Welcome to iGrow News, Your Source for the World of Indoor Vertical Farming
Singapore To Host Major Multi Stakeholder Virtual Event On Food Security & Sustainability In Partnership With UNDP & APEC
To address the potential impact to the global food system from the twin effects of the Covid-19 pandemic and climate change, government officials and top-level executives from the Asia Pacific region will be attending the Global Food Security & Sustainability Virtual Summit 2021 on 26 August 2021
12 August 2021, Singapore – To address the potential impact to the global food system from the twin effects of the Covid-19 pandemic and climate change, government officials and top-level executives from the Asia Pacific region will be attending the Global Food Security & Sustainability Virtual Summit 2021 on 17 September 2021.
Singapore’s Minister for Sustainability and the Environment, Ms. Grace Fu will be delivering the opening address for the event. Providing the keynote address will be A/Prof Matthew Tan, the co-chair for Sustainable Development in Agriculture & Fishery Sectors for APEC Policy Partnership on Food Security on the topic: Global Food Security – The Next Frontier In The Agriculture And Aquaculture Industry.
Organized by The Pinnacle Group International, a leading conference organizer headquartered in Singapore, the event is formed in partnership with UNDP and APEC with the support of multi agencies and NGOs around the world. This event is positioned as the Pan Asian multi-agency and private sector event to facilitate policy, business, and technological exchanges amongst key stakeholders in the global food community.
The event is expected to feature 35 influential speakers who will cover a wide range of topics including macro and regulatory issues, food technology, food waste, financing, food security & sustainability, cold chain & logistics, and nutrition. The event agenda, set against the conference theme “Towards A Future Safe Global Food System” will be developed in consultation with members of the summit’s board of advisors.
The appointed board of advisors are:
- A/Prof Matthew Tan – Co-Chair for Sustainable Development in Agriculture & Fishery Sectors - APEC Policy Partnership on Food Security/CEO Asia, Assentoft Aqua Asia
- Professor William Chen - The Michael Fam Chair Professor and Director of NTU Food Science and Technology Co-Director, Future Ready Food Safety Hub @ NTU, Consultant, Asian Development Bank
- Mr. Lim Hui Jie - CEO, VisionTech Pte Ltd
- Mr. Eugene Wang - Co-Founder & CEO, Sophie’s BioNutrients Pte Ltd
(Singapore)
- Mr. Rohit Behl - Interim CEO of EntomoVentures Pte. Ltd & Business
Development Lead of Cellivate Technologies Pte Ltd
- Mr. Wee-Meng Thoo - Partner and Head Of Investments, Digital and
Sustainability, Leonie Hill Capital
- Mr. Richard Hayler, CFO of Nutrition Technologies
- Mr. Robert (Bob) Nichol, Director Asia Pacific, Innovad Asia Pacific Pte. Ltd
- Mr. John Friedman, Executive Director, AgFunder Asia & GROW Accelerator
- Mr. Nick Hazell, CEO & Founder, v2food
- Ms. Mirte Gosker, Acting Managing Director, The Good Food Institute Asia
Pacific
- Mr. Christoph Langwallner, Initiator of Nutritional Paradox & CEO and Co-
Founder of WhatIF Foods
- Mr. John Cheng, Founder, and Managing Director Innovate 360
- Mr. Niels Arbjerg, Regional President of the Asia Pacific Region, Danfoss
- Mr. Tan Ernest, Head of Agribusiness & Animal Protein of United Overseas
Bank Limited (UOB)’s Sector Solutions Group – Consumer Goods Group
Wholesale Banking Division
- Dr. Ling Ka Yi, CTO & Co-Founder, Shiok Meats
- Mr. Saurabh Bajaj, CEO, Eat JUST Asia
- Mr. Yuki Hanyu, Founder & CEO at Integriculture Inc
- Ms. Elizabeth Hernandez, Head of External Affairs and Sustainability, Asia
Pacific, Corteva Agriscience
- Mr. Steve Rhodes, Chairman & CEO of Trendlines Investments Group
- Ms. Nathalie Lung, Program Manager for the Food Technology Accelerator
Programs, Brinc
- Ms. Rebecca Vaught, Founder, Van Heron Labs
- Mr. William Koo, Managing Director, Temasek Life Sciences Accelerator
(‘TLA’)
- Dr. Andrew Powell, CEO, Asia BioBusiness
- Mr. Puis Chong, Managing Director, Mergers, Acquisitions & Divestitures,
Deloitte Financial Advisory SEA
- Mr. Dominique Kull, Co-Founder, and CEO, SGProtein
The current confirmed prestigious panel of speakers are:
- Ms. Grace Fu, Minister for Sustainability and The Environment - Republic of Singapore
- A/Prof Matthew Tan, Co-Chair for Sustainable Development in Agriculture & Fishery Sectors - APEC Policy Partnership on Food Security/ CEO Asia, Assentoft Aqua Asia
- Mr. Riad Meddeb, Director ad-interim of UNDP Global Centre for Technology, Innovation and Sustainable Development(GC-TISD)
- Mr. Eric Paillard, Managing Director, Adisseo Asia Pacific
- Ms. Cecilia Ku, General Manager, Delta Electronics International Singapore
- Mr. Torben Funder-Kristensen, Head of Public and Industry Affairs, Danfoss
Climate Segment, Danfoss A/S (Denmark)
- Dr. Sun Hui, Chief Engineer of the Academy of the National Food and Strategic
Reserves Administration of China
- Ms. Mirte Gosker, Acting Managing Director, The Good Food Institute Asia
Pacific
- Mr. Nick Hazell, CEO & Founder, v2food
- Mr. Tan Ernest, Head of Agribusiness & Animal Protein of United Overseas
Bank Limited (UOB)’s Sector Solutions Group – Consumer Goods Group
Wholesale Banking Division
- Mr. Christoph Langwallner, Initiator of Nutritional Paradox & CEO and Co-
Founder of WhatIF Foods
- Dr. Viknish Krishnan-Kutty, Founder & CEO of Cellivate Technologies
- Mr. Eugene Wang, Co-Founder & CEO, Sophie’s BioNutrients Pte Ltd
(Singapore)
- Mr. John Friedman, Executive Director, AgFunder and GROW Accelerator
- Mr. Robert (Bob) Nichol, Business Director - Asia Pacific, Innovad Asia Pacific
Pte. Ltd
- Mr. Richard Hayler, CFO of Nutrition Technologies
- Mr. Rohit Behl, Interim CEO of EntomoVentures Pte. Ltd & Business
Development Lead of Cellivate Technologies Pte Ltd
- Mr. Will Cowling, Marketing Manager, FMCG Gurus
- Mr. Wee Meng Thoo, Partner and Head Of Investments, Digital and
Sustainability, Leonie Hill Capital
- Mr. Smith Taweelerdniti, CEO, Let’s Plant Meat – Managing Director, Nithi
Foods Co. Ltd, Innovator & Entrepreneur
- Mr. Jean Pasternak, Strategy Director, Nasekomo
- Dr. Emily Chang, Professor, Department of Agriculture Economics, National
Taiwan University
- Mr. Travin Singh, Founder & CEO, Crust Group
- Mr. Jean-Yves Chow, Agri-Food Sector Coverage Lead, Senior Vice-
President, Asia & Oceania Corporate Banking Department, Sector Coverage
Team, Mizuho Bank
- Mr. William Koo, Managing Director, Temasek Life Sciences Accelerator
(‘TLA’)
Supporting Organisation(s):
The organizers are expecting 700 participants to attend the online event. Global Food Security & Sustainability Virtual Summit 2021 is supported by the following sponsors:
For more information on the event, please visit:
https://pinnaclegroup.global/gfsss/ About
The Pinnacle Group International
The Pinnacle Group International - CDMC is a leader in the conference industry in Asia, designing and launching its own brand of conferences and events. The Pinnacle Group is headquartered in Singapore with supporting regional offices in Shanghai and Philippines. The Company’s renowned brands of conferences and events cover a wide spectrum of industries including finance, energy, education, aviation, food security and sustainability and real estate.
VIDEO: California Farmers Leave Fields Fallow As Drought Grows More Dire In West
Northern California reservoirs contain only half the water they normally do in late spring.
Both the State Water Project and the federal Central Valley Project have announced they intend to deliver only 5% of requested supplies this year
By TYNE MORGAN May 28, 2021
As rains drop needed moisture for areas of the country dealing with drought and in need of relief, the situation is growing more dire in the West.
The latest U.S. Drought Monitor shows improvement in the Plains, especially in the Southern Plains. Heavy rains also falling across western portions of the High Plains this week, lessening the drought conditions in the western Dakotas. Those moisture improvements also pilling over into western Nebraska and Kansas.
The drought has become a mainstay in California. The Drought Monitor released Thursday shows exceptional drought growing, including Kern County, one of the top ranked counties for ag production in the nation.
Northern California reservoirs contain only half the water they normally do in late spring.
Both the State Water Project and the federal Central Valley Project have announced they intend to deliver only 5% of requested supplies this year.
As California farmers rely on Mother Nature and ground water this year, one farmer says it won't be enough to even grow a crop, with some farmers choosing to not plant at all. Some producers are even pulling out trees.
"There are land areas out here that are going to get one acre foot of water from the ground. That's what they're allocated," says Tyler Ribeiro, a dairy farmer in Tulare, California. "Good luck growing cactus on one acre foot. You're not going to be able to feed with that you can't grow trees out there. And we align with a lot of these tree guys in a sense of we feed their byproduct, I need those all almond hulls, I need those orange peels. I need a lot of those things. That's how we stay efficient [as a day farmer]."
USDA meteorologists telling AgDay there's not much relief in sight for California and the West. Forecasters expect the drought west of the Rockies to only get worse.
AppHarvest Expands Support of Kentucky Food Banks
Together with our friends and neighbors in Central Appalachia, our goal is to build a more resilient food system and one that helps those in need. In Kentucky alone, 20% of children and nearly 15% of adults experience food insecurity
U.S. Rep. Andy Barr, Ky. Commissioner
of Agriculture
Ryan Quarles Join in The Celebration
Together with our friends and neighbors in Central Appalachia, our goal is to build a more resilient food system and one that helps those in need. In Kentucky alone, 20% of children and nearly 15% of adults experience food insecurity.[1]
We’re partnering with community organizations to address these needs and this week expanded our work with God’s Pantry Food Bank, which along with more than 400 distribution partners provides food to residents of 50 counties in Eastern and Central Kentucky. In its most recent fiscal year, the organization distributed nearly 14 million pounds of fresh fruits and veggies and more than 41 million pounds of food overall.
U.S. Rep. Andy Barr and Kentucky Commissioner of Agriculture Ryan Quarles joined AppHarvest Founder & CEO Jonathan Webb and God’s Pantry Food Bank CEO Michael Halligan this week in celebrating the expanded collaboration.
“God’s Pantry Food Bank is thrilled to work more closely with AppHarvest, as we nourish lives through sustainable agriculture,” said Halligan.
Added Commissioner Quarles: “Partnerships like these are important during the pandemic as all parts of our agricultural sector come together to help those in need. God’s Pantry Food Bank has been working overtime to support Kentuckians who have fallen on tough times, and I appreciate AppHarvest stepping up to the plate to provide fresh, Kentucky-grown products to support them in their mission to feed all Kentuckians."
The expanded collaboration builds on work in recent months by AppHarvest, along with more than a dozen Kentucky organizations, to provide aid after Kentucky’s ongoing historic levels of rainfall caused rising waters across many Appalachian counties. The Appalachia Rises initiative raised more than $1.2 million for flood relief and saw volunteers from AppHarvest and God’s Pantry Food Bank distribute healthy food to those affected.
“This is a great partnership that recognizes the needs in our communities and brings together organizations dedicated to serving Kentuckians,” said Rep. Barr. “In Congress, I voted for multiple bipartisan COVID-19 relief packages to boost our food supply by providing support to farmers, agribusinesses, and food banks around the country.”
Added Webb: “As a public benefit corporation and Certified B Corp, we at AppHarvest believe in good and are inspired daily by the faith and grit of those who’ve chosen to share their talents with us and join our mission. We’re working to create America’s AgTech capital here in Appalachia to provide affordable, nutritious, and delicious fruits and veggies that will help reduce hunger and food deserts.”
Forward-Looking Statements
Certain statements included in this press release that are not historical facts are forward-looking statements for purposes of the safe harbor provisions under the United States Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Forward-looking statements generally are accompanied by words such as “believe,” “may,” “will,” “estimate,” “continue,” “anticipate,” “intend,” “expect,” “should,” “would,” “plan,” “predict,” “potential,” “seem,” “seek,” “future,” “outlook,” and similar expressions that predict or indicate future events or trends or that are not statements of historical matters. All statements, other than statements of present or historical fact included in this press release, regarding AppHarvest’s future financial performance, as well as AppHarvest’s growth plans and strategy, ability to capitalize on commercial opportunities, future operations, estimated financial position, estimated adjusted EBITDA, revenues and losses, projected costs, prospects, plans and objectives of management are forward-looking statements. These statements are based on various assumptions, whether or not identified in this press release, and on the current expectations of AppHarvest’s management and are not predictions of actual performance. These forward-looking statements are provided for illustrative purposes only and are not intended to serve as, and must not be relied on as, a guarantee, an assurance, a prediction, or a definitive statement of fact or probability. Actual events and circumstances are difficult or impossible to predict and will differ from assumptions. Many actual events and circumstances are beyond the control of AppHarvest. These forward-looking statements are subject to a number of risks and uncertainties, including those discussed in the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (No. 333-252964) filed with the SEC by AppHarvest on February 10, 2021 under the heading “Risk Factors,” and other documents AppHarvest has filed, or that AppHarvest will file, with the SEC. If any of these risks materialize or our assumptions prove incorrect, actual results could differ materially from the results implied by these forward-looking statements. In addition, forward-looking statements reflect AppHarvest’s expectations, plans, or forecasts of future events and views as of the date of this press release. AppHarvest anticipates that subsequent events and developments will cause its assessments to change. However, while AppHarvest may elect to update these forward-looking statements at some point in the future, AppHarvest specifically disclaims any obligation to do so. These forward-looking statements should not be relied upon as representing AppHarvest’s assessments of any date subsequent to the date of this press release. Accordingly, undue reliance should not be placed upon the forward-looking statements.
[1] Feeding America
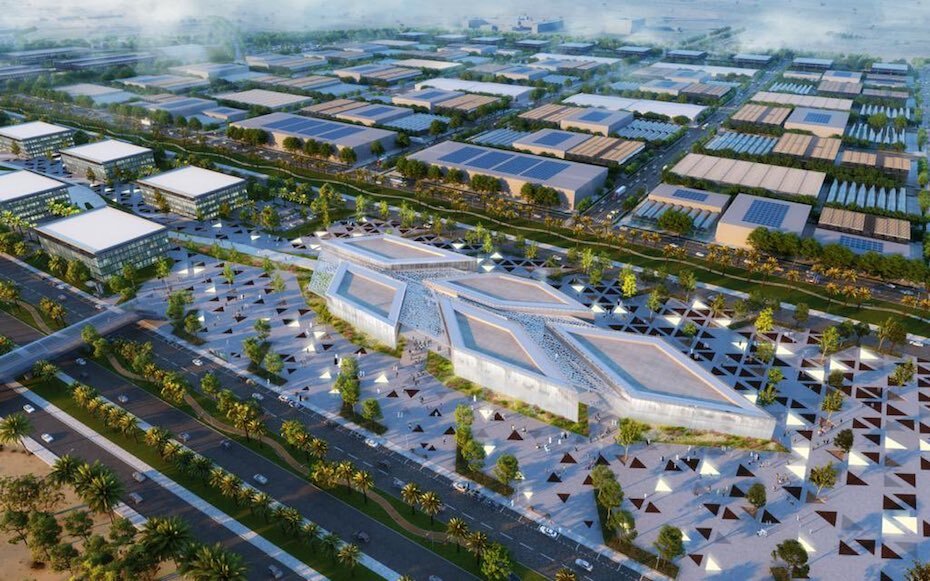
Sheikh Mohammed Launches Food Tech Valley In Dubai
It seeks to triple the UAE’s food production and will include a smart food logistics hub, R&D facilities as well as agricultural technology and engineering labs
It seeks to triple the UAE’s food production and will include a smart food logistics hub, R&D facilities as well as agricultural technology and engineering labs
MAY 2, 2021
The first phase of a new initiative that seeks to triple the UAE’s food production has been launched in Dubai.
The Food Tech Valley was launched on Saturday, May 1, by Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum, Vice President and Prime Minister of UAE and Ruler of Dubai, and is a partnership between the Ministry of Food and Water Security and Wasl Properties to explore urban planning of future smart and food independent cities.
The initiative that aims at helping the UAE meet its National Food Security Strategy 2051 targets, will – in the initial phase of its launch – focus on strategic projects to achieve food self-sufficiency while ensuring sustainability and conservation of resources, said Mariam Almheiri, Minister of State for Food and Water Security.
The Food Tech Valley will be home to four main clusters: agricultural technology and engineering, a food innovation centre, R&D facilities, and an advanced smart food logistics hub.
The agricultural technology and engineering cluster will have a vertical farm that will employ the latest food technologies to grow year-round vital crops, noted a statement issued by Sheikh Mohammed regarding the initiative. The cluster will also focus on developing innovative projects in bioengineering, automation, robotics and artificial intelligence and supporting capacity building across the food ecosystem.
The food innovation centre meanwhile will provide an integrated agri-business ecosystem to incubate promising ideas and support startups and entrepreneurs. The cluster, which will have a specialised food factory to produce new foods and second-generation restaurants (restaurants 2.0), will explore models that are based on sustainability and production sufficiency to reduce consumption and wastage of resources.
The third cluster will have world-class R&D facilities to train food specialists and support food establishments. The facilities will explore the use of agri-robotics to maximise yields and drought-resistant crops. Specialised researchers will also explore the application of 3D printing in algae cultivation and alternative protein production. The R&D facilities will also study the use of AI to monitor, analyse and manage agricultural crops, and detect environmental impact and climate change.
It will complement global food security research efforts by exploring successful saline agriculture, nutritional genomics, agricultural mechanisation and the use of drones in food production.
The fourth cluster will feature a fourth-generation food storage system that provides smart and automated logistical storage services. The smart storage system will apply blockchain technologies and big data in sorting, transporting and distributing various food products. It will track food quality, origin, components, processing methods, storage and delivery to ensure the efficiency of food supply chains.
The initiative aims to create an integrated modern city where over 300 varieties of crops will be produced using modern farming techniques and which will serve as a hub for future clean tech-based food and agricultural products and an incubator for researchers, entrepreneurs, startups and industry experts to develop solutions to address issued regarding food production.
It will support the use of technologies and applied research in food processing and agriculture and apply modern farming techniques – such as vertical farming, aquaculture and hydroponics – to accelerate self-sufficiency in fresh food produce and reduce wastage of resources.
“[The Food Tech Valley project] will be an economic zone, which is particularly significant considering that the size of the AgTech market is projected to grow from $13.5bn to $22bn over the next four years. The project is part of our efforts to achieve our strategic national goals with respect to food security, as it constitutes an incubator for advanced farms – including indoor and vertical farms – with more than 60 per cent of the project’s space allocated to these activities,” said Mariam Almheiri.
Read: Sheikh Mohammed reiterates UAE’s drive to enhance food and water security
“The project features a food innovation centre that has been designed to resemble a head of wheat and will incorporate laboratories, research centres and prototype agricultural systems. Strategically located close to universities and academic institutions, it will support the R&D ecosystem and explore and deliver sustainable solutions around food,” added Almheiri.
Hesham Abdullah Al Qassim, CEO of Wasl Asset Management Group, noted: “The project provides an integrated legislative framework that facilitates new food product development and access to the market. Its competitive incentives and services enable investors to utilise local and global demand for the UAE brand and leverage Dubai’s global commercial and trade networks to achieve the desired growth.”
According to the Ministry of Climate Change and Environment’s 2019 figures, the UAE has more than 177 advanced farms that use modern agricultural technologies and hydroponics, and over 100 entities that implement organic farming across the UAE. These facilitate the growth of locally sourced produce all year-round and reduce reliance on seasonal farming. The country currently hosts over 500 specialised food processing companies that supply to local markets and export globally.
As an economic zone, the Food Tech Valley is a valuable addition to the UAE’s 1,250 legislations that support agriculture and food production sectors in ensuring food safety, storage and transport. With food and beverage investments in the UAE currently totalling Dhs62bn, the initiative is expected to contribute to attracting further local and foreign direct investments within the field.
DUBAI FOOD FOOD TECH VALLEY MINISTRY OF FOOD AND WATER SECURITY SHEIKH MOHAMMED BIN RASHID AL MAKTOUM UAE WASL PROPERTIES
Vertical Farming Startup Oishii Raises $50m In Series A Funding
“We aim to be the largest strawberry producer in the world, and this capital allows us to bring the best-tasting, healthiest berry to everyone.”
By Sian Yates
03/11/2021
Oishii, a vertical farming startup based in New Jersey, has raised $50 million during a Series A funding round led by Sparx Group’s Mirai Creation Fund II.
The funds will enable Oishii to open vertical strawberry farms in new markets, expand its flagship farm outside of Manhattan, and accelerate its investment in R&D.
“Our mission is to change the way we grow food. We set out to deliver exceptionally delicious and sustainable produce,” said Oishii CEO Hiroki Koga. “We started with the strawberry – a fruit that routinely tops the dirty dozen of most pesticide-riddled crops – as it has long been considered the ‘holy grail’ of vertical farming.”
“We aim to be the largest strawberry producer in the world, and this capital allows us to bring the best-tasting, healthiest berry to everyone. From there, we’ll quickly expand into new fruits and produce,” he added.
Oishii is already known for its innovative farming techniques that have enabled the company to “perfect the strawberry,” while its proprietary and first-of-its-kind pollination method is conducted naturally with bees.
The company’s vertical farms feature zero pesticides and produce ripe fruit all year round, using less water and land than traditional agricultural methods.
“Oishii is the farm of the future,” said Sparx Group president and Group CEO Shuhei Abe. “The cultivation and pollination techniques the company has developed set them well apart from the industry, positioning Oishii to quickly revolutionise agriculture as we know it.”
The company has raised a total of $55 million since its founding in 2016.
Securing Food Supply For The Long Term
While officially classified by the United Nations as ‘food secure’, its arid climate and widespread desert conditions, mean that the GCC is heavily dependent on food imports to meet local demand. In the UAE for instance, nearly 90 percent of demand is met through imports.
The region’s dependence on imports is a significant food security risk to the region. The Covid-19 pandemic has further exposed the vulnerabilities of the global food supply chain, making it clear that any long-term disruptions to global food networks could have catastrophic consequences.
Investing in food security
Even before Covid-19, the region’s food industry was undergoing radical transformation as governments implemented new strategies in response to population growth and climate change, while producers were reacting to rapidly changing consumer behavior, and the need for greater efficiency and sustainability.
To counter the effects of the region’s arid climate, the UAE, along with other governments in the region, has invested in cutting-edge food production and distribution techniques such as hydroponics and vertical farming, smart irrigation, and aquaponics. And it is clear that advanced technologies such as robotics and AI offer exciting new opportunities for the food F&B sector.
Building food security
Countries that have steadily worked towards strengthening their internal production capabilities and logistics networks over recent years find themselves much better placed to ride out the crisis. This is evidenced by the relative ease with which GCC governments were able to manage food demand during the pandemic.
Securing Supply, the latest briefing paper produced by MEED in partnership with Dubai-based Mashreq Bank, discusses the food security strategies underway in the GCC and Egypt, including the shifting focus on self-sufficiency in sectors such as fisheries, dairy, and poultry; enhancing in-country reserves; and growing investments in agricultural technology.
Download the paper here.
29 Mar 2021
Hydroponics Startup Babylon Micro-Farms Raises $3m Seed Capital For US Expansion
Babylon will use the capital to fund its nationwide expansion. It offers a cloud-based, plug-and-play hydroponics system for indoor farming operations
March 18, 2021
US indoor agriculture startup Babylon Micro-Farms has closed a $3 million seed round led by previous investors including the Center for Innovative Technology (CIT).
New investors to take part in the fundraising included Hull Street Capital, VentureSouth, and CAV Angels – the University of Virginia‘s alumni angel investor group.
Babylon will use the capital to fund its nationwide expansion. It offers a cloud-based, plug-and-play hydroponics system for indoor farming operations.
The Richmond, Virginia-based startup claims that its 15 square-foot miniature farm can grow as much produce as 2,000 square-feet of outdoor cropland.
In January 2020, Babylon raised its initial seed investment of $2.3 million led by CIT’s early-stage investment group CIT GAP Funds and startup incubator Plug and Play Ventures.
Invest with Impact. Click here.
“2021 is on track to be a year of accelerating growth and major market penetration through national distribution as we continue to focus on deploying our indoor farming service,” Babylon CEO Alexander Olesen said in a statement.
“We’re enabling businesses and communities to grow their own fresh produce and demonstrating the benefits of our fleet of remotely managed vertical farms.”
Indoor farming startups have been bagging fundings left, right, and center of late. Babylon Micro-Farms is just one of the latest outfits to capture investors’ attention, along with the likes of New York’s Oishii, Germany’s Infarm, and recently SPACced Kentuckian player AppHarvest.
What makes Babylon unique — in its own estimation — is its “remotely managed,” easy-to-use growing platform. The technology could give aspiring or existing indoor growers a quick way to get into the game instead of building a new growing system from scratch, or having to learn the ropes through old-school, analog means, the startup suggests.
Babylon Micro-Farms’ machinery can squeeze into relatively smaller spaces compared to many other indoor ag solutions on the market. This may give users a foothold over larger operations by allowing them to enter the fray more quickly while bigger players are still shopping for real estate.
Through a two-year lease contract, Babylon users can dabble in the indoor farming craze without having to commit to a more long-term operation. This can also give flexibility when it comes to testing new markets.
“The Covid-19 pandemic highlighted a national food-supply system issue, putting the spotlight on a critical need for more locally-grown produce options. Babylon Micro-Farms has found their focus, and it is a reflection of their leadership team’s commitment to building a category-defining customer experience while making a positive impact,” Alex Euler, investment director at CIT GAP Funds, said in a statement.
“During a time when many people are experiencing isolation, being able to watch your own garden grow can improve one’s quality of life. The company’s innovative approach to developing a technology system that enables its own staff to remotely control the light, water, and nutrients for its farming systems is absolutely making them a leader in this space.
Improved Product Consistency
Introducing Travaglini FarmTech, a new business division that has been established by Travaglini S.p.a., the world leader in meat, cheese, and fish processing equipment. Travaglini FarmTech will deliver turnkey vertical farm solutions to food processors to help them improve product consistency and simplify their supply chain dynamics
12-03-2021 Philips Lighting
ITALY, Milan- Introducing Travaglini FarmTech, a new business division that has been established by Travaglini S.p.a., the world leader in meat, cheese, and fish processing equipment. Travaglini FarmTech will deliver turnkey vertical farm solutions to food processors to help them improve product consistency and simplify their supply chain dynamics.
“With vertical farming
we can grow and process consistent, high-quality produce in one location that can be close to retailers and consumers. We have full control over the entire process.”
- Luca Travaglini, leader Travaglini FarmTech
The challenge
Travaglini S.p.a. builds on 68 years of expertise in developing extremely accurate climate control, industrial automation, processing, and packaging equipment. The company is partnering with Philips Lighting, the world leader in lighting, to establish Italy’s first vertical farm research lab in Milan. This facility will be used to develop a state-of-the-art model for vertical farming growth strategies and technologies. The Italian vertical farm research lab will focus primarily on the production of leafy greens.
The right lighting
Vertical farming is a reply to the environmental problem that exists today in horticulture – how to provide fresh food to urban environments in a way that’s efficient and sustainable. “With vertical farming we are looking to answer many of the questions that the food industry is facing today and that will only become clearer and more pressing in the coming years,” said Travaglini. We can grow and process consistent, high-quality produce in one location in a vertical farm that can be close to retailers and consumers. Plus, we can fully control the entire supply chain, from seed to packaging.”
Luca Travaglini, leader of Travaglini FarmTech division said, “We chose to work with Philips Lighting because they have the strongest expertise in this field, and we trust them to help us expand our skillset and knowledge base over the long-term.
Photos Courtesy of Philips Lighting
Click here for more information.
US-VIRGINIA: Arlington’s Only Commercial Farm To Expand, Double Production
Virginia Gov. Ralph Northam announced this afternoon that Fresh Impact Farms will be getting a $30,000 grant — half from the state, half from the county — that will help it double production and create six jobs.
Believe it or not, Arlington County has a working commercial farm.
The farm, which is located in a commercial building along Lee Highway, uses hydroponic technology to grow a variety of edible plants indoors. And it’s about to expand.
Virginia Gov. Ralph Northam announced this afternoon that Fresh Impact Farms will be getting a $30,000 grant — half from the state, half from the county — that will help it double production and create six jobs.
Fresh Impact, Arlington County’s only commercial farm, is banking on its restaurant customers ramping up purchases as vaccinated customers flock back to the indoor dining. It also launched a direct-to-consumer Community Supported Agriculture program last year.
County Board Chair Matt de Ferranti hailed the business and its expansion.
“Governor Northam’s award to Fresh Impact Farms, Arlington’s only commercial farm, is an innovative way to celebrate unique uses of technology to help a small business pivot during the pandemic,” de Ferranti said in a statement. “I am thrilled that Fresh Impact Farms is growing and looking to the future of a sustainable food supply.”
More on the company’s expansion, below, from a press release issued by the governor’s office.
Governor Ralph Northam today announced that Fresh Impact Farms will invest $137,500, create six new jobs, and more than double production at its Arlington County indoor facility. Operating since 2018 as Arlington’s only commercial farm, Fresh Impact Farms uses proprietary hydroponic technology to grow a variety of specialty herbs, leafy greens, and edible flowers for sale to customers in the Greater Washington, D.C. metro area.
Like many companies, Fresh Impact Farms has pivoted its business model amid the COVID-19 pandemic. Seizing the opportunity created by more people cooking at home, the company initiated a Community Supported Agriculture (CSA) program targeting area residents. The CSA program, which focuses on leafy greens and home kitchen-friendly herbs, has grown steadily since its establishment in April 2020 and now includes smaller wholesale clients. Now, with vaccinations underway and the restaurant industry poised to rebound, Fresh Impact Farms is expanding, which will allow the company to resume supplying their restaurant customers, while also meeting new demand through their CSA program.
“Agriculture continues to be a key driver of our economic recovery in both rural and urban areas of our Commonwealth,” said Governor Northam. “Innovative, dynamic businesses like Fresh Impact Farms are demonstrating how exciting new opportunities can grow out of pandemic-related challenges. I congratulate the company on their success and am thrilled to award the first-ever AFID grant to Arlington County to support this expansion.”
This expansion by Fresh Impact Farms will include a second grow room, larger production facility, and an educational hub where, post-pandemic, customers will be able to see how their food is harvested. Over the next three years, the company expects to grow an additional 10,500 pounds of Virginia-grown leafy greens, herbs, and edible flowers for restaurant and CSA customers.
“Agriculture is Virginia’s largest private sector industry and the Commonwealth continues to be on the forefront of emerging agriculture technologies,” said Secretary of Agriculture and Forestry Bettina Ring. “I am inspired by Fresh Impact Farms’ commitment to not only bringing fresh, local produce to Virginians, but also for its commitment to educate our community about how local food is grown.”
“2020 was undoubtedly one of the hardest years in recent memory for many people and businesses, but I’m heartened by the strength and flexibility the entire Fresh Impact Farms team has shown in our deep pivot to consumers and a CSA model to help us get to the point where we are ready to expand our business,” said Fresh Impact Farms Founder Ryan Pierce. “The support and generosity from the Commonwealth and Arlington County will be valuable as we expand our production and move towards a hybrid model of serving both the needs of restaurants and consumers. As the owner of a local food business, nothing gets me more excited than seeing the community come together in support of local food. The future is bright for urban agriculture and this grant will help us make an even greater impact in our community.”
The Commonwealth is partnering with Arlington County and the Arlington County Industrial Development Authority (IDA) on this project through the Governor’s Agriculture and Forestry Industries Development (AFID) Fund, which is administered by the Virginia Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services (VDACS). Governor Northam approved a $15,000 grant from the AFID Fund to secure the project for Virginia, which Arlington County will match with local funds.
“The Arlington County IDA’s match of the Governor’s AFID grant to Fresh Impact Farms represents an important investment in urban agriculture, sustainability, and technology,” said Arlington County IDA Chair Edwin Fountain. “This project will advance the County’s innovative and forward-thinking approach to developing new sectors of economic activity in Arlington.” […]
“Congratulations to Fresh Impact Farms,” said Senator Janet Howell. “This expansion not only supports our local economy, but also has a significant impact promoting healthy families and vibrant communities as a whole.”
“I am delighted Governor Northam has approved a grant from the AFID Fund to deliver this project for the Commonwealth and Arlington County,” said Delegate Richard Sullivan. “Fresh Impact Farms has been a pivotal resource for providing fresh food to the community. This expansion shows a commitment not only to homegrown produce, but to a healthier community and local economy in Arlington.”
Vertical Farms vs Greenhouses – The First Consideration: Location
When and where to use a vertical farm versus a greenhouse, and what factors – both economic and environmental – make the difference.
In just the past decade or so, sustainable farming has seen a high-tech makeover in the form of Controlled Environment Agriculture, or CEA, which consists of two main technologies: Vertical farms and greenhouses.
When it comes to feeding the world, it’s not a choice between vertical farms or greenhouses. We’ll need both to feed our growing global population with healthy, sustainable food, and we need to understand the ideal situation for each.
But as a business decision, it often is a choice between the two – and that’s what we hope to explain in this five-part series of articles: When and where to use a vertical farm versus a greenhouse, and what factors – both economic and environmental – make the difference.
In this first post, we’ll cover the basic differences between vertical farms and greenhouses, and why location matters so much when deciding between the two. Then stay tuned because, in the next articles, we’ll dive deeper into energy and lighting costs, automation and other expenses, environmental and crop considerations, and finally, the future of farming.
Vertical Farms vs Greenhouses: The Basics
The two technologies are often confused, but there are significant differences between them in resource use, cost, output, and, perhaps most importantly, the ideal locations for each.
Greenhouses are the more traditional technology that you’re probably familiar with: A single layer of crops, planted inside an enclosed space with walls and a ceiling made of glass or plastic to allow natural light in. They’re semi-controlled environments.
Vertical farms, on the other hand, are a much more recent invention using trays of usually hydroponic plants, stacked in floor-to-ceiling towers, with LED lights illuminating each layer, and climate control constantly adjusting the temperature, humidity and more.
In the upcoming articles in this series, we’ll dive into each part of these differences in more detail. But for now, let’s start with the first question entrepreneurs always need answering: The price tag.
Henry Gordon-Smith is the CEO of Agritecture, an independent consultancy and software creator that helps clients decide between the two technologies. As he puts it, “Vertical farming represents the most expensive, most controlled form of agriculture.”
At first blush, vertical farms are, in fact, shockingly more expensive than greenhouses – six to 10 times as costly. Gordon-Smith says vertical farming costs 2,200 to 2,600 Euro per square meter of cultivation bed space, while high-tech greenhouses cost 250 to 350 Euro per square meter of cultivation space.
Both offer a year-round source of fresh, pesticide-free, locally-grown produce, which provides better nutrition than the same foods that arrive from far away.
But what else do farmers, entrepreneurs, and investors get for all the added expense of vertical farming?
The answer is pretty simple: A more compact farm with more production per square meter, less water use, and more control over both quantity and quality. (With iFarm, this predictability is part of the package, in the form of a guaranteed yield within a precise time frame.)
For some entrepreneurs or municipalities, the cachet of implementing a high-tech farming technique that’s only been in use for less than a decade is also a factor in favour of vertical farming. But most often, the choice comes down to location.
The Ideal Location for a Vertical Farm versus a Greenhouse
The first step in determining the feasibility of building a vertical farm or greenhouse is to look at the drivers and constraints – many of which are simply location-based.
Places with limited space, such as dense urban areas, and limited access to fresh water are ideal for vertical farms. Doubly so if they have access to low-cost, renewable energy, and if they’re near a market with high demand for the crops vertical farms excel at producing: Leafy-greens, micro-greens, herbs and berries grown locally, without pesticides.
But in areas with unlimited space, lots of natural sunlight, and high-cost and/or high-carbon electricity, greenhouses may be the better option and the extra expenses of vertical farming might not make sense.
How these considerations apply in broad regions of the world is illustrated below:
Agritech: Precision Farming With AI, IoT and 5G
For a company that grows and delivers vegetables, Boomgrow Productions Sdn Bhd’s office is nothing like a farm, or even a vertical farm. Where farms are bedecked with wheelbarrows, spades and hoes, Boomgrow’s floor plan is akin to a co-working space with a communal island table, several cubicles, comfortable armchairs, a cosy hanging rattan chair and a glass-walled conference room in the middle
Image from: Photo by Mohd Izwan Mohd Nazam/The Edge
For a company that grows and delivers vegetables, Boomgrow Productions Sdn Bhd’s office is nothing like a farm, or even a vertical farm.
Where farms are bedecked with wheelbarrows, spades and hoes, Boomgrow’s floor plan is akin to a co-working space with a communal island table, several cubicles, comfortable armchairs, a cosy hanging rattan chair and a glass-walled conference room in the middle.
At a corner, propped up along a walkway leading to a rectangular chamber fitted with grow lights, are rows of support stilts with hydroponic planters developed in-house and an agricultural technologist perched on a chair, perusing data. “This is where some of the R&D work happens,” says Jay Dasen, co-founder of the agritech start-up.
But there is a larger farm where most of the work behind this high-tech initiative is executed. Located a stone’s throw from the city centre in Ampang is a 40ft repurposed shipping container outfitted with perception technologies and artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities that mimic the ideal environment to produce more than 50,000kg of vegetables a year.
Stacked in vertical layers, Boomgrow’s vegetables are grown under artificial lights with Internet of Things (IoT) sensors to detect everything from leaf discolouration to nitrate composition. This is coupled with AI and machine learning algorithms.
Boomgrow is the country’s first 5G-connected vertical farm. With the low latency and larger bandwidth technology, the start-up is able to monitor production in real time as well as maintain key parameters, such as temperature and humidity, to ensure optimal growth conditions.
When Jay and her co-founders, K Muralidesan and Shan Palani, embarked on this initiative six years ago, Boomgrow was nowhere near what it is today.
The three founders got together hoping to do their part in building a more sustainable future. “I’ve spent years advising small and large companies on sustainability, environmental and social governance disclosures. I even embarked on a doctorate in sustainability disclosure and governance,” says Jay.
“But I felt a deep sense of disconnect because while I saw companies evolving in terms of policies, processes and procedures towards sustainability, the people in those organisations were not transforming. Sustainability is almost like this white noise in the background. We know it’s important and we know it needs to be done, but we don’t really know how to integrate it into our lives.
“That disconnect really troubled me. When we started Boomgrow, it wasn’t a linear journey. Boomgrow is something that came out of meaningful conversations and many years of research.”
Shan, on the other hand, was an architect who developed a taste for sustainable designs when he was designing modular structures with minimal impact on their surroundings between regular projects. “It was great doing that kind of work. But I was getting very dissatisfied because the projects were customer-driven, which meant I would end up having debates about trivial stuff such as the colour of wall tiles,” he says.
As for Murali, the impetus to start Boomgrow came from having lived overseas — while working in capital markets and financial services — where quality and nutritious produce was easily available.
Ultimately, they concluded that the best way to work towards their shared sustainability goals was to address the imminent problem of food shortage.
“By 2050, the world’s population is expected to grow to 9.7 billion people, two-thirds of whom will be in Asia-Pacific. Feeding all those people will definitely be a huge challenge,” says Jay.
“The current agricultural practice is not built for resilience, but efficiency. So, when you think of farming, you think of vast tracts of land located far away from where you live or shop.
“The only way we could reimagine or rethink that was to make sure the food is located closer to consumers, with a hyperlocal strategy that is traceable and transparent, and also free of pesticides.”
Having little experience in growing anything, it took them a while to figure out the best mechanism to achieve their goal. “After we started working on prototypes, we realised that the tropics are not designed for certain types of farming,” says Jay.
“And then, there is the problem of harmful chemicals and pesticides everywhere, which has become a necessity for farmers to protect their crops because of the unpredictable climate. We went through many iterations … when we started, we used to farm in little boxes, but that didn’t quite work out.”
They explored different methodologies, from hydroponics to aquaponics, and even started growing outdoors. But they lost a lot of crops when a heat wave struck.
That was when they started exploring more effective ways to farm. “How can we protect the farm from terrible torrential rains, plant 365 days a year and keep prices affordable? It took us five years to answer these questions,” says Jay.
Even though farmers all over the world currently produce more than enough food to feed everyone, 820 million people — roughly 11% of the global population — did not have enough to eat in 2018, according to the World Health Organization. Concurrently, food safety and quality concerns are rising, with more consumers opting for organically produced food as well as safe foods, out of fear of harmful synthetic fertilisers, pesticides, herbicides and fungicides.
According to ResearchAndMarkets.com, consumer demand for global organic fruit and vegetables was valued at US$19.16 billion in 2019 and is anticipated to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5% by 2026.
Meanwhile, the precision farming market was estimated to be US$7 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach US$12.8 billion by 2025, at a CAGR of 12.7% between 2020 and 2025, states MarketsandMarkets Research Pte Ltd.
Malaysia currently imports RM1 billion worth of leafy vegetables from countries such as Australia, China and Japan. Sourcing good and safe food from local suppliers not only benefits the country from a food security standpoint but also improves Malaysia’s competitive advantage, says Jay.
Unlike organic farming — which is still a soil-based method — tech-enabled precision farming has the advantage of catering for increasing demand and optimum crop production with the limited resources available. Moreover, changing weather patterns due to global warming encourage the adoption of advanced farming technologies to enhance farm productivity and crop yield.
Boomgrow’s model does not require the acres of land that traditional farms need, Jay emphasises. With indoor farms, the company promises a year-round harvest, undisturbed by climate and which uses 95% less water, land and fuel to operate.
Traditional farming is back-breaking labour. But with precision technology, farmers can spend less time on the farm and more on doing other things to develop their business, she says.
Boomgrow has secured more than RM300,000 in funding via technology and innovation grants from SME Corporation Malaysia, PlaTCOM Ventures and Malaysia Digital Economy Corporation, and is on track to build the country’s largest indoor farms.
Image from: Boomgrow
The company got its chance to showcase the strength of its smart technology when Telekom Malaysia Bhd (TM) approached it to be a part of the telco’s Smart Agriculture cluster in Langkawi last October.
“5G makes it faster for us to process the multiple data streams that we need because we collect data for machine learning, and then AI helps us to make decisions faster,” Jay explains.
“We manage the farm using machines to study inputs like water and electricity and even measure humidity. All the farm’s produce is lab-tested and we can keep our promise that there are no pesticides, herbicides or any preserving chemicals. We follow the food safety standards set by the EU, where nitrate accumulation in plant tissues is a big issue.”
With TM’s 5G technology and Boomgrow’s patent-pending technology, the latter is able to grow vegetables like the staple Asian greens and highland crops such as butterhead and romaine lettuce as well as kale and mint. While the company is able to grow more than 30 varieties of leafy greens, it has decided to stick to a selection of crops that is most in demand to reduce waste, says Jay.
As it stands, shipping containers are the best fit for the company’s current endeavour as containerised modular farms are the simplest means of bringing better food to local communities. However, it is also developing a blueprint to house farms in buildings, she says.
Since the showcase, Boomgrow has started to supply its crops to various hotels in Langkawi. It rolled out its e-commerce platform last year after the Movement Control Order was imposed.
“On our website, we promise to deliver the greens within six hours of harvest. But actually, you could get them way earlier. We harvest the morning after the orders come in and the vegetables are delivered on the same day,” says Jay.
Being mindful of Boomgrow’s carbon footprint, orders are organised and scheduled according to consumers’ localities, she points out. “We don’t want our delivery partners zipping everywhere, so we stagger the orders based on where consumers live.
“For example, all deliveries to Petaling Jaya happen on Thursdays, but the vegetables are harvested that morning. They are not harvested a week before, three days before or the night before. This is what it means to be hyperlocal. We want to deliver produce at its freshest and most nutritious state.”
Plans to expand regionally are also underway, once Boomgrow’s fundraising exercise is complete, says Jay. “Most probably, this will only happen when the Covid-19 pandemic ends.”
To gain the knowledge they have today, the team had to “unlearn” everything they knew and take up new skills to figure what would work best for their business, says Jay. “All this wouldn’t have been possible if we had not experimented with smart cameras to monitor the condition of our produce,” she laughs.
These Buildings Combine Affordable Housing And Vertical Farming
Inside each building, the ground level will offer community access, while the greenhouse fills the second, third, and fourth floors, covering 70,000 square feet and growing around a million pounds of produce a year
A Million Pounds of Produce A Year, Along With Housing And Jobs.
[Image: Harriman/Gyde/courtesy Vertical Harvest]
02-18-21
Some vertical farms grow greens in old warehouses, former steel mills, or other sites set apart from the heart of cities. But a new series of projects will build multistory greenhouses directly inside affordable housing developments.
“Bringing the farm back to the city center can have a lot of benefits,” says Nona Yehia, CEO of Vertical Harvest, a company that will soon break ground on a new building in Westbrook, Maine, that combines a vertical farm with affordable housing. Similar developments will follow in Chicago and in Philadelphia, where a farm-plus-housing will be built in the Tioga District, an opportunity zone.
[Image: Harriman/Gyde/courtesy Vertical Harvest]
“I think what we’ve truly understood in the past year and a half—although we’ve been rooted in it all along—is that we have in this country converging economic, climate, and health crises that are rooted in people’s access to healthy food, resilient, nourishing jobs, and fair housing,” Yehia says. “And we saw this as an urban redevelopment tool that has the potential to address all three.”
Nona Yehia [Image: Harriman/Gyde/courtesy Vertical Harvest]
The company launched in 2015 on a vacant lot in Jackson, Wyoming, aiming in part to create jobs for people with physical and developmental disabilities in the area. In 2019, it got a contract from Fannie Mae to explore how its greenhouses could help with the challenge of food security and nutrition, studying how a farm could be integrated into an existing affordable housing development in Chicago as a model for new projects.
Now, as it moves forward with the Chicago project and expands to other cities, it will also create new jobs for people who might have otherwise had difficulty finding work, working with local stakeholders to identify underserved populations. “Part of this is providing healthy, nutritious food,” Yehia says, “but also jobs at livable wages. We’re positioning all of our firms to address the new minimum wage level of $15 an hour with a path towards career development.”
[Image: Harriman/Gyde/courtesy Vertical Harvest]
Inside each building, the ground level will offer community access, while the greenhouse fills the second, third, and fourth floors, covering 70,000 square feet and growing around a million pounds of produce a year. (The amount of housing varies by site; in Maine, the plan includes 50 unites of housing, and the project will also create 50 new jobs.) In Chicago, there may be a community kitchen on the first level. In each location, residents will be able to buy fresh produce on-site; Vertical Harvest also plans to let others in the neighborhood buy greens directly from the farm. While it will sell to supermarkets, restaurants, hospitals, and other large customers, it also plans to subsidize 10-15% of its harvest for local food pantries and other community organizations. “By creating a large-scale farm in a food desert we are creating a large source of healthy, locally grown food 365 days a year,” she says.
Correction: We’ve updated this article to note that the project in Maine has 50 units of housing, not 15, and the company received a contract—not a grant—from Fannie Mae.
ADELE PETERS
ADELE PETERS IS A STAFF WRITER AT FAST COMPANY WHO FOCUSES ON SOLUTIONS TO SOME OF THE WORLD'S LARGEST PROBLEMS, FROM CLIMATE CHANGE TO HOMELESSNESS. PREVIOUSLY, SHE WORKED WITH GOOD, BIOLITE, AND THE SUSTAINABLE PRODUCTS AND SOLUTIONS PROGRAM AT UC BERKELEY, AND CONTRIBUTED TO THE SECOND EDITION OF THE BESTSELLING BOOK "WORLDCHANGING: A USER'S GUIDE FOR THE 21ST CENTURY."
Bringing The Future To life In Abu Dhabi
A cluster of shipping containers in a city centre is about the last place you’d expect to find salad growing. Yet for the past year, vertical farming startup Madar Farms has been using this site in Masdar City, Abu Dhabi, to grow leafy green vegetables using 95 per cent less water than traditional agriculture
Amid the deserts of Abu Dhabi, a new wave of entrepreneurs and innovators are sowing the seeds of a more sustainable future.
Image from: Wired
A cluster of shipping containers in a city centre is about the last place you’d expect to find salad growing. Yet for the past year, vertical farming startup Madar Farms has been using this site in Masdar City, Abu Dhabi, to grow leafy green vegetables using 95 per cent less water than traditional agriculture.
Madar Farms is one of a number of agtech startups benefitting from a package of incentives from the Abu Dhabi Investment Office (ADIO) aimed at spurring the development of innovative solutions for sustainable desert farming. The partnership is part of ADIO’s $545 million Innovation Programme dedicated to supporting companies in high-growth areas.
“Abu Dhabi is pressing ahead with our mission to ‘turn the desert green’,” explained H.E. Dr. Tariq Bin Hendi, Director General of ADIO, in November 2020. “We have created an environment where innovative ideas can flourish and the companies we partnered with earlier this year are already propelling the growth of Abu Dhabi’s 24,000 farms.”
The pandemic has made food supply a critical concern across the entire world, combined with the effects of population growth and climate change, which are stretching the capacity of less efficient traditional farming methods. Abu Dhabi’s pioneering efforts to drive agricultural innovation have been gathering pace and look set to produce cutting-edge solutions addressing food security challenges.
Beyond work supporting the application of novel agricultural technologies, Abu Dhabi is also investing in foundational research and development to tackle this growing problem.
In December, the emirate’s recently created Advanced Technology Research Council [ATRC], responsible for defining Abu Dhabi’s R&D strategy and establishing the emirate and the wider UAE as a desired home for advanced technology talent, announced a four-year competition with a $15 million prize for food security research. Launched through ATRC’s project management arm, ASPIRE, in partnership with the XPRIZE Foundation, the award will support the development of environmentally-friendly protein alternatives with the aim to "feed the next billion".
Image from: Madar Farms
Global Challenges, Local Solutions
Food security is far from the only global challenge on the emirate’s R&D menu. In November 2020, the ATRC announced the launch of the Technology Innovation Institute (TII), created to support applied research on the key priorities of quantum research, autonomous robotics, cryptography, advanced materials, digital security, directed energy and secure systems.
“The technologies under development at TII are not randomly selected,” explains the centre’s secretary general Faisal Al Bannai. “This research will complement fields that are of national importance. Quantum technologies and cryptography are crucial for protecting critical infrastructure, for example, while directed energy research has use-cases in healthcare. But beyond this, the technologies and research of TII will have global impact.”
Future research directions will be developed by the ATRC’s ASPIRE pillar, in collaboration with stakeholders from across a diverse range of industry sectors.
“ASPIRE defines the problem, sets milestones, and monitors the progress of the projects,” Al Bannai says. “It will also make impactful decisions related to the selection of research partners and the allocation of funding, to ensure that their R&D priorities align with Abu Dhabi and the UAE's broader development goals.”
Image from: Agritecture
Nurturing Next-Generation Talent
To address these challenges, ATRC’s first initiative is a talent development programme, NexTech, which has begun the recruitment of 125 local researchers, who will work across 31 projects in collaboration with 23 world-leading research centres.
Alongside universities and research institutes from across the US, the UK, Europe and South America, these partners include Abu Dhabi’s own Khalifa University, and Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence, the world’s first graduate-level institute focused on artificial intelligence.
“Our aim is to up skill the researchers by allowing them to work across various disciplines in collaboration with world-renowned experts,” Al Bannai says.
Beyond academic collaborators, TII is also working with a number of industry partners, such as hyperloop technology company, Virgin Hyperloop. Such industry collaborations, Al Bannai points out, are essential to ensuring that TII research directly tackles relevant problems and has a smooth path to commercial impact in order to fuel job creation across the UAE.
“By engaging with top global talent, universities and research institutions and industry players, TII connects an intellectual community,” he says. “This reinforces Abu Dhabi and the UAE’s status as a global hub for innovation and contributes to the broader development of the knowledge-based economy.”
Warehouse Becoming Vertical Farms — And They’re Feeding New Jersey
New Jersey's vertical farms are transforming agriculture by helping farmers meet growing food demand. New Jersey Agriculture Secretary Doug Fisher said that while conventional farming in outdoor fields remains critical, vertical farming has its advantages because of its efficiency and resistance to pests and thus less need for chemicals
Image from: New Jersey 101.5
New Jersey's vertical farms are transforming agriculture by helping farmers meet growing food demand.
New Jersey Agriculture Secretary Doug Fisher said that while conventional farming in outdoor fields remains critical, vertical farming has its advantages because of its efficiency and resistance to pests and thus less need for chemicals.
Vertical farming is the process of growing food vertically in stacked layers indoors under artificial light and temperature, mainly in buildings. These plants receive the same nutrients and all the elements needed to grow plants for food.
Vertical farms are also versatile. Plants may be growing in containers, in old warehouses, in shipping containers, in abandoned buildings.
"That's one of the great advantages — that we can put agriculture in the midst of many landscapes that have lost their vitality," said Fisher.
ResearchandMarkets.com says the U.S. vertical farming market is projected to reach values of around $3 billion by the year 2024.
The one drawback is that its operational and labor costs make it expensive to get up and running.
Image from: AeroFarms
In the past decade, however, vertical farming has become more popular, creating significant crop yields all over the state.
AeroFarms in Newark is the world's largest indoor vertical farm. The farm converted a 75-year-old 70,000-square-foot steel mill into a vertical farming operation. AeroFarms' key products include Dream Greens, its retail brand of baby and micro-greens, available year-round in several ShopRite supermarkets.
Kula Urban Farm in Asbury Park opened in 2014. Vacant lots are transformed into urban farms and there's a hydroponic greenhouse on site. That produce is sold to local restaurants.
Beyond Organic Growers in Freehold uses no pesticides and all seeds and nutrients are organic. There's a minimum of 12,000 plants growing on 144 vertical towers. On its website, it says the greenhouse utilizes a new growing technique called aeroponics, which involves vertical towers where the plant roots hang in the air while a nutrient solution is delivered with a fine mist. It also boasts that by using this method, plants can grow with less land and water while yielding up to 30% more three times faster than traditional soil farming.
Vertical farms in New Jersey help feed local communities. Many are in urban areas and are a form of urban farming.
Fisher predicts that vertical farms will be operational in stores and supermarkets around the state.
"It's continued to expand. There's going to be many, many ways and almost any area in the state has the opportunity to have a vertical farm," Fisher said.
Vertical Farming: Ugandan Company Develops Solution for Urban Agriculture
We speak to Lilian Nakigozi, founder of Women Smiles Uganda, a company that manufactures and sells vertical farms used to grow crops in areas where there is limited space
We speak to Lilian Nakigozi, founder of Women Smiles Uganda, a company that manufactures and sells vertical farms used to grow crops in areas where there is limited space.
Image from: How We Made It in Africa
1. How Did You Come Up with the Idea to Start Women Smiles Uganda?
Women Smiles Uganda is a social enterprise formed out of passion and personal experience. I grew up with a single mother and eight siblings in Katanga, one of the biggest slums in Kampala, Uganda. I experienced hunger and poverty where we lived. There was no land for us to grow crops and we didn’t have money to buy food. Life was hard; we would often go to sleep on empty stomachs and our baby sister starved to death.
Growing up like that, I pledged to use my knowledge and skills to come up with an idea that could solve hunger and, at the same time, improve people’s livelihoods, particularly women and young girls living in the urban slums. In 2017, while studying business at Makerere University, I had the idea of developing a vertical farm. This came amid so many challenges: a lack of finance and moral support. I would use the money provided to me for lunch as a government student to save for the initial capital of my venture.
I managed to accumulate $300 and used this to buy materials to manufacture the first 20 vertical farms. I gave these to 20 families and, in 2018, we fully started operations in different urban slums.
2. Tell Us About Your Vertical Farms and How They Work.
Women Smiles vertical farms are made out of wood and recycled plastic materials. Each unit is capable of growing up to 200 plants. The product also has an internal bearing system which turns 360° to guarantee optimal use of the sunlight and is fitted with an inbuilt drip irrigation system and greenhouse material to address any agro-climatic challenges.
The farms can be positioned on a rooftop, veranda, walkway, office building or a desk. This allows the growth of crops throughout the year, season after season, unaffected by climatic changes like drought.
In addition, we train our customers on how to make compost manure using vermicomposting and also provide them with a market for their fresh produce.
Image from: How We Made It in Africa
3. Explain Your Revenue Model.
Women Smiles Uganda generates revenue by selling affordable, reliable and modern vertical farms at $35, making a profit margin of $10 on each unit. The women groups are recruited into our training schemes and we teach them how to use vertical farming to grow crops and make compost manure by vermicomposting. Women groups become our outgrowers of fruits and vegetables. We buy the fresh produce from our outgrowers and resell to restaurants, schools and hotels.
We also make money through partnering with NGOs and other small private organisations to provide training in urban farming concepts to the beneficiaries of their projects.
4. What Are Some of the Major Challenges of Running This Business?
The major challenge we face is limited funds by the smallholder farmers to purchase the vertical farms. However, we mitigate this by putting some of them into our outgrower scheme which helps them to generate income from the fresh produce we buy. We have also linked some of them to financial institutions to access finance.
5. How Do You Generate Sales?
We reach our customers directly via our marketing team which moves door to door, identifying organised women groups and educating them about the benefits of vertical farming for improved food security. Most of our customers are low-income earners and very few of them have access to the internet.
However, we do also make use of social media platforms like Facebook to reach out to our customers, especially the youth.
In addition, we organise talk shows and community gatherings with the assistance of local leaders with whom we work hand in hand to provide educational and inspirational materials to people, teaching them about smart agriculture techniques.
6. Who Are Your Main Competitors?
Just like any business, we have got competitors; our major competitors include Camp Green and Spark Agro-Initiatives.
Image from: The Conversation
7. What Mistakes Have You Made in Business and What Did You Learn From Them?
As a victim of hunger and poverty, my dream was for every family in slums to have a vertical farm. I ended up giving some vertical farms on credit. Unfortunately, most of them failed to pay and we ended up with huge losses.
This taught me to shift the risk of payment default to a third party. Every customer who may need our farms on credit is now linked to our partner micro-finance bank. By doing this, it is the responsibility of the bank to recover the funds from our customers and it has worked well.
8. Apart from This Industry, Name an Untapped Business Opportunity in Uganda.
Manufacturing of cooler sheds for the storage of perishable agricultural produce is one untapped opportunity. Currently, Ugandan smallholder farmers lose up to 40% of their fresh produce because of a lack of reliable cold storage systems.
Providing a cheap and reliable 24/7 cold storage system would dramatically reduce post-harvest losses for these farmers.
Is AppHarvest the Future of Farming?
In this video from Motley Fool Live, recorded on Jan. 28, Industry Focus host Nick Sciple and Motley Fool contributor Lou Whiteman discuss AppHarvest, one such SPAC that is looking to disrupt the agriculture industry. Here are the details on what AppHarvest wants to do, and a look at whether the company represents the future of farming.
Special purpose acquisition companies, or SPACs, are red-hot right now, with investors clamoring to get into promising young companies.
In this video from Motley Fool Live, recorded on Jan. 28, Industry Focus host Nick Sciple and Motley Fool contributor Lou Whiteman discuss AppHarvest, one such SPAC that is looking to disrupt the agriculture industry. Here are the details on what AppHarvest wants to do, and a look at whether the company represents the future of farming.
Nick Sciple: One last company I wanted to talk about, Lou, and this is one I think it's -- you pay attention to, but not one I'm super excited to run in and buy. It was a company called AppHarvest. It's coming public via a [SPAC] this year. This vertical farming space. We talked about Gladstone Land buying traditional farmland. AppHarvest is taking a very different approach, trying to lean into some of the ESG-type movements.
Lou Whiteman: Yeah. Let's look at this. It probably wouldn't surprise you that the U.S. is the biggest global farm exporter as we said, but it might surprise you that the Netherlands, the tiny little country, is No. 2. The way they do that is tech: Greenhouse farm structure. AppHarvest has taken that model and brought it to the U.S. They have, I believe, three farms in Appalachia. The pitches can produce 30x the yields using 90% less water. Right now, it's mostly tomatoes and it is early-stage. I don't own this stock either. I love this idea. There's some reasons that I'm not buying in right now that we can get into. But this is fascinating to me. We talked about making the world a better place. This is the company that we need to be successful to make the world a better place. The warning on it is that it is a SPAC. So it's not public yet. Right now, I believe N-O-V-S. That deal should close soon. [Editor's note: The deal has since closed.] I'm not the only one excited about it. I tend not to like to buy IPOs and new companies anyway. I think the caution around buying into the excitement applies here. There is a Martha Stewart video on their website talking up the company, which I love Martha Stewart, but that's a hype level that makes me want to just watch and see what they produce. This is just three little farms in Appalachia right now and a great idea. This was all over my watchlist. I would imagine I would love to hold it at some point, but just be careful because this is, as we saw SPACs last year in other areas, people are very excited about this.
Sciple: Yeah. I think, like we've said, for a lot of these companies, the prospects are great. I think when you look at the reduced water usage, better, environmentally friendly, all those sorts of things. I like that they are in Appalachia. As someone who is from the South, I like it when more rural areas get some people actually investing money there. But again, there's a lot of execution between now and really getting to a place where this is the future of farming and they're going to reach scale and all those sorts of things. But this is a company I'm definitely going to have my radar on and pay attention to as they continue to report earnings. Because you can tell yourself a story about how this type of vertical farming, indoor farming disrupts this traditional model, can be more efficient, cleaner, etc. Something to continue paying attention to as we have more information, because this company, like you said, Lou, isn't all the way public yet. We still got to have this SPAC deal finalized and then we get all our fun SEC filings and quarterly calls and all those sorts of things. Once we have that, I will be very much looking forward to seeing what the company has to say.
Whiteman: Right. Just to finish up along too, the interesting thing here is that it is a proven concept because it has worked elsewhere. The downside of that is that it needed to work there. Netherlands just doesn't have -- and this is an expensive proposition to get started, to get going. There's potential there, but in a country blessed with almost seemingly unlimited farmland for now, for long term it makes sense. But in the short term, it could be a hard thing to really get up and running. I think you're right, just one to watch.
London Food Bank Is Going Greener With Greenhouse
CTV's Nick Paparella check in on the progress as the food bank aims to grow some of its own fresh produce for use during the winter months.
Nick Paparella CTV News London Reporter
Inside the London Food Bank's greenhouse in London, Ont. on Friday, Jan. 29, 2021. (Nick Paparella / CTV News)
LONDON, ONT. -- The outdoors may be covered in a blanket of white in January, but at the London Food Bank these days everything seems to be coming up green.
After a year of planning and with donations from the community, the new greenhouse is bearing fruit - or in this case vegetables.
“This is what Londoners a few years ago wanted more than anything else, to donate funds towards fresh fruits, fresh produce and that's what they have done,” says Glen Pearson from the London Food Bank. “So we've just taken it to a different level so we can grow our own as well.”
The man with the green thumb here is horticulturalist Luis Reyes.
“A couple of weeks ago we received the heaters and since then you can see the growth in only a couple of weeks,” says Reyes.
Like many from the food bank, Reyes is passionate about helping those in need.
“I am a grower and that's what I like to do and now to do it directly to people makes me proud,” he says.
The greenhouse is expected to grow about 15,000 plants a year which amounts to about four tons of food.
“You're not going to get anything fresher than this in a supermarket,“ says Reyes. “So probably you're going to harvest today here and the people or clients are going to receive it tomorrow or the same day.”
In the winter months, they are growing cold-weather plants like lettuce, spinach and even kale, but once summer arrives they will switch to tomatoes, cucumbers and fruit-bearing plants.
Adds Pearson, “It just expands the nutrition we're able to give to other people.”
AppHarvest Makes Initial Donation of 2,500 Pounds of Tomatoes To God’s Pantry Food Bank
AgTech leader AppHarvest today announced it has delivered 2,500 pounds of Beefsteak tomatoes from its first harvest this week to God's Pantry Food Bank, which will distribute them to those in need
Company designated portion of the first harvest of fresh, sustainably grown tomatoes to feed Kentuckians in need
JANUARY 22, 2021 — MOREHEAD, KY — AgTech leader AppHarvest today announced it has delivered 2,500 pounds of Beefsteak tomatoes from its first harvest this week to God's Pantry Food Bank, which will distribute them to those in need.
Through its 400-plus distribution partners, God’s Pantry Food Bank provides food to residents of 50 Kentucky counties, focused on Eastern and Central Kentucky. The organization, which operates a distribution center in Morehead — the home of AppHarvest’s 60-acre indoor farm — distributed nearly 14 million pounds of fresh fruits and veggies and more than 41 million pounds of food overall during its most recent fiscal year.
“The faith and grit of Eastern Kentuckians has built one of the world’s largest high-tech greenhouses, and we appreciate the opportunity to share what we’re growing with those in need as we all work to create a resilient food system,” said AppHarvest Founder & CEO Jonathan Webb in delivering the donated tomatoes on Friday. “We’re working to create America’s AgTech capital here in Appalachia to provide affordable, nutritious, and delicious fruits and veggies that will help reduce hunger and food deserts.”
“God’s Pantry Food Bank is thrilled to engage with AppHarvest to nourish more lives through sustainable agriculture,” said CEO Michael Halligan. “There are more than 250,000 kids, adults, and seniors across Central and Eastern Kentucky who are not sure when they might have their next meal. Imagine the impact of now having a sandwich with a fresh, Kentucky-grown slice of tomato on the top.”
The donation is one of many steps AppHarvest is taking to address America’s food crisis. In Kentucky alone, 20 percent of children and nearly 15 percent of adults experience food insecurity.1 Nationally, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has found only one in 10 adults eat enough fruits and veggies.2
By building closer to consumers, AppHarvest provides fresher fruits and vegetables at affordable prices. The company is also focused on helping students grow their own food through its high-tech educational container farm program. Started in 2018 prior to the company’s operations commencing at its indoor farm in Morehead, the program retrofits shipping containers with high-tech farming equipment to teach students to grow healthy leafy greens. The program started at Shelby Valley High School in Pike County and has since expanded to Rowan and Breathitt counties, with additional units planned. AppHarvest also recently partnered with Save the Children to provide more than 1,600 leafy green growing kits to Kentucky kids in need.
1 Feeding America
2 U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
“AppHarvest was founded as a benefit corporation and has also been certified as a B Corp by the independent non-profit B Lab, because we believe companies should be in the business of doing good,” said Amy Samples, AppHarvest’s Director of Community Outreach and People Programs. “We’re building America’s AgTech capital from within Appalachia and know that education is core to achieving that.”
Shipments from AppHarvest’s first harvest this week are now available at select national retailers such as Kroger, Publix, Walmart, Food City, and Meijer. The company’s Morehead facility alone is expected to produce about 45 million pounds of tomatoes annually from about 720,000 tomato plants, a mix of Beefsteak and “Tomatoes on the Vine.”
AppHarvest has two more facilities under construction—a similar 60-plus acre facility outside Richmond, Ky., and a 15-acre facility to grow leafy greens in Berea, Ky. AppHarvest also is planning for more facilities across Kentucky and Central Appalachia, with the goal of 12 total farms by the end of 2025.
About AppHarvest
AppHarvest is an applied technology company building some of the world’s largest indoor farms in Appalachia. The Company combines conventional agricultural techniques with cutting-edge technology and is addressing key issues including improving access for all to nutritious food, farming more sustainably, building a home-grown food supply, and increasing investment in Appalachia. The Company’s 60-acre Morehead, KY facility is among the largest indoor farms in the U.S. For more information, visit https://www.appharvest.com/.
Forward-Looking Statements
Certain statements included in this press release that are not historical facts are forward-looking statements for purposes of the safe harbor provisions under the United States Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Forward-looking statements generally are accompanied by words such as “believe,” “may,” “will,” “estimate,” “continue,” “anticipate,” “intend,” “expect,” “should,” “would,” “plan,” “predict,” “potential,” “seem,” “seek,” “future,” “outlook,” and similar expressions that predict or indicate future events or trends or that are not statements of historical matters. All statements, other than statements of present or historical fact included in this press release, regarding Novus Capital’s proposed acquisition of AppHarvest, Novus Capital’s ability to consummate the transaction, the benefits of the transaction and the combined company’s future financial performance, as well as the combined company’s growth plans and strategy, future operations, estimated financial position, estimated revenues and losses, projected costs, prospects, plans and objectives of management are forward-looking statements. These statements are based on various assumptions, whether or not identified in this press release, and on the current expectations of AppHarvest’s management and are not predictions of actual performance. These forward-looking statements are provided for illustrative purposes only and are not intended to serve as, and must not be relied on as, a guarantee, an assurance, a prediction, or a definitive statement of fact or probability. Actual events and circumstances are difficult or impossible to predict and will differ from assumptions. Many actual events and circumstances are beyond the control of AppHarvest. These forward-looking statements are subject to a number of risks and uncertainties, including those discussed in Novus Capital’s registration statement on Form S-4, filed with the SEC on October 9, 2020 (the “Registration Statement”), under the heading “Risk Factors,” and other documents Novus Capital has filed, or will file, with the SEC. If any of these risks materialize or our assumptions prove incorrect, actual results could differ materially from the results implied by these forward-looking statements. In addition, forward-looking statements reflect AppHarvest’s expectations, plans, or forecasts of future events and views as of the date of this press release. AppHarvest anticipates that subsequent events and developments will cause its assessments to change. However, while AppHarvest may elect to update these forward-looking statements at some point in the future, AppHarvest specifically disclaims any obligation to do so. These forward-looking statements should not be relied upon as representing AppHarvest’s assessments of any date subsequent to the date of this press release. Accordingly, undue reliance should not be placed upon the forward-looking statements.
Developing And Improving Productivity In Vertical Farms
Growing food in our increasingly variable climate is a challenge. Growing crops in a controlled environment provides an alternative approach to conventional farming which is free from the pressures created by extremes and variations in our weather, isolated from pests and allows crop growth at a wider range of latitudes
27-01-2021 | Agritech Tomorrow
Growing food in our increasingly variable climate is a challenge. Growing crops in a controlled environment provides an alternative approach to conventional farming which is free from the pressures created by extremes and variations in our weather, isolated from pests and allows crop growth at a wider range of latitudes.
Vertical farming is a relatively recent development with the first commercial vertical farm being reported as developed in 2012 in Singapore. Grand View Research estimated that the value of the vertical farming market would reach almost US$10 billion by 2025.
Developing indoor vertical farms requires a good understanding of all the requirements each crop plant will need for optimal growth and development. As a relatively new technology, research can have a big impact on how successful these enterprises will be in the longer term with expertise in plant physiology supporting improvements to these systems.
Dr. Antony Dodd’s research into the plant circadian clock had found that optimizing growing conditions to match the clock resulted in plants that contained more chlorophyll, allowing them to convert more of the available light into biomass and grow faster. Experimentally, productivity could be doubled by matching the circadian rhythm to the photoperiod in the growing environment. The capacity to control conditions precisely within a vertical farm means that the environment can be fine-tuned to the requirements of the crop to maximize yield.
In 2019 Dr. Antony Dodd was awarded a Royal Society Short Industry Fellowship to support the development of a collaboration with LettUs Grow. The collaborative team combines expertise in biological science with engineering, with Dr. Dodd’s research group providing expertise on optimal circadian rhythms, light quality, and plant physiology to inform developments in light provision for crop plants in vertical farming systems.
The team, from LettUs Grow, University of Bristol, and the John Innes Centre, have worked together on several projects since the fellowship was first awarded. This has not only enabled them to develop strategies to better analyze the performance of plants within vertical farms, but also to identify the areas of research which would accelerate the development of aeroponics for precision agriculture. And so together they have developed a Roadmap for aeroponics development.
The impacts so far have been:
Awarded a Royal Society Industry Fellowship supported the development of a team to develop improvements to aeroponics technology through the incorporation of circadian biology and plant physiology
· Development of a roadmap to inform on what future research is required to accelerate sustainable growth in vertical farming using aeroponics, reducing operational costs whilst maximizing productivity
· BBSRC funding has supported two studentship schemes to help LettUs Grow improve their processes to optimize lighting regimes for crop growth
Jack Farmer, Chief Scientific Officer and co-founder of LettUs Grow said: “Vertical farming is an emerging industry with a lot to offer that, alongside both greenhouse and organic agricultural practices, offers a potential pathway towards continuing to meet the worlds demand for nutritious produce without degrading large tracts of agricultural land. In many ways, each of these attempt to move forward from the chemically-driven intensive agricultural practices of the recent decades towards a system that factors-in environmental externalities.
However, if we want to manifest the environmental benefits vertical farming has to offer, we need to maximize productivity and efficiency for growers. We know it is important as a technology provider to collaborate with the best plant scientists to get the most out of our systems – elegant engineering will only take you so far. Internal collaboration between growers, engineers, and scientists is foundational to what we do here, and it’s been a real pleasure to expand that collaboration to include the talented staff at the John Innes Centre.”
LettUs Grow are now developing systems to allow growth of crops which are more technically challenging such as strawberries and tree whips through their award-winning aeroponic system, which is already being used to produce leafy green crops such as salads and herbs.
There are numerous benefits to be gained from growing crops in vertical farms. We are better able to keep out pests and disease reducing the requirement for pesticides, we can maintain an optimum environment for efficient plant growth which speeds up time to harvest and enables more accurate scheduling of crops thereby reducing food waste. Vertical farms can be located close to urban conurbations reducing food miles and year-round production means that we can become less reliant on imports, guaranteeing local food supply chains which in turn can stabilize prices as well as product consistency.
The next steps for further impact from this research will involve tackling the knowledge gaps identified in the roadmap and implementing changes to identify key growing formulae for specific crops which will allow vertical farming businesses to become more productive. This in turn will enable the potential benefits of vertical farming to be fully realized.
Source and Photo Courtesy of Agritech Tomorrow
Israel’s Vertical Field Inks Deal To Deploy Its Farming System In UAE
Ag-tech company to launch pilot in Emirates ahead of wider roll-out; its vertical farming system could lessen food insecurity in water-scarce Gulf state
By LUKE TRESS
Produce grown using Israeli start up Vertical Field's farming system. (Courtesy/Vertical Field)
Vertical Field, a startup that has developed a vertical farming system, has signed an accord with an Emirati company to deploy its products to the United Arab Emirates.
The Israeli ag-tech firm signed the agreement with Emirates Smart Solutions & Technologies, Vertical Field said in a statement on Wednesday.
Vertical Field will set up pilot vertical farms in the Emirate of Umm Al Quwain ahead of a wider roll-out in the UAE, the company said. The pilot will aim to determine which crops are best for the local market and will be supported and overseen by Vertical Field’s Israeli agronomists.
The firm expects the project to expand into a multimillion-dollar venture that will include distributing Vertical Field’s products to additional Gulf states, the company said.
Roughly 80 percent of agricultural food products in the UAE is imported from abroad, amounting to $10 billion in trade in 2018. The increasing cost of transporting food and concerns over food security played a part in the new partnership, Vertical Field said.
“Arid desert regions face many challenges surrounding the production of high-quality agricultural produce at low prices. With the help of various agricultural technologies and new developments, we believe that we can successfully align the demands of the market with competitive prices without compromising quality,” Guy Elitzur, Vertical Field’s CEO, said in a statement.
Maher Makalde, the CEO of Emirates Smart Solutions & Technologies, said, “We are excited for the opportunity to partner with Vertical Field and bring advanced Israeli vertical technology that enables the growth of produce in a controlled and predictable way, overcoming harsh outdoor climate conditions.
“Our goal is to establish food security that is independent of imports and to develop a high-quality agricultural infrastructure that reaches the retail market,” Makalde said.
An illustration of vegetables growing on walls by Vertical Field. (Courtesy)
Vertical Field’s soil-based installations are made up of separate blocks of plants that can be rearranged at will to produce locally sourced vegetables. This green wall of vegetation is suitable for growing vegetables in stores, offices and apartment buildings, or anywhere in urban areas, which have little space but many walls.
The firm, formerly called Green Wall Israel, said that products grown with its farming method are pesticide-free, generate less waste than conventional agriculture and utilize 90% less water, growing in precise quantities in a controlled environment with shorter growing cycles.
Produce in its containers can grow 365 days a year and is free of the limitations usually imposed by seasons, weather, climate and location.
The farms are modular, expandable and moveable, with fully automated crop management and a sterile environment that requires significantly less human contact. The crops that are currently offered include lettuce, basil, parsley, kale, mint and others, and are competitively priced, the firm said in a statement.
Israel and the oil-rich UAE signed a US-brokered normalization agreement in September, opening the way for business and tourism between the two countries, after years of covert trade exceeding $1 billion annually by some estimates.
The UAE, a federation of seven desert sheikdoms dependent on petrodollars, has been keen to cash in on the influx of Israeli investment and travel, particularly after the pandemic diminished demand for oil and hammered international tourism.
Earlier this month, Vertical Field signed an agreement with Moderntrendo S.R.O, an agricultural distributor in Ukraine, to deploy its plant installations in supermarket chains nationwide.
In December Vertical Field also signed a “multi-million dollar” agreement with Israeli discount supermarket chain Rami Levy for the installation of its vertical farming containers on the stores’ premises.
Vertical Field is based in Ra’anana in central Israel and was founded in 2006.