ecobloom, a startup based in Stockholm, provides two different solutions to the vertical farming space. The first solution is a B2B product, namely an AI solution ensuring automated growing of the plant and monitors plant food production at the same time
By Rebekka Boekhout
July 9, 2021
“We’re helping farmers optimize their food production through more efficient yield management,” says Hamza Qadoumi, CEO and founder of Ecobloom. “Also, cost reduction comes in through a significant reduction in labor and yield increases up to 2 times more per year through accurate predictions. The system allows us to reduce food waste up to 20% through yield prediction and our deviation analysis.”
Ecobloom, a startup based in Stockholm, provides two different solutions to the vertical farming space. The first solution is a B2B product, namely an AI solution ensuring automated growing of the plant and monitors plant food production at the same time. With already a successful consumer product on the market, their focus is to offer smart technology solutions for the indoor farming market.
The pilot farm
Smart sensor - EcoSense
The company provides a software-connected plug-and-play solution named EcoSense. EcoSense is a small box that can basically be placed anywhere on the farm, such as above shelves to monitor plant growth. EcoSense comes in two formats: a camera for growth and plant analysis, sensors for water analysis and sensors for air analysis. Next to that the sensors predict yield, so lots of data can be gathered to keep improving this. Hamza notes, “We’re now looking at venturing with flowers and fruit greenhouse growers in Spain, Holland, The UK and the Middle East region.
The core solution of the device is hardware, sensors and cameras. Through these elements, the environmental sensors and plant environment is captured by data collectors and cameras throughout the plant’s life cycle. According to Hamza, farmers need about 1 device per 100m2. The wifi-connected cameras and sensors are modular solutions, using machine learning to constantly monitor and analyze plant development, health and stress. Through camera recognition, a certain yield outcome and deviations can be predicted.
Read the rest of the article here
For more information:
Hamza Qadoumi, CEO and founder
Ecobloom
hamza@ecobloom.se
www.ecobloom.se
US (IA): Removing Seasonality by Rolling Out Multiple Farms Throughout The State
“We want Nebullam Farms to be available in every city throughout the US, so we can fulfill our mission of creating access to reliable and local food for everyone, year-round,” says Clayton Mooney, founder of Nebullam
By Rebekka Boekhout
July 6, 2021
“We want Nebullam Farms to be available in every city throughout the US, so we can fulfill our mission of creating access to reliable and local food for everyone, year-round,” says Clayton Mooney, founder of Nebullam.
Over half of the Nebullam team is comprised of Iowa State University Alumni. Today, Nebullam HQ and its Nebullam Farm 1 in Ames, located in the Iowa State University Research Park. At the end of this year, the company will be launching Nebullam Farm 2, which will be in another location in Iowa.
Clayton Mooney, founder
Tomatoes as a cash cow
The company’s staple food is Red Butterhead Lettuce. Next to that, Nebullam grows Red Oakleaf lettuce, pea shoots, micro radish, broccoli sprouts, and cherry- and slicer tomatoes. “What we grow comes from direct feedback from our subscribers. Tomatoes are a great example, as we started trialing them in mid-2020, delivered samples to chefs, produce managers, and subscribers,” notes Clayton. He says that their feedback helped to bring the tomatoes to market 3 months earlier than expected, which has continued to add to Nebullam’s revenue. Now, the company is looking at peppers, cucumbers, strawberries, and spinach, which are subscriber requests.
Read the rest of the article here
For more information:
Clayton Mooney, founder
Nebullam
c@nebullam.com
www.nebullam.com
Design Firms Eye Efficiency, Speed To Market And Turnkey Design Solutions
Many of these transactions have included product and technology firms, but there is one acquisition, in particular, that is going to have quite a significant impact not only on the cannabis industry but on the larger indoor Controlled Environment Agriculture sector
By Andrea Di Pastena
July 13, 2021
Recently, consolidation within the cannabis industry has been seen through several mergers and acquisitions. Many of these transactions have included product and technology firms, but there is one acquisition, in particular, that is going to have quite a significant impact not only on the cannabis industry but on the larger indoor Controlled Environment Agriculture sector.
urban-gro has agreed to acquire the architecture firm MJ12 Design Studio in a move that makes urban-gro a one-stop company supporting growers with full-building turnkey design solutions including architecture, engineering, and cultivation systems integration. “Our role as an Architecture and Engineering firm truly sets us apart from the rest of the industry,” says Sam Andras, AIA, senior principal and partner at MJ12 Design Studio. “This acquisition has created a company that truly integrates turnkey design solutions under one roof.”
MJ12 Started Early in Cannabis Facility Design
The story of MJ12 Design Studio goes back to the very inception of the cannabis industry. “MJ12 Design Studio’s parent company of 2WR,” Andras recounts. “For 20 years, we had offices in the deep south, and we were working on federal projects. Then, we saw a tremendous opportunity with the legalization of cannabis in Colorado. So, we had to come up with a different brand for our cannabis design services. If you dig back in history, President Harry Truman had a group whose mission was to investigate alien activity. This secret group was called The Majestic 12, and the acronym was MJ12. So, since we were going to be a ‘secret’ architectural firm, MJ12 was the perfect name. From that moment on, we have designed over 100 cultivation facilities, with projects across North America and beyond - including Gibraltar, North Macedonia, and New Zealand.”
Read the rest of the article here
For more information:
urban-gro
720-390-3880
marketing@urban-gro.com
urban-gro.com
Wells Fargo Picks 5 Indoor Ag Companies For Its Latest Innovation Incubator Program
Five early-stage indoor agriculture companies will participate in the ninth cohort of the Wells Fargo Innovation Incubator (IN2), which works with cleantech companies and entrepreneurs across food and housing sectors
By Jennifer Marston
July 8, 2021
Five early-stage indoor agriculture companies will participate in the ninth cohort of the Wells Fargo Innovation Incubator (IN2), which works with cleantech companies and entrepreneurs across food and housing sectors. Chosen participants for this cohort will focus on tools and processes that can make indoor farming more environmentally and financially sustainable.
The Wells Fargo Foundation funds the program, which is co-administered by the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL).
Indoor ag has seen some major milestones and investments in 2021, but whether its a truly sustainable endeavor (financially and environmentally) remains a hotly debated topic. For example, growing greens inside fully controlled environments like vertical farms might cut down on inputs like land and water usage, but an enormous amount of energy is needed to run a farm off fully on artificial lighting. (Greenhouses, because they use natural sunlight, are usually a different story.) Additionally, leafy greens are still the only crop large-scale vertical farms can grow in huge quantities, and from a calorie perspective, salad can’t fully feed a growing world population.
Claire Kinlaw, director of Innovation Commercialization at the Donald Danforth Plant Science Center, said in a statement today that this year’s cohort is “focused on validating technologies that address key challenges in the indoor agriculture industry, including environmentally and financially sustainable ways to deliver light, control growth environments, evaluate environmental impacts and solve the need for crop varieties that are well-adapted for indoor environments.”
Companies chosen for the program address these issues and others:
Atlas Sensor Technologies monitors water hardness in real-time to reduce waste and cost of water and improve how water softeners operate
GrowFlux makes intelligent horticulture lighting via an IoT platform the company says can save 20-30 percent in energy costs
Motorleaf specializes in AI for indoor ag in order to give growers information around yields and carbon footprint
New West Genetics does genomics-assisted breeding for the hemp industry
SunPath uses patented fiber optics tech to improve lighting for indoor farms
All participants will receive up to $250,000 in non-dilutive funding from Wells Fargo. Over a 12 to 18 month period, companies will conduct research and development at NREL and at the Donald Danforth Plant Science Center in St. Louis, Missouri.
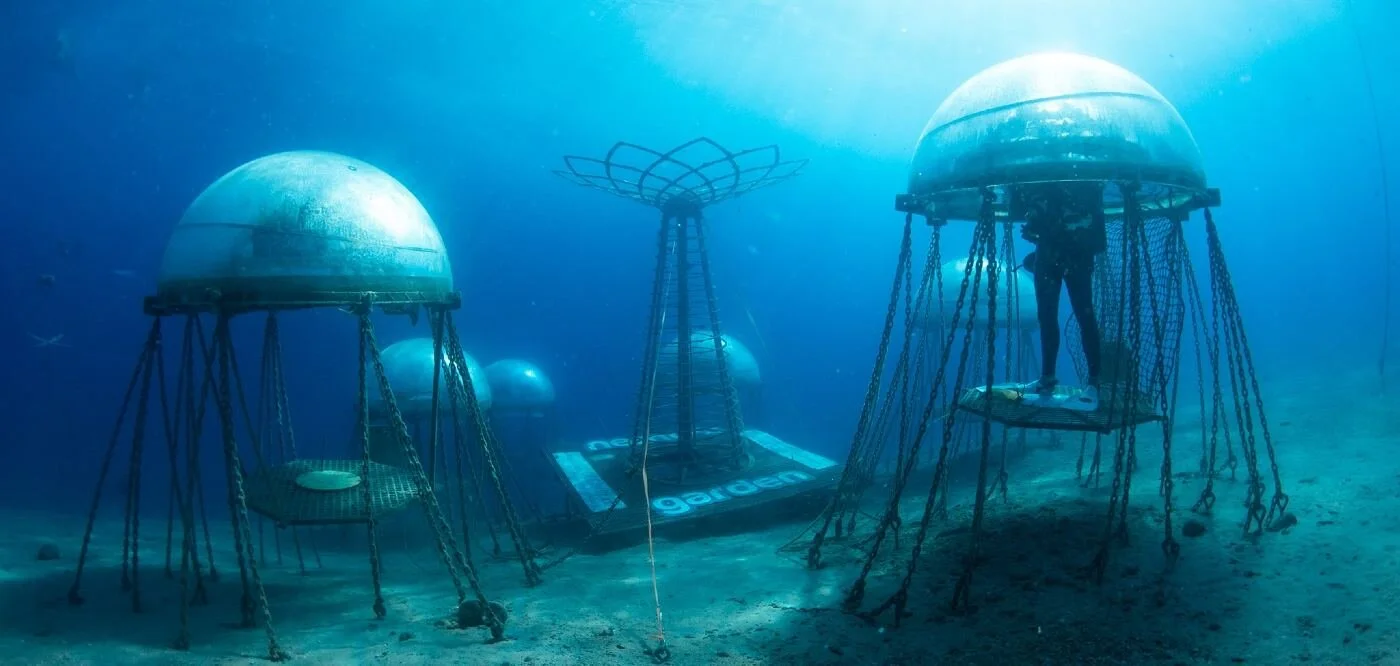
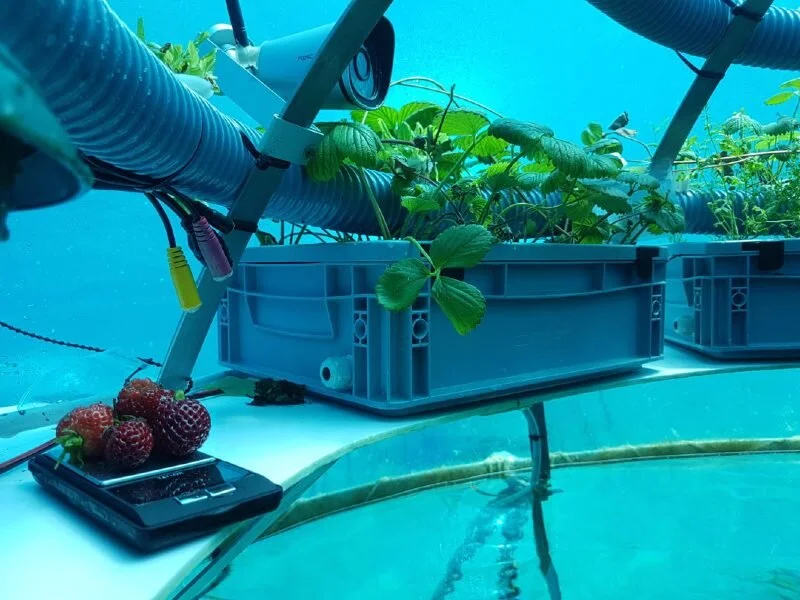
World’s First Underwater Vegetable Garden Reopens Growing Lettuce And Basil In Perfect Temperature
From the ancient rice terraces of Yunnan to modern vertical hydroponics, agriculture comes in many different forms. Now a group of Italian brainiacs have created the world’s first underwater garden for terrestrial plants
By Andy Corbley
July 13, 2021
From the ancient rice terraces of Yunnan to modern vertical hydroponics, agriculture comes in many different forms. Now a group of Italian brainiacs have created the world’s first underwater garden for terrestrial plants.
Seaweed and kelp have been cultivated along shorelines for centuries, but in small submersible glass domes, pots of basil, lettuce, tomatoes, and even zucchini flowers, green peas, aloe vera, and mushrooms are growing like in any other home garden.
Called Nemo’s Garden, the project was launched by the Ocean Reef Group as a means to experiment with food supply diversity, should climatic changes make parts of Italy too dry to farm.
The large self-sustaining, totally-contained biospheres would in theory be scalable, and perhaps in the future might look like the underwater city from Star Wars: The Phantom Menace.
The challenges inherent in growing plants underwater, given that they are normally at home in soil, was but one hurdle Nemo has had to overcome. The six air-filled greenhouses (or should that be bluehouses?) suffered major storm damage in October 2019, and before they could be fully repaired, COVID-19 had all the researchers sheltering in place.
Yet the team never gave up hope, as Euronews reports, and the months of abandonment did not harm the facility in any way. June 6th saw the garden fully-operational again, including their livestream where one can watch the plants literally grow.
The biospheres, which sit eight meters under the surface off the coast of Noli in Liguria, use solar energy for their minimal electrical needs, and evaporated seawater condenses on the glass of the ceiling which waters the plants. A diver swims under and up into the air pocket of the pod to harvest what’s ready to eat.
The project website says that increased pressure like that found under the ocean is actually beneficial to the speed at which plants can germinate, though they admit very little research has been published on the topic—after all, not so many people are currently trying to grow strawberries underwater.
The conditions create a really intense flavor in the vegetables, and also allow the plants’ environment to be completely controlled, with nothing impacting their life that the growers don’t want.
Nemo’s Garden, OceanReef
For now Nemo’s Garden is essentially a research lab, but if the idea were expanded, it’s expected to be able to reinforce food security for the peninsula, and the world.
(SEE Inside Nemo’s Garden in the video below.)
Can A New Initiative Spur Agricultural Revolution In Alaska?
When Eva Dawn Burk first saw Calypso Farm and Ecology Center in 2019, she felt enchanted. Calypso is an educational farm tucked away in a boreal forest in Ester, Alaska, near Fairbanks
By Max Graham
July 6, 2021
This story by Max Graham originally appeared in High Country News and is republished here as part of Covering Climate Now, a global journalism collaboration strengthening coverage of the climate story.
When Eva Dawn Burk first saw Calypso Farm and Ecology Center in 2019, she felt enchanted. Calypso is an educational farm tucked away in a boreal forest in Ester, Alaska, near Fairbanks. To Burk, it looked like a subarctic Eden, encompassing vegetable and flower gardens, greenhouses, goats, sheep, honeybees, a nature trail, and more. In non-pandemic summers, the property teems with local kids and aspiring farmers who converge on the terraced hillside for hands-on education.
Calypso reminded Burk, 38, who is Denaakk’e and Lower Tanana Athabascan from the villages of Nenana and Manley Hot Springs, of her family’s traditional fish camp in the Alaskan Interior, where she spent childhood summers. “I just felt like I was home,” Burk said. “[Calypso] really spoke to my heart.”
Eva Dawn Burk stands on the bank of the Tanana River in late April in her home village of Nenana, AK. Burk is a graduate student at the University of Alaska Fairbanks and is developing biomass-heated greenhouses for rural Native communities. Photo credit: Brian Adams / High Country News
When Burk was still young, though, her family drifted away from its traditions. As fish stocks dropped and the cost of living rose, they stopped going to fish camp. Burk studied engineering in college and, in 2007, found a stable job in the oil and gas industry at Arctic Slope Regional Corporation. But after she had a series of revelatory dreams — first of an oil spill, then of a visit from her departed grandmothers — and heard elders discussing threats to traditional food sources, Burk committed herself to advocating for tribal food sovereignty.
A few months after her first visit to Calypso, Burk became a graduate student at the University of Alaska Fairbanks, where she currently researches the link between health and traditional food practices. In 2020, Burk received the Indigenous Communities Fellowship from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology to develop a business model for implementing biomass-heated (or wood-fired) greenhouses in rural Native villages. The greenhouses will grow fresh produce year-round while also creating local jobs and mitigating wildfire risk.
The driveway leading to Calypso Farm in late April as the last of the winter’s snow melts. Photo credit: Brian Adams / High Country News
Now, Burk is partnering with Calypso to promote local food production and combat food insecurity in Alaska Native communities. The initiative involves building partnerships with tribes to teach local tribal members, particularly youth, about agriculture and traditional knowledge. The project is still in its infancy, but Burk hopes to help spur an agricultural revolution in rural Native villages, where food costs are exorbitant and fresh produce is hard to come by.
Alaska Native communities face numerous challenges to food security. Many communities are accessible only by boat or plane, and some lack grocery stores altogether. The residents of Rampart, a small Athabascan village on the Yukon River, have to order groceries from Fairbanks, delivered by plane at 49 cents per pound plus tax, or else travel there to shop — a $202 round-trip flight, a five-hour trip by boat and truck, or a four-and-a-half-hour drive overland. Sometimes orders are delayed due to weather, or because the delivery plane is full, said Brooke Woods, chair of the Yukon River Inter-Tribal Fish Commission, who is from Rampart. “You’re getting strawberries that are molded,” Woods said. “And you’re just throwing them away in front of an elder.”
Grocery store in Nenana, AK. Photo credit: Brian Adams / High Country News
Indigenous families that depend on traditional foods, such as salmon and moose, have to contend with rapidly shifting ecosystems and declining wild food sources, largely due, according to Indigenous leaders as well as several studies, to climate change. Perhaps the biggest food challenge is the dizzying system of joint wildlife management among Alaskan tribes and the state and federal governments. In 2020, the Inuit Circumpolar Council reported that Alaskan Inuit “recognized the lack of decision-making power and management authority to be the greatest threat to Inuit food security.” Last summer, during a pandemic-related food crisis, the Tlingit village of Kake had to get federal approval before tribal members could hunt on the land around their community, as High Country News reported.
“This is work that has to be done by us, by people in the community, not from the outside.”
Despite the clear and unique obstacles to food security for many families, a 2018 review in the International Journal of Circumpolar Health found that “studies that estimate the prevalence of food insecurity in remote Alaska Native communities … are virtually absent from the literature.” The limited and outdated data available indicates that about 19 percent of the Alaska Native population — 25 percent in rural areas — experiences food insecurity, compared to 10.5 percent of the total population nationwide, according to the USDA.
Burk is not the first to look to growing food locally as a solution. Over the last two decades, several Indigenous-led agricultural projects have emerged across Alaska. Burk’s vision, however, is particularly ambitious: In addition to building community gardens and year-round greenhouses, she wants to form a statewide network of Indigenous farmers.
Susan Willstrud, co-founder of Calypso Farm, waters seedlings in late April. Photo credit: Brian Adams / High Country News
In late April, Burk met with Deenaalee Hodgdon and Calypso Farm staff on a sunny deck at the farm, just yards from swarms of bees delivering pollen to their hungry hive. Hodgdon, 25, founder of On the Land Media, a podcast that centers Indigenous relationships with land, is collaborating with Burk and Calypso on the farmer training initiative.
Hodgdon, who is Deg Xit’an, Sugpiaq, and Yupik, worked at Calypso as a farmhand for a summer after sixth grade. Calypso provided them a new language for working with the land. At one point during the meeting, Hodgdon motioned toward the farmland and said, “This could literally feed a lot of our villages in Alaska.”
Burk’s first target is Nenana, her hometown, where she is working with the tribal office, Native corporation, and city government to implement a community-run biomass-heated greenhouse.
The biomass-heated greenhouse at the Tok school in Tok, Alaska. Photo credit: Brian Adams / High Country News
The project was inspired by a wood-fueled energy system and heated greenhouse built almost a decade ago in Tok, about a four-hour drive southeast of Nenana. Many Alaskan towns have productive gardens. The growing season lasts barely 100 days, however, and only a handful have year-round growing capacity. The Tok School came up with a clever solution: The facility is powered by a massive wood boiler and steam engine, and the excess heat is piped into the greenhouse. The school has a wide array of hydroponics.
Inside the greenhouse, you could easily forget you’re in Alaska. On a brisk day in late April, when the ground outside was brown and barren, dense green rows of tomato plants, lettuce, zucchini and other salad crops reached towards the 30-foot ceiling. During one week in April, when outside temperatures dropped below minus-30 degrees Fahrenheit, greenhouse manager Michele Flagen said she harvested 75 pounds of cucumbers that the students had helped plant. Altogether, the greenhouse provides fresh produce for the district’s more than 400 students.
Nenana is at least a year away from installing its biomass system, but Burk plans to begin planting a garden next spring if the greenhouse is not yet ready.
Jeri Knabe, administrative assistant at Nenana’s tribal office, loves Burk’s plan. “I can’t wait. I’m very excited,” she said. High food costs have long been a challenge for Nenana residents, she explained: “When I was growing up, we were lucky to get an orange.”
Eva Dawn Burk’s children play with a friend in the Tanana River in Nenana, AK in late April. Photo credit: Brian Adams / High Country News
Burk and Hodgdon hope to address Native food security statewide, and local community members like Knabe are central to their initiative. During their meeting at Calypso, Burk and Hodgdon emphasized that grassroots agriculture is more than a way to feed people; it’s also another step towards tribal sovereignty and self-management. “This is work that has to be done by us, by people in the community, not from the outside,” Hodgdon said.
In August 2021, the group will host its first training program for Alaska Native gardeners at Calypso. With so many greenhouses and gardens yet to be built, Burk’s latest dream has only just begun to grow.
Lead Photo: A student-led strawberry-growing project inside the greenhouse at the Tok School. The biomass-heated greenhouse grows enough produce to feed the district’s students year-round. Photo credit: High Country News
Harvesting Cherries At Night To Protecting Apples With Nets, Record Heat Takes Toll On Fruit Crop
Record-breaking heat that blasted the West over the weekend is also proving to be lethal to crops. Even with the heat breaking a bit on Monday, daily records were tied or broken over the weekend across California, Nevada and Arizona, with extreme heat also hitting Idaho and portions of the Pacific Northwest
By Tyne Morgan
July 12, 2021
Record-breaking heat that blasted the West over the weekend is also proving to be lethal to crops. Even with the heat breaking a bit on Monday, daily records were tied or broken over the weekend across California, Nevada and Arizona, with extreme heat also hitting Idaho and portions of the Pacific Northwest.
Much of the West and Southwest have been under a heat warning for more than a week, with more than 28 million Americans seeing triple-digit heat, including Arizona, Nevada, California’s Central Valley and even parts of Washington State. The relentless heat comes just more than a week after the Pacific Northwest saw a “thousand year” heat wave that killed hundreds.
The heat and extreme drought conditions are also fueling wildfires, as well as causing orchards and farm workers to change their schedules in order to beat the heat. That’s as the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) says last month was officially the hottest June on record.
Trying to Beat the Heat with Nighttime Harvest
According to Reuters, the hottest days last month forced farm laborers to start picking cherries at 1 a.m., earlier than the normal 4 a.m. start. According to Reuters, headlamps and roving spotlights were used to aid the workers in an earlier start time in order to beat the daytime heat that threatened the workers’ safety. The extreme heat also made the fruit too soft to harvest during the day.
Reuters reports Northwest Cherry Growers still expects to see an average-sized cherry harvest this year.
"We think we probably lost about 20% of the crop," B.J. Thurlby, president of the Northwest Cherry Growers, a grower-funded trade group representing top cherry producer Washington and other Western states, told Reuters.
As reported on "The Packer" earlier this month, the Northwest Cherry Growers said the heat will force some growers to abandon a portion of their crop due to the damage caused by the heat. The issue surrounds quality. The Northwest Cherry Growers says fruit exposed to such a prolonged period of intense heat wouldn’t meet the stringent standards upheld by the Northwest growers. Unfortunately, that means that a few growers lost some or all of their crop this season.
The hot weather taking a toll on the cherry crop comes as USDA's latest sweet cherry production forecast showed production higher than 2020, but down 6% from what producers saw in 2019. USDA says the later blooming varieties were well behind the rest of the crop, which is already leading to lower yields.
Shipping Concerns
Also according to "The Packer," with temperatures topping 105 degrees for several days from June 27-30 in Wenatchee, Wash., shipping was also impacted by the extreme heat. Shippers said the heat wave could reduce the crop volume some and hold back sizing temporarily but expressed confidence there will be plenty of high-quality Washington cherries for retailers to promote in July and into August. Some are even hydro cooling cherries and taking other steps to take the heat out of fruit and using advanced sorting technology to send only strong fruit to market.
Eyes on the Apple Crop
But it’s also adding uncertainty to what the Washington apple crop will produce this year. Apples are Washington’s most valuable crop, with an estimated revenue of $2 billion each year. Apple harvest is still six weeks away, but the heat has caused the apples to stop growing for now.
"We really don't know what the effects are. We just have to ride it out," Todd Fryhover, president of the Washington Apple Commission, told Reuters.
The Washington Apple Commission says growers are doing what they can to protect their fruit against sunburn. That includes using expansive nets and spraying water vapor above the trees.
USDA's meteorologist Brad Rippey expects the heat to continue in the West for the remainder of July. View his forecast here.
Lead Photo: Heat and extreme drought are causing orchards and farmworkers to change their schedule in order to beat the heat. NOAA says last month was officially the hottest June on record, as heat continues to blast the West.
LettUs Grow, GrowStack, Digital Farming & Farm Urban Collaborating To Deliver Four Social-Impact Vertical Farming Projects In Wales
Vertical farming, a way of growing crops indoors on stacked shelves, can be beneficial for people, plants and the planet. It allows growers to provide fresh, healthy produce to their local area 365 days of the year and can help to supplement outdoor growing
Source: LettUs Grow
07/12/21
Four major UK vertical farming companies, LettUs Grow, Digital Farming, Farm Urban and GrowStack, are collaborating to bring the benefits of controlled environment agriculture (CEA) to Welsh communities. This is one of the widest collaborations between leading CEA tech providers in the UK to date, with a focus on delivering vertical farms across different locations in Wales as part of a social impact and community-focused project called Crop Cycle.
Vertical farming, a way of growing crops indoors on stacked shelves, can be beneficial for people, plants and the planet. It allows growers to provide fresh, healthy produce to their local area 365 days of the year and can help to supplement outdoor growing. It diversifies our supply chains and boosts local food security. It also has a long stream of environmental benefits, such as using fewer resources including land or water, removing the use of chemical pesticides and reducing the need to transport food across seas. However, a common criticism of vertical farming is that it’s not always accessible or affordable to areas under-served by our food networks.
Crop Cycle is looking to bring the benefits of vertical farming directly to communities that could benefit most and is being funded by the Welsh Government through the Foundational Economy Challenge Fund. The project is being led by Social Farms and Gardens, supported by Welsh Government's NutriWales CEA Special Interest Group and BIC Innovation.
The project enables multiple different CEA systems to be tailored to fit different community settings, whilst also allowing them to be assessed in coordination across the pilot sites. This approach is unique, facilitating the testing of new socially focused business models, the engagement of the local communities and businesses with CEA and the development of new technical solutions. LettUs Grow, Digital Farming, GrowStack and Farm Urban are working together to share their specialisms and apply different technologies to where they are best suited within four sites in Wales, two of which are in the Valleys.
This project will introduce year-round food growing right into the heart of Welsh communities, where they’ll be connected to the particular dynamics of the local area. Activities will test new community-based engagement models, focusing on social well-being, local entrepreneurship and environmental impact. In this way, the project will be bringing together community, businesses and local public sector organisations.
Gary Mitchell, the Wales Manager for Social Farms and Gardens who is leading the project team stated, "we are excited to be running the pilot project across a diverse set of sites to gain insight and further knowledge into how new agricultural systems can successfully support communities in delivering local, fresh and nutritious foods as well as important social benefits in a sustainable manner."
Welcome To Our Woods
Welcome To Our Woods in Treherbert is nestled in the heart of the Rhondda Valleys, where LettUs Grow and GrowStack will be delivering an aeroponic and hydroponic vertical container farm. This proactive community group has been actively engaging with its communities through partnerships with the Green Valleys CIC and their joint ‘Skyline’ project. This partnership has led to several funding investments in the region, exploring community ownership of land and the benefits of allowing the community to utilise their surrounding natural green assets.
Chris Nelson, director of GrowStack said: “Growstack are delighted to be working alongside LettUs Grow and Digital Farming as part of this important social enterprise. It is always fantastic to be part of a project that champions vertical farming and really shares in the values of what this approach to food production can offer, including the benefits to the local community. Working in partnership with innovative farming companies is always a pleasure, as together we can combine our expertise to deliver outstanding results.”
Ian Thomas from Welcome To Our Woods said, “We are excited to be bringing such an innovative and progressive project to our local high street. We have already been engaging with the Upper Rhondda community to explore the projects that actively use our woodlands for the benefit of those they surround, and initiatives such as this help give local people an idea of what can be achieved."
Cultivate
Two linked sites will be in Newtown, one within the established community growing space attached to the Newtown Campus of the Neath Port Talbot College Group, and one within a new town centre ‘Circular Economy’ shop. The two CEA systems, provided by LettUs Grow and Digital Farming, are being integrated into an active college site and managed by a community group, with a cafe and kitchen, shop, deli and veg box scheme in place. The site is supported by Cultivate, which is a membership cooperative linking food and community. Cultivate aims to address many of the issues associated with the modern food system, and focus on creating sustainable local food solutions.
Charlie Guy, co-founder and CEO of LettUs Grow said this about the collaborations: “LettUs Grow is delighted to be working alongside these leaders of the UK vertical farming ecosystem and inspiring community projects. The UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) were implemented the same year as our foundation and have never been far from our minds. SDG 17 ‘Partnerships for the Goals’ rings especially true for us. We believe a brighter future can only be realised with inclusive partnerships and strong cooperation, built on shared values and a vision which places people and the planet at its epicentre.”
Greenmeadow Community Farm
Greenmeadow Community Farm in Cwmbran is being delivered by Digital Farming. It is one of only two ‘city farms’ in Wales and one which connects people to food and farming in a very public way. It is owned and operated by Torfaen County Borough Council, bringing with it a high-level partnership. The farm already welcomes thousands of visitors through its gates and connects locally through a number of schools and college partnerships – making it an ideal ‘showcase’ location for this pilot. Digital Farming were commissioned to deliver the Digital Farm in a container for pilot production of high nutrition greens and herbs. The system uses V-Farm patented growing systems linked to Digital Farming’s smart digital management system powered by solar PV.
Dr Gareth Jones, CEO of Digital Farming, said, “we were delighted to be awarded this project and have been enjoying working with the team at Social Farms and Gardens and Greenmeadow to bring together a new concept to explore the business of growing locally using controlled environment agriculture to enhance nutrition for communities.”
Xplore! Science Discovery Centre
The final site is in Xplore! Science Discovery Centre, situated in the centre of Wrexham: a brand new science centre that will support the promotion of urban agriculture in north Wales’ largest urban area. The vertical farming system is provided by Farm Urban. It will reach out to all generations, showcasing new technology and modern horticulture methods, blended with traditional growing experience. Xplore! welcomes public visitors, school groups and provides a range of educational workshops.
Paul Myers, Managing Director of Farm Urban said: “We are thrilled to be able to offer our hydroponic Edible Wall systems, Produce Pod aquaponic systems and learning programmes across all four sites involved in the Crop Cycle project. The team at Farm Urban have loved working alongside the four community organisations, they are all so enthusiastic and engaged which is exactly what we need for the social and environmental benefits of CEA to be shared across the UK and beyond. It has been a privilege to work alongside industry leaders GrowStack, LettUs Grow and Digital Farming learning more about their systems and approach. One of the many highlights of this project has been the openness and willingness to share and collaborate between all partners which is so important to drive the industry forward.”
To follow the progress of the community grow sites, you can follow Crop Cycle on social media, and technology providers LettUs Grow, Digital Farming, GrowStack and Farm Urban.
Tags: Indoor & Vertical Farming, Processing & Supply Chain | AgTech
Growfoam Welcomes New Chief Financial Officer
Growfoam, world leader in biodegradable foams for controlled environment agriculture, announced today that drs. Janet Koolman RA, a seasoned financial expert, has joined the company’s executive team as Chief Financial Officer.
July 1, 2021
Growfoam, the world leader in biodegradable foams for controlled environment agriculture, announced today that Drs. Janet Koolman RA, a seasoned financial expert, has joined the company’s executive team as Chief Financial Officer.
Koolman brings over 20 years of experience in management, accounting, and controlling. Before joining Growfoam, she worked in various roles at the Dutch Accell Group, most recently as Senior Holding Controller. Accell Group is a publicly owned company with a position on the EURONEXT Amsterdam Stock Market and is the European market leader in e-bikes. Their portfolio includes brands such as Koga, Raleigh, and Batavus. Koolman’s impact on the mobility sector is not to be underestimated. During her career at Accell, the company grew from a European player to a multinational with branches all over the world. Koolman and her team were instrumental in initiating the immense professionalization and growth of the Accell finance department.
“Koolman’s impressive background and career make her a great fit for her new role at Growfoam,” said Growfoam CEO Martin Tietema. “As well as her financial management expertise, she shares our mission and vision of making the world better for future generations, and enabling reliable and safe food production.”
Koolman’s hire follows Growfoam’s strong growth perspective since its market introduction at Greentech 2019. The company’s growth is fuelled by a financial injection from venture capitalists SHIFT Invest and Future Food Fund, alongside a global portfolio of CEA clients that has rapidly expanded over the last few months.
“I am excited to join the executive team at Growfoam,” said Koolman. “I am impressed by the team’s commitment to positively impacting the world by enabling their clients to grow greener, safer and faster, which is a core priority of the company. The time for making a big impact on food safety and quality is now. I am determined to contribute to that and, in my field of expertise, the difference between making an impact in mobility or food production is not as big as one might think. And I still commute to work by bike. Old habits die hard.”
Koolman’s hire is effective starting July 1st.
Farmers Already Forced To Abandon Crops As Additional Water Restrictions Loom
Bringing into focus some of the California crop losses caused by the 2021 drought, Western Growers has released a series of videos called “No Water = No Crops”
By Tom Karst
July 12, 2021
Bringing into focus some of the California crop losses caused by the 2021 drought, Western Growers has released a series of videos called “No Water = No Crops.”
The videos feature three California farmers who talk about the losses they are suffering this year.
“This is one of the most difficult decisions I’ve had to make in a long time,” Joe Del Bosque of Del Bosque Farms, Firebaugh, Calif., who sacrificed his asparagus field that still had five years’ productivity left, said in one video. “Seventy people are going to lose their jobs here. Next year, there will be no harvest here. Those 70 people lose two months of work. It’s a very difficult hit for them.”
Another video features Ross Franson of Fresno, Calif.-based Woolf Farming.
“Around this time of year, we’d normally be prepping for harvest,” Franson said in the video.
The farm has started knocking down almond trees in its 400-acre orchard, he said.
“But due to the dire drought that’s going on in the state of California right now, we made the decision to pull these trees out simply because we didn’t have the water to irrigate them.”
“These trees are all dead, and they shouldn’t be,” Jared Plumlee of Booth Ranches said in one video. The company produces citrus in Orange Cove, Calif., and destroyed 70 acres of trees because of the drought.
“It’s just a shame. This block had probably 20 years of productive life, and we were forced to push it out.”
Western Growers president and CEO Dave Puglia said in a news release that the future of agriculture in California is being compromised by the regulatory uncertainty of water deliveries to farms.
“Is that really what you want? Do you want a bunch of dust blowing through the center of the state interrupted by fields of solar panels, which don’t employ many people?” Puglia said in the release.
“It is a question that needs to be posed to Californians, generally, and their political leaders. Is that what you want? Because that is the path you are on.”
Lead Photo: Joe Del Bosque of Del Bosque Farms, Firebaugh, Calif. points to a melon field that was plowed under because of the drought.
Netled Signs €15 Million Contract With Oh My Greens To Deliver Vera Vertical Farm To Sweden
Netled and Oh My Greens (OMG) have signed a contract for a three-year investment programme that will see Netled deliver its Vera vertical farm to OMG, a Swedish supplier of potted herbs
July 13, 2021
Netled has signed a contract worth €15 million with Swedish herbs supplier, Oh My Greens.
Netled and Oh My Greens (OMG) have signed a contract for a three-year investment program that will see Netled deliver its Vera vertical farm to OMG, a Swedish supplier of potted herbs. The contract was signed in June 2021 and is worth a total of 15 million euros over three years. The contract also includes a five-year maintenance and cultivation consultancy service, and is estimated to be one of the largest turn-key technology deals specifically between the technology providers and farm operators in the indoor agriculture market to date.
The first delivery for the project is underway and is valued at 3.2 million euros; it is due in Q2 of 2022. After commissioning, Netled will continue to provide technical and consultancy services while OMG will focus on producing and supplying vegetables to retailers in Stockholm. The second phase of the investment plan is due to start in Q4/2022.
OMG is a farm operator company providing consumers with potted herbs and has ambitions to achieve a major market share in Sweden by the end of the investment program.
OMG is part of Applied Value Group, a Swedish-American investment, management consultancy, and social impact firm. OMG operates in Sweden together with its sister company, Bake My Day (BMD). BMD is a 25 million USD revenue company serving 800 customers with daily deliveries including around 400 grocery stores. Working together, BMD and OMG can offer a wide range of the highest quality fresh food products to retail throughout Stockholm and the Mälardalen region, covering 40% of the Swedish population.
“We considered 17 different vertical farming technology providers and came to the conclusion that, in terms of its technology, know-how, and delivery capabilities, Netled is years ahead of the competition,” says CEO of OMG, Moses Isik.
“Netled’s technical and horticultural knowledge, and decades of experience of growing technologies, combined with OMG’s superb logistic network and existing customer relationships, creates an unbeatable competitive advantage which will allow us to quickly increase our market share and supersede traditional herb production with sustainable and ecological vertical farming that will disrupt the existing supply structures.” he continues.
“Netled’s Vera vertical farming technology will allow us to provide customers throughout Sweden with fresher herbs and leafy greens, grown hyper-locally and with a significantly reduced carbon footprint”, Moses adds. “Not only does the customer benefit, but the planet does too!”
Netled Ltd. is the leading vertical farming technology provider in Finland. Netled’s Vera technology offers turn-key indoor farming systems which include a dynamic spacing system, LED lighting, HVAC, and a nutrition system. It also includes automation software, production management and horticulture intelligence software. The Vera family of growing systems range from the Instore growing cabinets to massive-scale Industrial systems.
“The cooperation with OMG and its sister company, BMD, creates a huge opportunity for Netled to increase its market presence in Sweden. It also solidifies our position as the global leader in vertical farming technology,” says CEO of Netled, Niko Kivioja. This contract is the first industrial-scale operation for Netled, which was previously focused on an urban farm scale.
“This contract not only allows OMG to produce fantastic products for customers throughout the whole of Sweden, but it also functions as a clear example to other farm operators of the industrial-scale applications and opportunities our Vera vertical farming technology is capable of.” Kivioja continues.
“Netled is now the premier provider of vertical farming technology globally and we intend to keep it that way.” he concludes.
More information:
Niko Kivioja
CEO, Netled Ltd.
+358 50 360 8121
Moses Isik
CEO, Applied Industries Holding AB
+46 704 269 267
Robert Brooks
Investor Relations & Communications Manager
+358 50 484 0003