Welcome to iGrow News, Your Source for the World of Indoor Vertical Farming
Eat Local, Think Global
Regardless of how large or small their community is, 70 percent of people recognize the importance of purchases that support their local economy, and about 60 percent value locally grown products when they go food shopping.
August 2, 2021
Confronted with so much uncertainty last year, many people took comfort in the simple act of supporting their neighborhood retailers. And when it comes to food shopping in particular, research suggests that Americans’ desire to buy from local and regional growers won’t be fading anytime soon. Regardless of how large or small their community is, 70 percent of people recognize the importance of purchases that support their local economy, and about 60 percent value locally grown products when they go food shopping.
It doesn’t hurt that local food is more readily available, even in the midst of a crisis, according to the majority of shoppers. But the benefits of filling grocery carts with locally sourced items, especially produce, extend well beyond convenience alone. For starters, purchases from local growers can generate income for other local businesses. Additionally, produce that has traveled shorter distances to reach grocery store shelves tastes fresher and retains more of its nutrients. Moreover—and perhaps most important for today’s environmentally conscious consumers—shopping from local and regional growers can help curb carbon emissions, waste and pesticide use.
A harvest crew manager transports fresh kale to the Consalo Family Farms central warehouse in Vineland, N.J.
“It's about building relationships. We grow our business together, so we’re both in it together.”
Ricardo Dimarzio, Mid-Atlantic Produce Sales Manager for Safeway
A harvest crew manager transports fresh kale to the Consalo Family Farms central warehouse in Vineland, N.J.
Some grocery stores are helping lead the way forward for a local food movement that benefits the environment. Safeway, for example, has been working with sustainable local and regional farmers for generations, and more recently began sourcing vegetables and herbs from low-impact vertical farms in the D.C. area. These efforts are reducing negative effects on the planet, while also ensuring that shoppers get the freshest blueberries and crispest salad greens. What’s more, Safeway’s approach is helping support a network of family growers and modern farming companies alike.
“It's about building relationships. We grow our business together, so we’re both in it together,” said Ricardo Dimarzio, Mid-Atlantic Produce Sales Manager for Safeway.
How local farming provides a foundation for a sustainable food system
Over the past two years, half of consumers have adjusted their eating habits in an effort to live more sustainably, whether that has meant cutting down on food waste, paying more attention to food companies’ environmental impacts, or adding more fresh and local foods to their diets. But the pandemic showed people just how important those habits can be to their health and survival, according to food industry experts. Eating certain fruits and vegetables can boost immunity, for example, especially if they are picked fresh.
“Locally grown crops are being harvested at their peak. That's when they're dense in nutrients,” said Chelsea Consalo, who represents the fourth generation of New Jersey-based Consalo Farms, which began doing business with Safeway in the 1960s. After they’re picked, local fruits and vegetables spend less time in transit, ultimately reaching grocery stores and consumers more quickly and with nutrients intact. On the other hand, when produce is shipped across long distances, factors such as air quality, artificial lighting and temperature changes during transport can lower foods’ nutritional value, according to Consalo. Her family farm specializes in growing, packing and shipping blueberries, citrus fruits, cooking greens, herbs, salad items and hard squash, all of which can be found at Safeway stores in the Mid-Atlantic region.
Peppers grow at Consalo Family Farms.
Workers harvest beets at Consalo Family Farms.
A worker harvests blueberries.
Blueberries at Consalo Family Farms.
Chelsea Consalo, vice president of produce operations for Consalo Family Farms (left), and her sister Sarah, the finance manager.
Consalo Farms also exemplifies how growers can contribute to a more sustainable food system. For starters, shorter shipping distances mean less fuel consumption and air pollution. Consalo Farms also has a local recycling program and is working to reduce waste by using top-seal packaging that contains 35 percent less plastic than conventional packaging materials. Another big priority for the farm is water conservation, which the family achieves through an app-controlled drip irrigation system that sends just enough water to crops at specific time intervals. Soil health also contributes to the farm’s overall sustainability and helps cut down on water use, according to Consalo.
“Something as simple as mulching increases moisture retention in the soil, and it can regulate the soil temperature,” she said.
How a local food supply chain works
Local produce can benefit our health, our planet and our taste buds.
The environmental benefits of choosing local food at the grocery store
The basis of Safeway’s relationship with Consalo Farms—high quality products, delivered consistently—is still there. What has changed is how both sides approach sustainability. For the Consalo family, new technologies are making it possible to boost water conservation and soil health and cut back on packaging waste. For Safeway, efforts to work with more regional and local growers have only intensified. The company has stopped shipping California produce to its East Coast stores, for instance, in favor of stocking its produce sections with seasonal, regional specialties, whether it’s blueberries from New Jersey in June, honeycrisp apples from Pennsylvania in the fall, or corn and watermelon from Maryland during the summer.
“They grow it right there and they ship it right there, and it's in our warehouse within two hours. That's what's going to be the future.”
Ricardo Dimarzio, Mid-Atlantic Produce Sales Manager for Safeway
Harvested rainbow chard at Consalo Family Farms.
Fostering relationships with local growers has been crucial for Safeway, according to Dimarzio. By giving local and regional farmers regular business, Safeway can be among the first to know when new products come available. To that end, Safeway has also branched out beyond traditional agriculture to work with a new integrated farming company called Bowery Farming, which grows a variety of salad greens and herbs at its vertical greenhouse in Baltimore. The company is also experimenting with growing strawberries and cucumbers, according to Dimarzio. Safeway is able to specify which products they want to buy, how much they need and when they need it, reducing food waste and ensuring a fresher product. Lettuce, microgreens, and basil, for instance, are all cut to order.
“They grow it right there and they ship it right there, and it's in our warehouse within two hours,” Dimarzio said. “That's what's going to be the future.”
These kinds of efforts ultimately help ensure that shoppers can access the freshest possible products, get the most nutritional benefits, and know that they’re doing their part to help reduce waste and carbon emissions. And they’ll be supporting people like Consalo, who is paying it forward by donating blueberry plants to a local school and speaking to students about local agriculture and sustainability. In turn, she said, “the community can support the farms.”
Lead Photo: Driven by the pandemic and the growing environmental movement, grocery shoppers and stores alike have a renewed appreciation for locally grown products
How Do We Build Sustainable Local Food Systems?
Food Tank, in partnership with the Danone Institute North America, is hosting a very special virtual event, "One Planet. One Health," to discuss solutions to build more sustainable local food systems on Thursday, May 6, 2021, at 12 p.m. ET
Let's Work Together to Build Sustainable,
Local Food Systems With a Global Impact
Food Tank, in partnership with the Danone Institute North America, is hosting a very special virtual event, "One Planet. One Health," to discuss solutions to build more sustainable local food systems on Thursday, May 6, 2021, at 12 p.m. ET.
We’ve curated a terrific lineup of speakers, including luminaries like N. Diane Moss (Project New Village), Dariush Mozaffarian (Friedman School of Nutrition Science & Policy, Tufts University), Jose Oliva (HEAL Food Alliance), A-dae Romero-Briones (Cochiti/Kiowa, First Nations Development Institute), Tambra Raye Stevenson (WANDA), and more.
I’ll be moderating. You can register here.
Also, I strongly urge eligible nonprofits to apply for the Danone Institute North America grant program to help local communities live the "One Planet. One Health" vision.
Danone Institute North America will award a total of up to $160,000 for this initiative. Individual team grants of $30,000 plus a $10,000 incremental award for the team with the strongest communications plan will be awarded for work to be conducted over a two-year period. The call for entries is open now through June 6, 2021. For information and to submit an application, visit Danone Institute North America here.
Danone Institute North America launched the "One Planet. One Health" Initiative grant program in 2019 to support local projects that strengthen food systems, reflecting Danone’s belief that the health of people and the health of the planet are interconnected.
"The pandemic has not only sparked a health crisis but also has emerged as one of the most destructive economic and societal challenges of our time," says Leslie Lytle, President of Danone Institute North America and professor at the Gillings School of Global Public Health at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill.
Please let me know if you apply for the grant, and join me for free on May 6 by registering HERE.
All the very best,
Dani
A Greenhouse In A Box For Small Farmers
Hyderabad-based startup Kheyti’s focus on small farmers has attracted the interest of US-based impact investment firm Acumen
Lush growth inside a low-cost Kheyti greenhouse in Telangana.
With one-tenth of the water and pesticides required and a manifold increase in yield, greenhouses can be transformative. The catch is that their upfront investment cost puts them beyond the reach of those who need them the most—small farmers dependent on rain or borewells. But what if a minimalistic greenhouse is designed from the outset, keeping in mind the needs and limitations of small farmers?
Hyderabad-based Kheyti has partnered with manufacturing and design companies to introduce such a concept. Its modular greenhouse kit, including a drip irrigation system, occupies just a tenth of an acre and costs less than ₹1 lakh. That’s much smaller and cheaper than normal greenhouses which only large farmers can afford. Around 500 farmers in Telangana are the early adopters of this “greenhouse in a box", which comes along with inputs like the appropriate seeds and fertilizers.
It began on a 1.8-acre farm in Narayanpur village, 60km north of Hyderabad, in 2017, recalls Kaushik K., co-founder, and CEO of Kheyti. “Venkatesh and his wife Lakshmi were growing rice along with some vegetables on the side. They worked hard, but their annual income of ₹30,000 barely sufficed for a family of five. The biggest challenge for them was that they could not fully utilize even their 1.8 acres of land because their borewells would run dry in the summer months," says Kaushik.
Model farm
Kheyti had set up an R&D farm on the outskirts of Hyderabad to demonstrate its greenhouse to small farmers. Venkatesh was among the first to visit the farm. “We showed him he could grow high-quality vegetables with so much more yields. But he had only one question: How much water would it need? When we explained that for the greenhouse he would run his borewell pump for only five minutes compared to an hour’s running time for his open field, he was ready to sign up," says Kaushik.
There was a hitch. The ₹5 lakh cost of the greenhouse was relatively low but still too much to raise for the likes of Venkatesh. So, why not make it even smaller and more affordable? It’s from such interactions that Kheyti’s greenhouse designs evolved.
“Venkatesh was the first one and after getting his greenhouse, he continued to give us feedback on what we should do for the next version," recounts Kaushik.
Today, Kheyti offers a 400 sq. m greenhouse for ₹80,000, with insect netting, shade netting, and polyethylene sheets to protect crops from pests, heat and excessive rain. That compares favourably with the ₹25 lakh that a one-acre (4,047 sq. m) greenhouse of this type would cost.
Local Vertical Farm Startup Joins Growing Global Market
Ortaliza Urban Farms is a dream that has been sprouting for some time now.
What if there was a more sustainable way to provide fresh, truly local greens to our communities? And what if there was a way to do it while bringing diverse flavors to the table year-round?
It sounds like an ambitious goal. But it is one that Carina Biacchi and her partner, Alvaro Fernandes, are set to meet.
Ortaliza Urban Farms is a dream that has been sprouting for some time now.
Carina Biacchi is no stranger to business. With a bachelor’s and postgrads in business administration, she has worked in several different sectors, from NGOs to massive corporations. “I’ve mostly worked in sales and marketing” Carina states. “And I have entrepreneurship in my DNA. My parents were entrepreneurs long before I was born.”
And as formidable as Carina is, she is among good company. Alvaro Fernandes, her partner, is an Agronomist Engineer. “He’s a passionate specialist in controlled environment agriculture” Carina explains.
When the two met they quickly started dreaming about their own indoor farm. Years passed, and the two immigrated to Canada and started a family. But those entrepreneurial sparks continued to fly.
“It took us a while to build our lives in Canada,” Carina states. “But we continued to research the idea we had. We kept visiting other businesses in the industry and we even traveled to New York and other areas to see what they had to offer in terms of vertical farms.”
But what is vertical farming? Vertical farming is a growing worldwide phenomenon set to add significant value to the food system. Food security and sustainability continue to be some of the top concerns for city planners, and venture capital firms are investing big into vertical farm operations.
And what is an urban farm? Simply put, urban farming is growing food in urban areas. “We’re located right on Main Street,” Carina states. “In a commercial zoning area. That is pretty unique by itself, and the town of Kingsville has proven to be the perfect partner to help us launch our dream.”
A hyper-local farm-to-plate experience
And while Ortaliza is not the first micro green seller in the region, they are the first to create a storefront, creating an exciting farm-to-plate experience, loaded with flavor and freshness.
“We are truly local!” Carina stresses. “Sometimes, when you see that something is “local” on your grocery shelves, it’s actually from another part of the Province. That might be fine for large vegetables, but greens are special. Think of all the nutrients you would get from a full vegetable but concentrated to deliver all that deliciousness in every single bite. Microgreens require just-picked freshness, so we are super, hyper-local. We’re only growing and selling here in our County.”
This business model, Carina explains, also allows them to reduce food mileage and consequently, food waste. “Leafy greens in Canada can sometimes travel thousands of miles before reaching their destination” Carina reports. “And it can take up to two weeks for the produce to get there. We have a commitment to sustainability, and we will always be local, no matter where we spread our roots to in the future.”
One of Ortaliza’s business Advisors, Adam Castle of WEtech Alliance says the launch of this business in Kingsville represents a unique opportunity for the Startup. “Here we are in the very heart of greenhouse agriculture, not just for Canada but seconded only to Holland from a global perspective,” says Castle. “So you’re planting yourself in a community that lives and breathes agriculture, who knows the value of being able to see where your food comes from and how it’s grown, at a time when the average consumer is more engaged than ever in providing the freshest, most sustainably grown food they can for themselves and their family. I applaud Kingsville for making room at their table for new kinds of agriculture, and being a business-friendly partner that our clients can count on.
“…it certainly fits hand-in-hand with the innovation and the diversification that we’re trying to identify with.”
One enthusiastic supporter of this innovative new business is Nelson Santos, the Mayor of Kingsville and the Deputy Warden of Essex.
“This isn’t your typical business, but it certainly fits in with the entrepreneurial spirit that we have in our community,” Nelson explains. “And it certainly fits hand-in-hand with the innovation and the diversification that we’re trying to identify with. They are touching on all the different aspects of what the community is looking for. Their business is one that is certainly going to turn quite a few heads. It’s very exciting, both in regards to the food aspect and the extension of agriculture.”
Ortaliza is now taking pre-orders for their home delivery service at www.Ortaliza.ca, which promises to deliver a lot more than leafy goodness.
“We want to be more than a farm-to-table service,” says Carina. “We want our customers to think of us as their weekly dose of living, natural vitamins that add easy nutrition to just about every recipe they can think of!”
To learn more and become a friend of the farm, head to www.ortaliza.ca or find them on social media at @OrtalizaFarms
A New FEZ "Karakalpak-Agro" Established In Uzbekistan
“….increasing the production of agricultural products, expanding its deep processing and increasing exports, effectively using the production potential of the region…”
Tashkent, Uzbekistan (UzDaily.com) - The Cabinet of Ministers adopted a resolution”On measures to organize the activities of the free economic zone “Karakalpak-Agro”.
In accordance with the decree of the President “On measures for the comprehensive socio-economic development of the Republic of Karakalpakstan in 2020–2023” on an area of 875.4 hectares in Amu Darya, Buzatausky, Kegeili, Konlikul, Kushgirot, Muynak, Nukus , Takhiatash, Turtkul, Khodjeyli, Shumanai and Ellikala districts, the SEZ "Karakalpak-agro" was created.
The functions of managing the activities of the FEZ "Karakalpak-Agro" are assigned to the State Unitary Enterprise "Directorate of the free economic zone" Nukus ".
The main tasks and directions of the SEZ "Karakalpak-Agro":
- attracting direct foreign and domestic investments for organizing modern greenhouses on a cluster basis, including hydroponic ones, as well as organizing the production of structures, equipment and other components for the construction of modern energy-efficient greenhouses;
- increasing the production of agricultural products, expanding its deep processing and increasing exports, effectively using the production potential of the region;
- encouraging the organization of the complete process of agricultural production from seeds to delivery to the market;
- introduction of effective mechanisms for providing greenhouses with seeds and seedlings of high-yielding crops demanded by the market, by creating conditions for organizing nurseries, as well as seed production;
- formation of a modern infrastructure for the provision of logistics services, assistance to agricultural producers in organizing the export of their products;
- widespread introduction of modern resource-saving technologies, the use of alternative sources of thermal energy in the organization of greenhouses;
- creation of research and production centers to assess the compliance of products with international standards.
The Council of Ministers of Karakalpakstan, together with the Ministry of Investments and Foreign Trade, the Chamber of Commerce and Industry and commercial banks, was instructed to develop a targeted program of facilities for the production of structures for greenhouses on the territory of Karakalpak-Agro within two months, with the allocation of vacant non-agricultural land.
"We’re Retrofitting With The Variables We Have In Place"
Planted Detroit introduces new 20.000 sq. ft. growing facility
“The Square Room is a big block of pink lights with eight levels, where all our growing is done. Everything after germination is done in the same room, both harvesting of our baby greens and microgreens. Because we’re almost done with our PARS (Planted Automated Racking System), which is the big automation,” says Megan Burritt, Managing partner at Planted Detroit.
From a mix-fused downtown neighborhood in Detroit, daily deliveries of ready-to-eat salads and fresh greens are transported to local retailers and restaurants. Planted Detroit makes a large contribution to the city’s share of fresh produce.
New facility
Planted Detroit has been in the middle of the construction of its new 20.000 sq. ft growing facility. The growing space has been a massive update to the company compared to its previous 6-level growing facility which was between 1500-2000 sq. ft. The same room was used for processing, packaging, harvesting, and so on. “It was rather crowded, says Megan, but the main goal was to keep everything tight for the construction to continue in the near surrounding. We’re very serious about biosecurity and we have a daily procedure for everyone who sets foot in our grow room to go through. Making sure our greens don’t come into contact with pathogens is our top priority.
The new growing room
The Square Room, one of our growing rooms, is highly automated, including an automatic harvester to ensure work-efficiency. Once everything is big enough to be transplanted out of their plug trays, PARS (Planted Automated Racking System) will be transplanted with gutters and then go into harvesting. On the other side of PARS, the gutters are taken down and harvested through Planted’s new automatic harvester.
Delivering directly to consumers
The company wants to reach a higher volume of customers as it’s aiming to obtain a consumer brand status. Next to that, the company is always on the lookout for finding more customers through other venues. “We want to go directly to consumers via our web-store to shorten food miles as much as possible, delivering the freshest and most delicious greens,” Megan says. In order to do that the company needed to have a bit more scale, trying to maximize the space they already had.
She adds: “Our farm maybe isn’t the square footage which we could have built from scratch, but we’re retrofitting with the variables we have in place. That is why we have done a combination of a microgreen vertical nursery and PARS for baby greens. Our direct customers wanted meal solutions and we’ve been able to deliver them that. We’ve been doing everything from seed to plate basically.”
Megan Burritt, Managing partner
New projects coming up
On the same campus, 10 meters away, a new farm will be constructed, under the company's office space. In this farm herbs and edible flowers will be grown in response to different customers' demands. Megan says that Planted Detroit’s wholesale customers got them to this point as they were very interested in herbs and edible flowers. “However we weren’t able to perfect these as well in the systems that our baby greens were in perfectly. That’s why we’ve been leaning into R&D lately because once finishing the construction of Farm 2 it will have excellent growing conditions that are better than they have been for those crops.”
Edible flowers are an interesting thing, says Megan, but the company has gotten so much interest in it. According to Megan there aren’t many farms in the US that are growing them. “They’re high priced at this point. It sort of sticks to our original innovation, namely what exists here in the food system and what does not. Where can we fill the ‘does not exist niche’ and satisfy the needs of our customers.”
The company is rolling out a subscription program sometime this year and figuring out where it fits into the fresh food subscription system and how they can partner with other parties in order to get produce closer to society. “It’s great to have this ag job, applied science to be able to do. In all the things we’ve been doing is hiring these Detroiters and showing that we can really create a really great culture of work. It’s really great to see we’re contributing to a better Detroit and a better tomorrow,” Megan states.
Team expansion
During 2020 most of the team stayed on by moving around working hours, so the farm could come back in full force. By the time all equipment was in place, 10 to 12 people were added to the team to have them fully trained before the system would be functioning. “It has been really wonderful to expand the team to see what our capacity is,” says Megan.
“Luckily we’ve been able to develop systems that have been resilient. We’ve seen so many different patterns in consumer behavior but they seem to have fallen in our favor. People are eating more at home, shopping for groceries more, and that triggered our pivot focusing on direct consumers. But now, it’s perfectly in line with our strategy on how we go to market. As long as we can supply our customer needs we’ll be on the right path. Nothing but bright hopes for the future right now,” Megan affirms.
For more information:
Planted Detroit
Megan Burritt, Managing partner
megan@planteddetroit.com
www.planteddetroit.com
Author: Rebekka Boekhout
© VerticalFarmDaily.com
New York’s Gotham Greens Plans Solano County Indoor Produce Farm
It will be located on 33.6 acres of agricultural land purchased from the university adjacent to Interstate 80.
GARY QUACKENBUSH
FOR THE NORTH BAY BUSINESS JOURNAL
Example of the greenhouse operated by Gotham Greens which announced plans to open in Solano County (Photo courtesy of Gotham Greens)
Gotham Greens Holdings LLC, a firm with indoor agriculture operations across the U.S., Tuesday, announced plans to build a facility next to the University of California, Davis.
The first phase of this 10-acre Solano County facility is expected to open later this year. It will be located on 33.6 acres of agricultural land purchased from the university adjacent to Interstate 80.
The company stated its plans will provide it with the ability to deliver fresh leafy greens, herbs, plant-based dressings, dips and cooking sauces to more retailers, foodservice operators and consumers on the West Coast.
“… We are partnering with one of the highest-ranked agricultural research centers in the world to advance the entire agriculture system,” said Viraj Puri, co-founder and CEO of Gotham Greens. “California is responsible for growing one-third of the country’s vegetables and two-thirds of the nation’s fruit, yet in recent years, issues surrounding drought, food safety and worker welfare have demonstrated the need for continued innovation.”
The greenhouse will generate 60 full-time jobs and provide UC students with the opportunity to learn first-hand how to sustainably grow produce year-round in a safe, clean, climate-controlled environment. The company stated its facilities use 95% less water and 97% less land than conventional farming. Nationwide, Gotham Greens has 500,000 square feet of greenhouse space at five locations staffed by 400 employees.
The UC Division of Agriculture and National Resources and the UC Davis College of Agriculture and Environmental Sciences has entered into a partnership with Gotham Greens to advance research and innovation in the areas of indoor agriculture, greenhouse technology, and urban agriculture to help advance the science, workforce technology, and profitability of indoor agriculture globally.
“We are building a Controlled Environment Agriculture Consortium to support and advance the indoor farming industry, grow more fresh produce on less land and create new jobs for Californians,” said Gabriel Youtsey, the division’s chief innovation officer. “Gotham Greens is an anchoring partner of this research and industry collaboration that we hope will spur innovation, create a new indoor farming workforce and support industry growth.”
Helene Dillard, dean of the college, said, “This partnership will offer our students the chance to learn best practices from leading experts in indoor farming.”
Gotham Greens recently raised $87 million in new equity and debt capital bringing the company’s total financing to $130 million to fuel the next phase of growth.
Founded in 2009 in Brooklyn, New York, Gotham Greens (gothamgreens.com) owns and operates greenhouses in New York, Illinois, Rhode Island, Maryland and Colorado. Its produce is available in more than 40 states and 2,000 retail stores, including Albertsons Companies (Safeway, Jewel-Osco, and Shaw’s), Whole Foods Market, Target, King Soopers, Harris Teeter, and Sprouts.
The company’s products can also be purchased through e-commerce sites including AmazonFresh, FreshDirect and Peapod.
Lead Photo: Gotham Greens
7 New HDB Carpark Rooftop Sites Offered For Rental For Urban Farming In Public Tender
More local produce. Part of Singapore's efforts to strengthen its food security is increasing its capability to produce food locally
Part of Singapore's efforts to strengthen its food security is increasing its capability to produce food locally.
To do this, more sites for urban rooftop farms atop multi-storey Housing Development Board (HDB) carparks are being offered for rental, via a public tender process that was launched today (Feb. 23).
Seven new sites
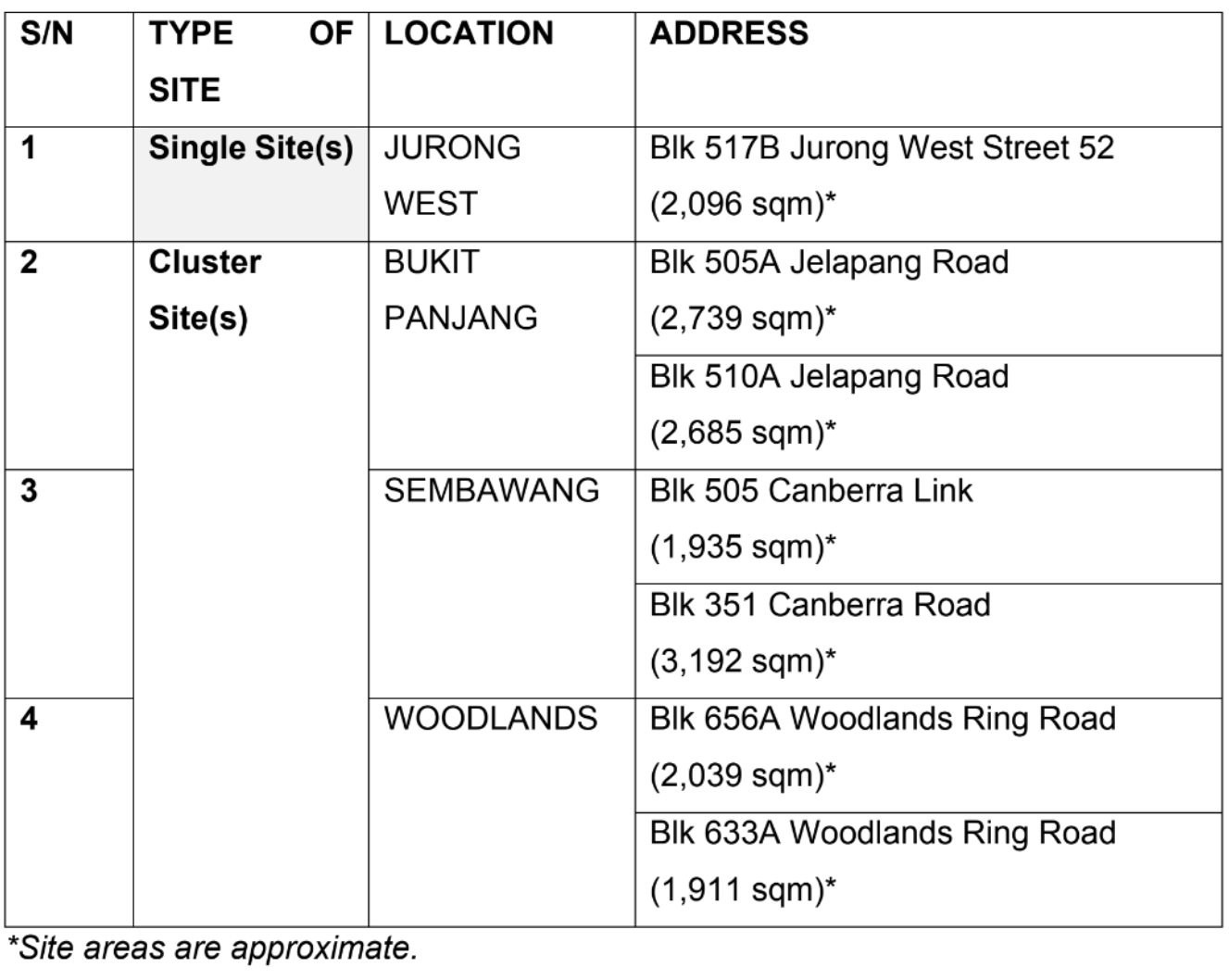
Seven sites have been identified in Jurong West, Bukit Panjang, Sembawang and Woodlands, according to the Singapore Food Agency (SFA) and HDB.
The sites will be used to farm vegetables and other food crops, and will also be used to pack and store produce.
They will be tendered out as a single site (in Jurong West) and three cluster sites (in Bukit Panjang, Sembawang and Woodlands).
Screenshot from SFA and HDB
Tenderers who successfully bid for cluster sites will be awarded all sites within the cluster, to allow them to cut costs through production at scale.
Single-site farms, on the other hand, provide opportunities to "testbed innovative ideas".
Tenderers must submit their proposals via GeBiz before the tender closes on Mar. 23, 4pm.
Proposals will be assessed on their bid price, production output, design and site layout, as well as their business and marketing plans.
More information can be found on SFA's website here.
Producing food locally
This is the second time tenders were launched for rooftop urban farms on carparks here — the first took place in Sep. 2020, with nine sites being awarded.
Collectively, the nine farming systems can potentially produce around 1,600 tonnes (1,600,000kg) of vegetables per year.
Having more space for commercial farming in land-constrained Singapore is one of SFA's strategies to achieve its "30 by 30" goal — which is to produce 30 percent of Singapore's food locally by 2030.
The move is also in line with HDB’s Green Towns Programme to intensify greening in HDB estates.
“Besides contributing to our food security, Multi-Storey Car Park (MSCP) rooftop farms help to bring the community closer to local produce, thereby raising awareness and support for local produce," said Melvin Chow, Senior Director of SFA’s Food Supply Resilience Division.
GoodLeaf Farms Launches Aggressive Expansion Plans
GoodLeaf will bring its innovative and proprietary controlled-environment agriculture technology to more Canadian markets over the coming year
NEWS PROVIDED BY
McCain invests in a national network of vertical farms to bring tasty, local food to Canadians
GUELPH, ON, - With the closure of a successful new funding round, GoodLeaf Farms is embarking on an aggressive growth and expansion plan to build a national network of vertical farms that will bring fresh, delicious, nutritious and locally grown leafy greens to Canadians across the country.
Backed by a sizeable investment from McCain Foods Limited — which has increased its total investment in GoodLeaf to more than $65 million — GoodLeaf will bring its innovative and proprietary controlled-environment agriculture technology to more Canadian markets over the coming year, providing more Canadian consumers with year-round local food that is typically imported from the Southern United States or Mexico.
"From our start in Truro to our first commercial farm in Guelph, GoodLeaf has built a strong foundation for future growth," says Barry Murchie, Chief Executive Officer of GoodLeaf. "We want to be a global leader in vertical farming. Our first step to accomplishing that is ensuring we have a strong footprint in Canada, giving Canadians access to top quality, nutrient-dense, sustainably grown and pesticide-free leafy greens 365 days a year."
GoodLeaf opened its first commercial vertical farm in Guelph, Ont., in the fall of 2019. By the end of 2021, GoodLeaf is planning two more indoor vertical farms — one to serve the grocery and foodservice networks in Eastern Canada, and one for Western Canada.
The exact locations will be announced shortly.
"It is our intention to build farms that support the Canadian grocery store network, foodservice industry and consumers," says Mr Murchie. "We want to change what people are eating by providing a fresh, healthy and local alternative that, until now, hasn't been available in Canada. We are driving a new way to grow food, with disruptive technology that brings consumers leafy greens from their own backyard. This is a fundamental game-changer."
GoodLeaf's vertical farm grows to produce on hydroponic trays stacked in multiple horizontal levels. A proprietary system of specialized LED lights is engineered to emulate the spring sun, giving plants the light they crave to maximize photosynthesis. The indoor controlled environment is almost clinical, meaning there are no pesticides, herbicides or fungicides used. It is also immune to weather extremes, such as summer droughts or late spring frosts that can be lethal to crops.
Furthermore, having a local source of year-round food is vital to Canada's food security and sovereignty, concerns that were in the spotlight at the height of the COVID-19 pandemic as shoppers were faced with rapidly dwindling supplies on grocery store shelves.
At its 45,000-square-foot Guelph farm, every day GoodLeaf is harvesting microgreens (Spicy Mustard Medley, Asian Blend, Micro Arugula, Micro Radish and Pea Shoots) and baby greens (Ontario Baby Kale, Ontario Baby Arugula and Ontario Spring Mix) for Ontario grocery stores, ensuring a local supply of fresh, nutrient-dense leafy greens all year long.
GoodLeaf produce is exceptional in a salad, as a topping for burgers and sandwiches, as a kick of nutrients in a smoothie or as an ingredient to elevate your favourite dish.
Follow GoodLeaf Farms on Instagram @goodleaffarms and Like it on Facebook at /GoodLeafFarms.
About GoodLeaf Farms:
With a passion for delicious, nutrient-rich greens, GoodLeaf was founded in Truro, NS, in 2011. Using innovative technology and leveraging multi-level vertical farming, GoodLeaf has created a controlled and efficient indoor farm that can grow fresh produce anywhere in the world, 365 days of the year. The system combines innovations in LED lighting with leading-edge hydroponic techniques to produce sustainable, safe, pesticide-free, nutrient-dense leafy greens. GoodLeaf has ongoing R&D Programs in collaboration with the University of Guelph, Dalhousie University and Acadia University.
Learn more at goodleaffarms.com.
About McCain Foods (Canada)
McCain Foods (Canada) is the Canadian division of McCain Foods Limited, an international leader in the frozen food industry. McCain Foods is the world's largest manufacturer of frozen potato specialities, and also produces other quality products such as appetizers, vegetables and desserts that can be found in restaurants and retail stores in more than 160 countries around the world. In Canada, the company has eight production facilities with approximately 2,400 employees and, in addition to its famous French fries and potato specialities, makes frozen desserts, snacks and appetizers.
SOURCE GoodLeaf Farms
For further information: Michelle Hann, Senior Consultant, Digital and Communications, Enterprise Canada, mhann@enterprisecanada.com, 613-716-2118
Little Leaf Farms Raises $90M to Grow Its Greenhouse Network
Massachusetts-based Little Leaf Farms has raised $90 million in a debt and equity financing round to expand its network of hydroponic greenhouses on the East Coast. The round was led by Equilibrium Capital as well as founding investors Bill Helman and Pilot House Associates. Bank of America also participated.
by Jennifer Marston
Image from: Little Leaf Farms
Massachusetts-based Little Leaf Farms has raised $90 million in a debt and equity financing round to expand its network of hydroponic greenhouses on the East Coast. The round was led by Equilibrium Capital as well as founding investors Bill Helman and Pilot House Associates. Bank of America also participated.
Little Leaf Farms says the capital is “earmarked” to build new greenhouse sites along the East Coast, where its lettuce is currently available in about 2,500 stores.
The company already operates one 10-acre greenhouse in Devins, Massachusetts. Its facility grows leafy greens using hydroponics and a mixture of sunlight supplemented by LED-powered grow lights. Rainwater captured from the facility’s roof provides most of the water used on the farm.
According to a press release, Little Leaf Farms has doubled its retail sales to $38 million since 2019. And last year, the company bought180 acres of land in Pennsylvania on which to build an additional facility. Still another greenhouse, slated for North Carolina, will serve the Southeast region of the U.S.
Little Leaf Farms joins the likes of Revol Greens, Gotham Greens, AppHarvest, and others in bringing local(ish) greens to a greater percentage of the population. These facilities generally pack and ship their greens on the day of or day after harvesting, and only supply retailers within a certain radius. Little Leaf Farms, for example, currently servers only parts of Massachusetts, Pennsylvania, New York, and New Jersey.
The list of regions the company serves will no doubt lengthen as the company builds up its greenhouse network in the coming months.
Bringing The Future To life In Abu Dhabi
A cluster of shipping containers in a city centre is about the last place you’d expect to find salad growing. Yet for the past year, vertical farming startup Madar Farms has been using this site in Masdar City, Abu Dhabi, to grow leafy green vegetables using 95 per cent less water than traditional agriculture
Amid the deserts of Abu Dhabi, a new wave of entrepreneurs and innovators are sowing the seeds of a more sustainable future.
Image from: Wired
A cluster of shipping containers in a city centre is about the last place you’d expect to find salad growing. Yet for the past year, vertical farming startup Madar Farms has been using this site in Masdar City, Abu Dhabi, to grow leafy green vegetables using 95 per cent less water than traditional agriculture.
Madar Farms is one of a number of agtech startups benefitting from a package of incentives from the Abu Dhabi Investment Office (ADIO) aimed at spurring the development of innovative solutions for sustainable desert farming. The partnership is part of ADIO’s $545 million Innovation Programme dedicated to supporting companies in high-growth areas.
“Abu Dhabi is pressing ahead with our mission to ‘turn the desert green’,” explained H.E. Dr. Tariq Bin Hendi, Director General of ADIO, in November 2020. “We have created an environment where innovative ideas can flourish and the companies we partnered with earlier this year are already propelling the growth of Abu Dhabi’s 24,000 farms.”
The pandemic has made food supply a critical concern across the entire world, combined with the effects of population growth and climate change, which are stretching the capacity of less efficient traditional farming methods. Abu Dhabi’s pioneering efforts to drive agricultural innovation have been gathering pace and look set to produce cutting-edge solutions addressing food security challenges.
Beyond work supporting the application of novel agricultural technologies, Abu Dhabi is also investing in foundational research and development to tackle this growing problem.
In December, the emirate’s recently created Advanced Technology Research Council [ATRC], responsible for defining Abu Dhabi’s R&D strategy and establishing the emirate and the wider UAE as a desired home for advanced technology talent, announced a four-year competition with a $15 million prize for food security research. Launched through ATRC’s project management arm, ASPIRE, in partnership with the XPRIZE Foundation, the award will support the development of environmentally-friendly protein alternatives with the aim to "feed the next billion".
Image from: Madar Farms
Global Challenges, Local Solutions
Food security is far from the only global challenge on the emirate’s R&D menu. In November 2020, the ATRC announced the launch of the Technology Innovation Institute (TII), created to support applied research on the key priorities of quantum research, autonomous robotics, cryptography, advanced materials, digital security, directed energy and secure systems.
“The technologies under development at TII are not randomly selected,” explains the centre’s secretary general Faisal Al Bannai. “This research will complement fields that are of national importance. Quantum technologies and cryptography are crucial for protecting critical infrastructure, for example, while directed energy research has use-cases in healthcare. But beyond this, the technologies and research of TII will have global impact.”
Future research directions will be developed by the ATRC’s ASPIRE pillar, in collaboration with stakeholders from across a diverse range of industry sectors.
“ASPIRE defines the problem, sets milestones, and monitors the progress of the projects,” Al Bannai says. “It will also make impactful decisions related to the selection of research partners and the allocation of funding, to ensure that their R&D priorities align with Abu Dhabi and the UAE's broader development goals.”
Image from: Agritecture
Nurturing Next-Generation Talent
To address these challenges, ATRC’s first initiative is a talent development programme, NexTech, which has begun the recruitment of 125 local researchers, who will work across 31 projects in collaboration with 23 world-leading research centres.
Alongside universities and research institutes from across the US, the UK, Europe and South America, these partners include Abu Dhabi’s own Khalifa University, and Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence, the world’s first graduate-level institute focused on artificial intelligence.
“Our aim is to up skill the researchers by allowing them to work across various disciplines in collaboration with world-renowned experts,” Al Bannai says.
Beyond academic collaborators, TII is also working with a number of industry partners, such as hyperloop technology company, Virgin Hyperloop. Such industry collaborations, Al Bannai points out, are essential to ensuring that TII research directly tackles relevant problems and has a smooth path to commercial impact in order to fuel job creation across the UAE.
“By engaging with top global talent, universities and research institutions and industry players, TII connects an intellectual community,” he says. “This reinforces Abu Dhabi and the UAE’s status as a global hub for innovation and contributes to the broader development of the knowledge-based economy.”
Fifth Season Takes Vertical Farming to a Whole New Level
Fifth Season’s verdant baby spinach screams farm fresh even though it’s grown nowhere near traditional farmland. The sweet and slightly crunchy greens are grown in a Braddock warehouse on racks stacked 30 feet high. Located just a stone’s throw from U.S. Steel’s Mon Valley Works Edgar Thomson Plant, it is urban farming at its core
Image from: Pittsburgh Post-Gazzette
Fifth Season’s verdant baby spinach screams farm fresh even though it’s grown nowhere near traditional farmland. The sweet and slightly crunchy greens are grown in a Braddock warehouse on racks stacked 30 feet high. Located just a stone’s throw from U.S. Steel’s Mon Valley Works Edgar Thomson Plant, it is urban farming at its core.
What makes the vertical farming operation especially unique is that it is automated and robots call the shots. About 40 to 60 machines are involved in every step of the life of the spinach and other leafy greens, from planting the seed to providing nutrients to the final packing.
Fifth Season does employ local “farm workers” to assist the robots in seeding, harvesting, packaging, quality assurance and control using computer software, but there is no human touch involved through it all.
“The first time someone ever touches the spinach leaf with a finger is when the package is opened,” says Grant Vandenbussche, chief category officer.
Co-founded by brothers Austin and Brac Webb and Austin Lawrence, Fifth Season started a year ago. Within months it was rolling out its baby spinach, leafy greens and salad kits.
“We wanted a name that represents what we are doing,” says Austin Webb, 32, who also is the CEO. “It is a call to the fact we have created an entirely new season. It is 24/7, 365 with the technology we have built.”
None of them planned to become modern farmers, says the Carnegie Mellon University grad, but they turned to vertical farming because it was an efficient, economically sustainable way to solve land and water woes.
Image from: thespoon.tech
‘Fields’ of Greens
Fifth Season grows an equivalent production of 200 acres in 25,000 square feet of grow space. Its “fields” are stacked on top of one another in vertical shelves. When you add up all that surface area of grow space, it is more like 126,000 square feet.
“We also quickly turn crops at the farm,” Mr. Vandenbussche says.
While spinach takes about 40 days to grow outdoors and can be harvested only twice during its peak season, it takes the crop only three or four weeks to grow in the controlled environment and is harvested 19 times. Once the plants are harvested, a new cycle of reseeding begins with fresh media, seeds and nutrients.
“That’s why we get so much more productivity,” he says. “We are immediately reseeding our ‘land.’”
This controlled environment yields quality produce because it is always peak season at Fifth Season, says Chris Cerveny, who heads the Grow R&D division. Greens are grown in the same conditions year-round, getting the exact amount of nutrients and water they need. Because pests and airborne toxins also are kept at bay, crops can be produced without pesticides.
All that TLC comes through in the slightly curled baby spinach, which is sweet and not grassy. The leaf doesn’t wilt or get slimy or lose its slight crunch even after two weeks of refrigeration.
A lot of thought was given even for the curl, which gives the spinach a stronger volume, making it look full and bountiful. The curl also makes the spinach more forkable unlike its flat-leaf counterpart that is hard to stab on a plate.
Other leafy greens such as kale, mustard, Chinese cabbage, green tatsoi and purple pac choi are featured in two blends — Bridge City and Three Rivers. Fifth Season plans to roll out its Romaine lettuce in spring.
The greens also are found in four types of salad kits — Sweet Grains (blended greens, quinoa, chickpeas, corn, feta and poppy seed dressing), Crunchy Sesame (blended greens, farro, sesame sticks, dried cranberries and ginger-mandarin dressing), Toasted Tuscan (spinach, lentils, sun-dried tomatoes, bagel chips and vinaigrette), and Spiced Southwest (blended greens, black beans, pepitas, cotija cheese, corn-salsa sticks and chipotle ranch dressing) — which are available online and in Giant Eagle stores. A fifth salad kit is in the works and is being called “a shakeup of one of the most classic salads.”
While machines are a big part of what Fifth Season does, it seeks to keep human connection alive. It recently launched a recipe blog for those who have an appetite for cooking and writing, The Green Room is devoted to cataloging personal memories, dream meals and recipes via short stories.
Fifth Season also has partnered with the Penguins and is providing greens for the team’s pregame meals for the 2020-21 season.
“We want people in Pittsburgh to be able to eat the exact same delicious blend of greens that Sidney Crosby and company are eating,” Mr. Webb says. “We want people to know that there’s a new way to grow food and to eat and experience it.”
Image from: Next Pittsburgh
It’s All Under Control
Everything from seeding to packaging is done in four rooms. The process starts in the seeding and processing room, where seeds and growing media are placed inside black planter-like boxes called inserts. Each has a unique code that’s traced by a software system. The inserts go on white trays that pass through a photo station, feeding information to the computer system, and then glide into the bio dome.
There are two rooms in the bio dome, each with a grow space of 12,500 square feet. They’re lit up with a pinkish-purplish glow from high-efficiency LED light bulbs that mimic the different seasons of the year.
“They are positioned over the plants at different heights depending on stage of growth,” Mr. Cerveny says. “This is partly how we can provide consistently ideal growing conditions.”
As the plants grow, they are moved by a robot to optimize their growth cycle. Full-grown crops are transferred to the harvesting room by another robot.
“Harvesting is where it becomes like a Willy Wonka factory,” Mr. Vandenbussche says.
Long rows of trays filled with tiny plants are sent on a conveyor system to a station where workers inspect them for quality with surgical tools. After inspection, the plants are harvested by a robot and then immediately ride up a tall conveyor to be packaged and sealed in a 34- to 36-degree room so they remain fresh.
“Every crop we grow gets evaluated for maximum flavor, volume, crunch and color,” he says.
The plants’ intense, dark color is controlled by LED light bulbs, which are dialed up or down to get the correct hue. Although they never see the sun, the greens don’t get into a funk as humans might.
“What humans see in terms of light and how chlorophyll responds during photosynthesis are two different things,” Mr. Cerveny says. “Plants really only need red and blue light to grow effectively. We include some additional colors to help bring out other quality aspects of our crops, but providing the full sunlight spectrum is effectively a waste of energy, especially indoors.
“To the human eye, it looks like the plants live in a land of purple and pink lights, but they are perfectly happy there.”
Even though the environment is controlled and the software system is constantly updated, no two plants are exactly the same. Some fight for light more than others. Some might fail the quality control test and end up in a compost waste facility if their flavor is off or their color is not right.
“That is what is so amazing. We have more control than any other farmer, and yet we have limitations. Every seed is different,” Mr. Vandenbussche says. “They are plants. They are real living organisms.”
Is AppHarvest the Future of Farming?
In this video from Motley Fool Live, recorded on Jan. 28, Industry Focus host Nick Sciple and Motley Fool contributor Lou Whiteman discuss AppHarvest, one such SPAC that is looking to disrupt the agriculture industry. Here are the details on what AppHarvest wants to do, and a look at whether the company represents the future of farming.
Special purpose acquisition companies, or SPACs, are red-hot right now, with investors clamoring to get into promising young companies.
In this video from Motley Fool Live, recorded on Jan. 28, Industry Focus host Nick Sciple and Motley Fool contributor Lou Whiteman discuss AppHarvest, one such SPAC that is looking to disrupt the agriculture industry. Here are the details on what AppHarvest wants to do, and a look at whether the company represents the future of farming.
Nick Sciple: One last company I wanted to talk about, Lou, and this is one I think it's -- you pay attention to, but not one I'm super excited to run in and buy. It was a company called AppHarvest. It's coming public via a [SPAC] this year. This vertical farming space. We talked about Gladstone Land buying traditional farmland. AppHarvest is taking a very different approach, trying to lean into some of the ESG-type movements.
Lou Whiteman: Yeah. Let's look at this. It probably wouldn't surprise you that the U.S. is the biggest global farm exporter as we said, but it might surprise you that the Netherlands, the tiny little country, is No. 2. The way they do that is tech: Greenhouse farm structure. AppHarvest has taken that model and brought it to the U.S. They have, I believe, three farms in Appalachia. The pitches can produce 30x the yields using 90% less water. Right now, it's mostly tomatoes and it is early-stage. I don't own this stock either. I love this idea. There's some reasons that I'm not buying in right now that we can get into. But this is fascinating to me. We talked about making the world a better place. This is the company that we need to be successful to make the world a better place. The warning on it is that it is a SPAC. So it's not public yet. Right now, I believe N-O-V-S. That deal should close soon. [Editor's note: The deal has since closed.] I'm not the only one excited about it. I tend not to like to buy IPOs and new companies anyway. I think the caution around buying into the excitement applies here. There is a Martha Stewart video on their website talking up the company, which I love Martha Stewart, but that's a hype level that makes me want to just watch and see what they produce. This is just three little farms in Appalachia right now and a great idea. This was all over my watchlist. I would imagine I would love to hold it at some point, but just be careful because this is, as we saw SPACs last year in other areas, people are very excited about this.
Sciple: Yeah. I think, like we've said, for a lot of these companies, the prospects are great. I think when you look at the reduced water usage, better, environmentally friendly, all those sorts of things. I like that they are in Appalachia. As someone who is from the South, I like it when more rural areas get some people actually investing money there. But again, there's a lot of execution between now and really getting to a place where this is the future of farming and they're going to reach scale and all those sorts of things. But this is a company I'm definitely going to have my radar on and pay attention to as they continue to report earnings. Because you can tell yourself a story about how this type of vertical farming, indoor farming disrupts this traditional model, can be more efficient, cleaner, etc. Something to continue paying attention to as we have more information, because this company, like you said, Lou, isn't all the way public yet. We still got to have this SPAC deal finalized and then we get all our fun SEC filings and quarterly calls and all those sorts of things. Once we have that, I will be very much looking forward to seeing what the company has to say.
Whiteman: Right. Just to finish up along too, the interesting thing here is that it is a proven concept because it has worked elsewhere. The downside of that is that it needed to work there. Netherlands just doesn't have -- and this is an expensive proposition to get started, to get going. There's potential there, but in a country blessed with almost seemingly unlimited farmland for now, for long term it makes sense. But in the short term, it could be a hard thing to really get up and running. I think you're right, just one to watch.
“I’m Opting For Localized Franchised Farming”
Engineering student wants to start her own farm in New Jersey
“In the States, the food system is so inefficient both in the way it’s produced, at a massive scale and in terms of quality,” says Natalie Radu. "The problem is that consumers are left in the dark. They don’t know what pesticide is used on the food they’re eating. GM foods are not labeled. Let aside the waste this industry has.” Natalie says that many don’t have access to healthy food. When walking around in the Bronx for instance, on the lookout for a grocery store, it’s so much easier to buy a pack of soda for half the price of fresh produce.
‘Localized franchised farming’
“McDonald's is known for real estate. If only we could do a Wholefoods / McDonalds franchise where customers could walk in and snip off lettuce, directly available to consumers. I’m opting for localized franchised farming. I have been trying to figure out a location in terms of real estate, but, from the perspective of a small business, New Jersey and New York prices are very high. I would have to start out in a place that’s cheaper on average. However, I would definitely apply for grants to fund the initial infrastructure for the farms."
Natalie Radu in action on her channel
Natalie has her passion for writing and her engineering study to her advantage when starting a farm. “I think because of this intersection I will be able to work with the science and also have the ability to convey that science. I can make the lettuce we’ll be growing feel personal for someone that’s in their own house, miles away or even across the world. That’s the biggest thing, you have to get people excited about vertical farming, at least as excited as you are. However, when it comes down to engineering I’m going to need some help.”
“My family immigrated from Moldova to the US around the collapse of the Soviet Union,” says Natalie. “My grandparents used to grow several fruits in the backyards and my affection for farming started right about there, it’s in my blood.” Natalie, an 18-year-old engineering student has been determined to run her own farm in the future. It all started with finding a proper research topic, which turned into her biggest passion nowadays.
As Natalie’s based in New Jersey, she is surrounded by several vertical farms. She wanted to pass by some farms near her to visit and stumbled upon Good Feeling Farms. Eventually, Natalie was able to do an internship at Good Feeling Farms to get a better understanding of every aspect of a vertical farm, from seeding to growing to harvesting. Good Feeling Farms is a New Jersey-based wholesale micro greenery that specializes in microgreens and hydro lettuce. The farm is run by a team of three, taking care of the cultivation and harvesting process.
Inside Good Feeling Farms' growing facility
Ever since her internship, Natalie is determined to run her own farm in the future. She currently runs a YouTube channel, where she experiments with indoor hydroponics. She recently spoke at a local TEDx event about the inefficacies in traditional food production and distribution systems.
Natalie says: “I’ve tried many growing conditions for plants and I think you can grow them under many different conditions. You have to work with your circumstances. Ideally, your indoor garden would be sustainable. The growth mediums could be sanitized and reused to lessen waste. Besides being water-efficient, vertical farming really shines in the areas of automation and data science. The ability to collect and analyze plant data constantly and instantly modify environmental factors has massive potential for produce cultivation as we know it.”
For more information:
Natalie Radu
natlydrad@gmail.com
Author: Rebekka Boekhout
© VerticalFarmDaily.com
A Leading NYC Mayoral Candidate Thinks Roof Farms Can Save America’s Cities
On the Eater’s Digest podcast, Eric Adams talks healthy eating, urban farming, and food deserts
Brooklyn Borough President Eric Adams distributing food
Photo by Andrew Lichtenstein/Corbis via Getty Images
Later this year, the voters of America’s largest city will elect a new mayor. New York’s next leader will contend with budget crises, a small business sector in a free fall, a struggling mass transit system, a school system in open revolt, and a grieving populous. They also have an opportunity to help the city redefine itself and its values and priorities.
Brooklyn Borough President Eric Adams, one of the leading candidates in the race right now, believes food is a key component in any future recovery. Passionate about urban farming, he wants to set up a citywide network of vertical and rooftop farms that feed hospitals, schools, prisons, and beyond while educating schoolchildren and getting trucks off the road. He believes in the ability of healthy food to fight the chronic illnesses the plague Black and brown communities across the city, having reversed his diabetes diagnosis with his diet. And he believes in cutting through the bureaucracy of city government to make it all happen.
Last month, Borough President Adams came on the Eater’s Digest podcast to discuss why food needs to be central to any conversation around environmental, economics, and health.
Read below for the full transcript of our conversation with Adams.
Amanda Kludt: Today on the show, we have Brooklyn Borough President and New York City mayoral candidate, Eric Adams. I wanted to have him on the show because he’s very passionate about rooftop farming, getting healthy food to food deserts, and using food as a weapon against chronic diseases like diabetes, which disproportionately impacts African-American communities. Borough President Adams, welcome to the show.
Eric Adams: Thank you, Amanda and Daniel. It’s great to be here and you started out, you said what I was passionate about, and I am probably one of the few people who have reached this level of government that I’m passionate about our universe. I think far too often when you are a part of the government, you become so scripted and you do not have personal narratives that make you and it forces you to look at life in a different way. I think that the dark moments in my life, I was able to take them from being burials to plantings. It led me to a journey of realizing the universality of our coexistence, not only with our mothers but mother earth.
I view everything through that prism. So sometimes you speak with me and you’ll say, “Okay. He’s an elected official.” Then another time, you say, “Wait a minute, this guy’s a hippie.” Then another time you’ll say, “Hey, this guy is some type of Sage.” I moved through all of these universes and it’s scary at first until people finally say, “Wait a minute, there’s more to life and our purpose than what we were told.”
AK: I love that. To that end, do you want to tell our listeners a little bit about your background, just a quick bio for those who are not familiar with your work and what you do?
EA: I was born in Brooklyn. Brooklyn is the largest borough county in the city of New York out of the five, 2.6 million people, extremely diverse, moved to Queens as a child. I was arrested by police officers who assaulted my brother and I, and that’s why the movement around police reform is so important to me. But instead of saying, “Woe is me.” I say, “Why not me?” I joined the police department. I started an organization for police reform and public safety at the same time. I became a Sergeant, Lieutenant, a Captain, and retired as a Captain. I went on to become a state Senator. Then after serving four terms, I became the first person of color to be the Borough President in Brooklyn. On the way, something called chronic disease hijacked or attempted to hijack my life. I was diagnosed with type two diabetes four years ago.
I woke up one morning and I could not see my alarm clock. I lost sight in my left eye. I was losing it in my right, had constant tingling in my hands and feet. That was permanent neuropathic nerve damage that would eventually lead to amputation, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, the American package. Instead of following the American route of using a prescription, I decided to use plants. In three weeks, after going through a whole full plant-based diet, my vision came back three months later, my diabetes went into remission, the nerve damage went away, and I dropped 35 pounds. I like to tell people I don’t have a six-pack. I have a case now.
AK: That is remarkable. One of the reasons I wanted you on here is because you have ideas around rooftop farming. You’ve talked about how Queens and the Bronx were farmland originally. So can you talk about what you’d like to do there and what kinds of businesses you’d like to build for the city?
EA: I’m in this place where one solution solves a multitude of problems. So we were an agrarian economy at one time. We’re cycling out of COVID. We are going to have a real problem around food. COVID reveals that comorbidities and preexisting conditions led to a higher rate of hospitalizations and deaths. We’re dealing with food deserts throughout our entire city, particularly in economically challenging communities. So look at all of those areas and now say to ourselves, “Our environment is going through a terrible time because there are too many trucks on the road. So why not use our rooftops? Why not look at using vertical farming, using everything from hydroponics, and let’s start with our school system.” We feed 960,000 children a day.
AK: Wow.
EA: Why not say, “Let’s turn to food.” And by growing the food using rooftops, using classrooms, using empty factory spaces, the person who invents and expands this system now will have enough money to leverage long contracts. So if I go to the companies and state that, “Hey, I’m going to give you a five year guarantee contract that you’re going to grow the vegetables and some of the fruits that you’re about to provide to our school system,” you now can leverage that to go into the science and to expand. What do we do in the process? You’re going to teach my young children a nutritionally-based education so they can learn this multibillion-dollar industry of urban farming. They’re going to be skillful in it. And these are the jobs of the future, because 40 percent of the jobs we’re training our children, for now, won’t be available because of computer learning and artificial intelligence. But we’re always going to eat.
Then we take the trucks off the road that are feeding our Department of Education. Then we have the children built into this civic educational plan of identifying food desert, food apartheid, and do nutritionally-based education in their communities so that you can go into the bodegas and local stores and storefronts and start making available fresh fruits and vegetables. Then we go to the Department of Correction and start feeding them healthy meals instead of the meals we’re feeding them. Then we supply them to the hospitals. So this will continue to expand based on the buying power and the leverage we have as a city.
Daniel Geneen: So have you actually been able to incentivize or figure out ways to incentivize or mandate some farms in Brooklyn already, or is this something you’re thinking about for the future?
EA: It’s here. We put a substantial amount of money into our schools, the Department of Education, one of the largest school systems in the country, and we put a substantial amount of money into schools with children, learning how to deal with growing food in the classroom. We partnered with an amazing organization called Farmshelf, and look at what happened with this group that we partnered with. They have this sort of unit that’s the size of a refrigerator with a growth of vegetables inside of the refrigerators in the classroom. The children are connecting with local public housing to give the freshly grown food to. But the children in this school, Democracy Academy, it was an alternative high school where the children were not coming to class. When we bought a couple of units and allowed them to be engaged with this farming inside the classroom, urban farming, the teacher said, “We can’t get them out of the school.”
“When we bought a couple of units and allowed them to be engaged with this farming inside the classroom, urban farming, the teacher said, ‘We can’t get them out of the school.’”
They found a purpose. Education is not feeding the creative energy of children. They’re not into this rote learning. They’re not into not being able to really look at their creative energies and find purpose. So some of the programs we have in the Department of Education, they have been extremely successful. We are trying to turn a public housing development called Marlboro Projects, we want to spend close to $13 million to build a two-story greenhouse that’s going to teach farming, education around farming, and how to deal with food deserts. The bureaucracy that’s in the way is unbelievable. We have been working on this project for about three years and that’s one of the problems we’re having. Too many people in government just don’t get it.
DG: Is it about getting the money together or is it about building it? What signatures do you need that you’re having trouble getting?
EA: Great question. It’s not about the money. I am allocating the money. We already have the money. The money is sitting there waiting to be spent. We have dueling rules and codes in our city and we don’t have a universal plan on, “Okay. We want to do urban farming. We want to do rooftop farms. We want to do vertical farming.” So our city and the city’s zoning and policies are stuck in the 20th century when the entire planet is evolving, technology is evolving. So when you go to people in these various agencies, they are professional naysayers, they say, “Well, we can’t do that.” And you say, “Why?” “Because we’ve never done that.”
DG: Right.
AK: Do you think there are opportunities for private/public partnerships here too, working with a lot of the landlords who might be looking for new opportunities to use their real estate right now?
EA: Yes. I think that is something that we are exploring because when you think about everyone is going to take a financial hit or through COVID, when I save, I diversify my savings. So if one part of my savings, a stock or my CDs go down, at least I’ve diversified it enough, but now landlords must start thinking outside the box. How do you diversify your plan? How do you diversify your buildings? We see that in some of the towers that are placed on buildings for cell phone usage, we can actually diversify the rooftops like some of the establishments in Industry City, The Navy Yard, they have different greenery grown on their rooftop. Our factories have an amazing amount of rooftop space. We’re not going to grow more land, but we have millions of feet of rooftop space that is underutilized and we believe we could use it a better way to grow food in a more healthier way.
DG: Because I assume education is a key component of this, but I imagine in a dream world for you, all of the rooftops would just be growing the food for New York to eat, right? It’s not just government-controlled farms. You’d want a lot of people growing their own stuff as well, right?
EA: Without a doubt. I believe that we... I think that we should return to an agrarian economy. I remember saying this to my team two years ago and they all walked out of the room and said, “He must be smoking that weed that’s illegal.” Now, they started talking to finance experts.
DG: And they’re like, “What if we grow that weed on the rooftops?”
AK: That’s how you make the money.
EA: But we partnered with NYU’s finance team there. They’re looking at it. They’re crunching the numbers and they said, “Wait a minute, this guy is onto something.” We partnered with Cornell University. People are seeing the do-ability of actually doing this, and I feel that all about rooftops can play a role. We can repurpose these rooftops to ensure that we can grow our food. We’re going to take trucks off the road ... There’s a great opportunity to redefine ourselves as a city.
“We can repurpose these rooftops to ensure that we can grow our food. We’re going to take trucks off the road”
DG: What is the red tape like for a private institution to grow on their rooftop? We’re very familiar with trendy restaurants having a farm on their roof and they’re like, “After your aperitif, come check out our farm,” or whatever. But if I have a big apartment complex and I’m like, “I want to turn my roof into a farm,” what kind of legal hurdles are there? Or can I just start doing it?
EA: Two pieces, Daniel. And that’s very important what you just stated and I hope listeners heard you. Racism is built into the structure of our society. We’re comfortable with a trendy restaurant in an affluent community, saying, “When you finish your tea and you finish your Merlot, now, go on up to the rooftop and we’re going to handpick some of your microgreens,” and it’s acceptable. But now, you go out to Brownsville and you have a group of residents that have stated, “We have all of this footage, all of the square feet of rooftop. We want to grow and have our gardens here.” Now, all of a sudden, the rules come out. All of a sudden, it becomes impossible to do.
It’s as though in our mind, people in economically challenged communities are not deserving of some of the finer things that we placed in other communities. So what the Department of Buildings, the Fire Department, the Department of Health, all of these different entities have not come together and started to say, “How do we make this happen?” That’s what we have to go do. I partnered with the former Councilman in Brooklyn, and we came together and said it’s time to get all of our agencies together that are in this space and come up with ways of making this happen. That is one of the goals that we have because they’re all over the place, they’re disjointed and that prevents us from moving forward. So you’ll get an approval in one agency just for another agency to be a complete contradiction of another agency.
DG: Yeah. No, it’s a great point. It’s also the perception of what they’re growing too. The trendy, New York restaurant, the perception of what’s being grown, people would be excited about it like, “Oh, that’s so cool. It’s grown right here,” but if it’s more industrial and it’s grown in a lower income neighborhood, the perception would be that it’s more like crops for feeding and not anything that people should be excited about.
EA: So true. I think that people miss the connection that we long for and we need with nature, not only with the growing of food locally, the plants are not only going to feed your body, but it feeds the anatomy of your spirit. Living in a concrete environment, not seeing the health of the food that you’re growing, not being a part of, not being connected to nature, we don’t realize it, but it plays on us and it takes away from who we are as human beings. That’s why when you go around public housing, you see a high level of violence, high level of chronic diseases, a high level of stress, mental health illnesses. It’s because of the environment people are in. I truly believe that if you turn it into a more green environment, more inclusiveness with nature, you’ll get a different outcome.
AK: I think that’s a great segue back into your personal journey. You actually just wrote a book about this, “Healthy At Last,” where you talk about how you change your diet to fight chronic disease and how in so many communities, there needs to be a push for this. There needs to be a push for eating healthier. Can you talk a little bit about your goals there and how you want to change the way that people eat in certain communities?
EA: Think about this for a moment. Three months of going to a whole food plant based diet, and I went from losing my vision, permanent nerve damage that was reversed, diabetes was also reversed, my ulcers went away, my blood pressure normalized, my cholesterol normalized in three months. Think about that for a moment. The people and I spent the entire ... Has it been nine months now with COVID? Every day of those nine months, I have been in the streets and I’m sure I’ve been around people who have had COVID. I’m pretty sure I was in their presence. I would deliver in masks. I moved into Borough Hall and put a mattress on the floor and I slept here and I used it as mobilization from my office in Borough Hall.
Now, if we would have spent the last three months — we were feeding people in this city for three months — if we would have said, “On our dime, we’re giving you healthy foods. We’re not giving you nacho chips. We’re not giving you processed food. We’re going to give you healthy food like quinoa, which is one of the most nutritional meals people can have. We’re going to introduce you to new food.” We would have number one, we would have fed people, which was important. Number two, we would have started the process of building their immune system so they can have a stronger immune system to fight off COVID-19. Three, we would have started changing the habits that people are so wedded to that believe they could only eat fast food, junk food. So we were missing a golden opportunity.
My goal is, as my program is at Bellevue Hospital, was first of its kind in New York, if not America, where we’re doing lifestyle medicine. 750 people on a waiting list, 230 people are in the program and we are helping people to cycle off their disease and medicine and using this new term called, “reversing chronic diseases.” That is what I believe our hospitals should do and what I want to continue to do to show people how you use food as medicine. That is what’s important. That’s what my book wanted to point out. Many people believe that their culture is tied to the food that’s poisoning them. I wanted to give a very real, honest story of exposing my weakness. “Hey, I’m the Borough President. Yes, I’m a former state Senator, but I’m just an everyday person that I was digging my grave with my knife and fork,” and I want to show people how they can live a healthy life. That’s why my 80-year-old mother was able to reverse her diabetes, also, get off insulin after only two months of going whole food plant-based.
AK: About restaurants in general, do you have a position speaking to your constituents about how they can get out of this crisis? Like many small business owners, they have been so impacted by COVID and I’m wondering if you see a path forward for them.
EA: Yeah, especially with my small restaurants. I hear some people say restaurants are for rich people. They should try the days when I was a kid and I was a dishwasher helping my mother pay the mortgage by washing dishes in a restaurant. Restaurants are for everyday people. Inside a restaurant is a cook, is a dishwasher, waiter, waitress, busboy/girl, low skill, low salary, they’re eking out a living and we have to get our restaurants back open. I believe that a bellwether of a city if you don’t get them up and operating, it’s an indicator of how bad your city’s doing.
I think the city can do a better job. Stop purchasing our food from outside the city and outside the state. Let’s localize the production of food. Let’s allow our local restaurants to use their kitchens to supply the food. We are providing millions of meals. Let’s allow our local restaurants to handle this distribution of food to communities and really engage them to keep them afloat, to keep people hired right here in our city. We spend too much money out of our city and I’m pretty sure other big cities are spending too much money outside of their city limits going to places that it may be cheaper in the short term, but in the long term, keeping your people employed, engaged and your small businesses open is extremely important.
AK: Awesome. I love that. Yeah.
DG: So as you look to a mayoral run, how much of this are you incorporating into your platform? Are these the kinds of things that you will be talking about constantly, or is it just a portion of your plan?
“What good is it to have a fancy hospital when you go in there to have your legs cut off because of diabetes neuropathic nerve damage?”
EA: A substantial portion. Our crisis, our health system, Daniel, is not sustainable. We have 30 million Americans diabetic, 84 million are pre-diabetic. We spend 80 cents on the dollar on chronic diseases. Diabetes is the leading cause of blindness, leading cause of non-trauma limb amputation, leading cause of kidney failure. We can’t continue to go down this road. I am really disappointed. Which presidential candidate talked about food and healthy food? What are candidates running for statewide, citywide offices all across this country, who are engaged in preventive medicine about healthy food? Everyone is talking about access to healthcare. What good is it to have a fancy hospital when you go in there to have your legs cut off because of diabetes neuropathic nerve damage? We have to become proactive and that’s my message. I’m going to use health in hospitals to ensure we have a proactive approach and give people choices, so they don’t have a lifetime of being on prescriptions, but they could have a lifetime that’s healthy on being on plants.
DG: Final thing, you said in the beginning that some people call you a hippie or sometimes you’re a hippie. All right. What does it mean to be a hippie? And are you a hippie?
EA: I think I am. I should’ve been born in the sixties. I just really... Let me tell you. I think that we had a very unique cosmic shift in a universe where people are really looking for their purpose and they’re no longer looking to just go through the motion of being on Valiums and statins and going home every day being unhappy. In Bhutan when I was there, they judged their country not by the gross national product, they judge it by the happiness of their people. We may be financially sound, but we’re emotionally bankrupt and it’s time to really start investing in what’s important and that’s family, friends and happiness.
DG: All right. Let’s grow happiness.
AK: Thank you for your work and thank you. Your book is, “Healthy At Last.” It just came out in October. Everyone should check it out. Thanks so much.
BrightFarms Promotes Jackie Hawkins To Director Of Food Safety & Quality
Hawkins will oversee all aspects of food safety and quality assurance as the company continues its rapid growth into new markets
BrightFarms, a leading supplier of locally grown packaged salads, recently announced that Jackie Hawkins has been promoted to director of food safety & quality. She will report directly to Josh Norbury, BrightFarms’ senior vice president of operations.
Jackie Hawkins
Hawkins will oversee all aspects of food safety and quality assurance as the company continues its rapid growth into new markets. Her responsibilities will include the development and execution of BrightFarms’ food-safety protocols across five facilities, as well as the coordination of customer, regulatory and third-party audits.
“Under Jackie’s leadership, BrightFarms is delivering the safest and freshest leafy greens to the nation’s largest retailers,” said Josh Norbury, senior vice president of operations. “She has built an industry-leading food safety program for the indoor production of leafy greens, and our rigorous protocols have set the standard for other companies in our space. We are fortunate to have her leadership and expertise as we continue to grow.”
Since joining BrightFarms in 2016, Hawkins contributions have been critical to the success of the company’s world-class operations team. She has designed and implemented the most comprehensive food-safety program in the indoor farming industry and maintains close working relationships with leading food-safety experts in the produce industry.
In 2018, Hawkins led the development of the Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) Food Safety Coalition, an independent and member-governed organization whose membership is comprised of controlled environment leafy greens growers who subject their production processes to external audit. She also led BrightFarms’ early adoption of IBM’s Food Trust platform to enhance traceability with blockchain technology.
“Food safety is a personal passion that I’ve dedicated my career to, and I couldn’t be more thrilled to step into my expanded role,” said Hawkins. “I’m thrilled that I have the opportunity to work for a company that places food safety at the centre of everything we do. I look forward to continuing to advance our leading protocols and providing our consumers with the safest, freshest and most nutritious greens on the market.”
Hawkins graduated from Oregon State University in 2016 with a B.S. in Environmental Science.
For more information about BrightFarms, visit www.brightfarms.com.
Coimbatore’s Hydroponic Farm Delivers Fresh Greens Within Three Hours of Harvest
I grab a leaf of peppermint from a bed of mint leaves and taste the intense freshness.
Sustainable farming and fresh, zero-carbon food are the philosophy behind the city’s first urban hydroponic farm, located inside an industrial building campus. To know more, MetroPlus makes a visit
I grab a leaf of peppermint from a bed of mint leaves and taste the intense freshness. Next, I look at thyme and smell the powerful aroma. A little away, purple basil with a beautiful, coppery glow beckon. I crush a lemon balm leaf and take in the uplifting, mild scent.
I am at Parna Farms, Coimbatore’s first urban hydroponic farm, located right in the heart of the city at an industrial building campus. Spread across 3,000 square feet, it grows 2,520 plants.
Akhila Vijayaraghavan | Photo Credit: S Siva Saravanan
“Our fresh lemon balm leaves impart a subtle flavour and fragrance, making it especially nice for custards, jam and jellies, cakes and tea,” says Akhila Vijayaraghavan, owner of the farm. “The purple basil is used for colour in salads. Except maybe amaranthus and palak (spinach), you can eat all the greens we grow here raw,” says Akhila pointing to varieties of lettuce, basil, bok choy, and kale.
Asian water spinach (kang kong), red gongura, mustard leaves and methi (fenugreek) are some of the new additions. “We also grow dill leaves, which are used as a garnish for fish and meat dishes and pasta. Fresh peppermint extracts are used in baking. We constantly try new crops based on demand, after rounds of trial-and-error.”
Peppermint grown at the hydrophonic Farm | Photo Credit: S Siva Saravanan
A graduate of Molecular Biology from the University of Glasgow, Akhila ran her own environmental consultancy for over 10 years before turning an urban farmer. “I worked with a lot of companies, from pharmaceuticals to FMCG, and learnt that the supply of quality end-product is a difficult task. Agriculture has always been one of my passions; I was interested in food crops. A herb can be used in cooking, to extract oil, extract nutrients in dry form, and maybe in alternative medicine, perfumery… the possibilities are exciting,” adds Akhila.
She researched hydroponic methodology and educated herself on farming before diving into it. “Anyone can do it, it is not rocket science,” she says.
“Hydroponics combines both sustainability and technology. In indoor hydroponic cultivation, the control on nutrient supply ensures more quality products, for example, improved oil content in herbs, as well as better crop yield. A hydroponic mint has more methanol content than a soil-grown one. The system also uses 80% less water than conventional agriculture. The water is upcycled for reuse.”
At Parna Farms, greens are grown using the nutrient film technique (NFT), where a thin ‘film’ of nutrient-rich water with macronutrients like nitrogen, potassium, phosphorous and calcium nitrate, and micronutrients like manganese and zinc nourish the roots of the plants.
Seedlings at the nursery at the hydroponic farm | Photo Credit: S Siva Saravanan
The farm has a germination area that uses coco peat to sprout plants and a nursery where net cups (small planters) are filled with clay pebbles. There is also the growing system, which involves metal stands and PVC pipes attached to a covered nutrient tank that pumps water to the plants. “We incubate the net cups in a plastic tray for a couple of weeks. Once the plant grows roots, it is transferred to the main system with higher nutrients in the water. This is where it is fully grown and harvested,” explains Akhila.
Hydroponic agriculture, she says, has existed for over 3,000 years, with the Hanging Gardens of Babylon being one of the often-quoted examples of this technique. “It is one of the more accessible forms of modern agriculture, tackling the dual problems of water scarcity and shortage of farmland. It reduces soil-borne pests and diseases.”
Akhila says the objective is to ensure that customers get fresh, pesticide-free produce within three hours of harvest. “Though a palak bunch from here costs ₹130, they are willing to pay the premium to enjoy good health,” says Akhila, adding, “You are what you eat. In hydroponics farming, every day is a learning curve.”
Follow @parnafarms on Instagram to know more
Start-Up Launches London’s First Delivery Service For Vertically-Farmed Eco-Friendly Greens
A London-based company is offering vertically-farmed, ultra fresh produce delivered straight to Londoners doors.
Crate To Plate Says All Its Greens Are Picked
Within 24-hours of Being Delivered To Your Door
Crate To Plate grow greens both vertically and horizontally, without soil, inside giant crates on the Isle of Dogs / Crate To Plate
A start-up is offering to deliver vertically-farmed vegetables to Londoners homes within 24 hours of harvesting in a first for the capital.
Crate to Plate, founded by former banker and scion of the supermarket dynasty, Sebastien Sainsbury, currently grows all its leafy greens inside three giant shipping containers on the Isle of Dogs.
The type of indoor farming the start-up uses has been tipped as the future of food production, and investors have spotted the trend.
The company, launched in London earlier this year, grows salad and herbs using hydroponics - which means seeds are grown year-round on vertical and horizontal racks without any soil or pesticides. The amount of water, light and “specially mixed” nutrients each kale or basil plant receives is carefully controlled.
(Crate To Plate staff include agriculture MA students / Crate To Plate)
The process uses around 95% less water than traditional farming, in a tiny space. In recent film A Life on Our Planet, David Attenborough recently warned of the critical importance of moving away from exhaustive farming practices to innovative solutions.
At the height of the November lockdown the team - which includes agriculture MA students - branched out into high-end “leafy veg box” deliveries spanning Zones 1-3. Each delivery is made on electric vehicle.
A £15 variety “farm to table” box will buy you 3 lettuce varieties, 3 bags of other leafy greens and 4 herbs - all harvested within 24-hours of arriving at your door.
Crate To Plate is now planning to expand around the capital. A second site is opening in Elephant & Castle in the new year, and the firms aims to have up to 15 “farms” by 2021. Each will produce up to six tonnes of fresh food per year.
Sainsbury, who previously founded the Hush Restaurant and organic baby food company Goodness Gracious, told the Standard he began exploring the business idea in 2015, after visiting a hydroponic farmer in Canada.
“I’m all about food wattage. One of the reasons I set up this business is for the environmental sustainability element of it. “Now technology has enabled us to move from growing on one row [as on the Canadian farm ] to growing both vertically and horizontally,” he said. Of the veg boxes, he said: “I did a bit of research and Londoners’ searches for ‘where does my food come from?’ increased by 40% in the pandemic.
“The pandemic was an opportunity to focus on home delivery. We’ve been sold out every week.”
“Everyone is talking about 15 minute cities now. Effectively that was what I was talking about - I want everyone to be able to get fresh leafy greens no more than a mile away from where they live.”
Critics of vertical farming have said it is just too expensive a method to realistically become the future of UK farming. But Sainsbury said the team is already working with farmers around the country to get them on board, with the aim of eventually expanding UK-wide.
Published by Dani Kliegerman for iGrow.News
Pure Harvest Smart Farms, How To Grow Local In The Middle East ?
In the UAE where the climate is arid and very hot most of the time of the year, growing local and fresh vegetables can be a challenge or even impossible
03.11.20
Pure Harvest Smart Farms is a tech company that tries to disrupt the agricultural market in the UAE by tackling the problem of food security.
In the UAE where the climate is arid and very hot most of the time of the year, growing local and fresh vegetables can be a challenge or even impossible. There are imports from other countries to secure fresh vegetable supply year-round, but due to the air freight, the products aren’t fresh and are expensive. An issue that Pure Harvest farm tries to address by bringing the best of agriculture technology to develop fresh and locally grown tomatoes in the UAE. Today the company has raised $100 million to expand its production, and start growing in Saudi Arabia and Kuwait. We met Sky Kurtz, its CEO, and Co-Founder.
What is controlled environment agriculture and why is it so important in the UAE today?
Controlled environment agriculture (CEA) is the strategy taken by Pure Harvest to tackle the issue of food security. This means we engage in CEA with hybrid growing solutions that provide precise climate and environmental controls to deliver quality fresh produce. Pure Harvest’s CEA ensures increased productivity and reduced waste (including water, energy, time, and transport). The UAE is the perfect starting point for us to expand our agritech solutions into other import-reliant regions. There is a huge amount of sun energy waiting to be harnessed!
In which aspects is Pure Harvest disrupting the industry compared to other traditional greenhouses?
The UAE’s arid climate is the right laboratory for the conditions needed for this kind of project and as a result, Pure Harvest is now entering the world stage as a tech-agricultural business tackling the problem of food security. Some other vertical farming countries in the world such as the United States, Holland, France are looking at similar solutions but don’t have the right conditions or a laboratory. The gap between traditional greenhouse countries and import countries has been bridged, this is particularly relevant given the risk of long term import reliance exposed by the Covid-19 pandemic.
What kind of technologies do you use to grow fresh vegetables in the hostile climate of the UAE?
Pure Harvest integrates world-leading Dutch greenhouse growing technologies together with our proprietary climate management systems. Pure Harvest seeks to leverage innovative semi-closed growing technology (with overpressure climate control and mechanical cooling) in order to pioneer year-round production of affordable, premium quality fresh produce.
What kind of crops do you grow in your greenhouses today?
We are currently growing 26 varieties of tomatoes and 6 varieties of strawberries. We are creating new markets, not just displacing existing commercial import markets. There are over 400 commercial varieties of tomato, and Pure Harvest is proud to grow six that have never before been seen. We’re aiming to be able to produce anything which already grows under a Mediterranean climate in any variety.
Last April, you secured a multi-stage investment commitment valued at over USD 100 million with Wafra Investment company. Which kind of developments do you expect for the company?
This year, the company entered into a first-of-its-kind retailer-integration partnership with The Sultan Centre (TSC) in Kuwait, creating a ‘farm center’ that will include edutainment, a retail farmers’ market, and an integrated café. We are completely committed to supporting public initiatives focused on improved food security, water conservation, skilled job creation, and economic diversification. Through constant engagement with governments, schools, and research institutions, we believe that together, we can lead the Middle East into the next generation of sustainable agriculture.
SEE ALSO A French-Tunisian startup changes the future of sustainable agriculture with insect proteins
3 November 2020
How Hydroponic Farming Can Bring You Produce That Aren’t Locally Grown……With No Soil Needed
Derived from Greek terms hydro (water) and pono (work), hydroponics literally means “working water” as plants are grown in water beds, with liquid solution feeding them the minerals and nutrients they need
September 24, 2020
When we think of farming or planting, the basic ideas that come to mind are digging up soil, dumping in seeds, sprinkling it with some water, and letting the power of nature turn the seed into a plant. Of course, humans take part in the process. But looking at the big picture, the soil plays the most crucial role in growing plants and vegetables. It’s going to be their cradle and, for some, their longtime home. Its quality and location will determine the life of a seedling and affect the fruits it will bear. After all, as soil scientist, Charles E. Kellogs said, “all life depends upon the soil… There can be no life without soil and no soil without life.”
But what if the soil is taken out of that picture? Now that is what we call hydroponics. Thanks to the advancements made in science and agriculture, we can now manage to cultivate crops without soil. Derived from Greek terms hydro (water) and pono (work), hydroponics literally means “working water” as plants are grown in water beds, with liquid solution feeding them the minerals and nutrients they need.
This method of horticulture may sound like a recent breakthrough, but studies about soilless farming dates back to the 1600s with works of English philosopher Francis Bacon and geologist John Woodward. According to a 1981 article in The New York Times, since nutrients are brought right to the roots, plants do not have to branch out and fight for food. Unlike farming on soil, hydroponics allows plants to be placed closer together as nutrients are equally distributed.
In the Philippines, many have adopted the hydroponic way of farming, as it offers vegetables that are safe from soil-related disease and typhoon damages.
For business owners Kevin and Kristine Co, hydroponics has also paved a way for a more eco-friendly process of bringing produce to the table. Their brand Herbivore Philippines not only provides vegetables that are free from pesticides and other harmful chemicals, it gives produce that can’t be grown locally.
The couple chats with Manila Bulletin Lifestyle and details the benefits Filipinos can get from hydroponic farming, its sustainable impact, and how their work has been during the pandemic.
How long has Herbivore PH been operating?
Kevin: Herbivore has been operating for a little over a year now. It took us nine months to construct and set the system up. Kristine is a big proponent of clean and healthy living. The idea started during a casual dinner conversation with some friends. It was about the difficulty of sourcing good quality produce and how anybody can easily claim and label themselves as “organic,” “farm fresh,” and the like. We spoke about how there was a lack of customer education on how fruits and vegetables are being grown.
For example, did you know that fruits and vegetables sold in supermarkets in developed countries have Price Look-Up codes to help customers distinguish how the produce are grown? This can be conventionally-grown (most probably with pesticides and chemicals in nutrient-depleted soil), genetically modified (unnatural and has been known to cause various diseases), or certified organic. The desire to grow top-notch, truly “clean” produce is what fueled us to bring this idea to life. We even have our produce tested to make sure that we are completely pesticide and chemical-free.
What is the advantage of using hydroponics compared to other indoor gardening?
Kristine: Some hydroponic farms are not temperature-controlled, hence the quality of the veggies aren’t that great. With our system we can give the plants optimum temperature, light, and nutrients to give them the best possible opportunity to reach their full potential, making better and more consistent quality produce. They are like spoiled babies. By having a completely controlled environment, we could grow produce that are typically imported—our contribution to reducing the carbon footprint of having to keep importing these vegetables.
How did the pandemic affect your operations?
Kristine: The pandemic shifted our business to be more retail-focused because of the increased demand from retail customers. We saw a significant drop in our wholesale business as many restaurants’ operations substantially decreased during the lockdown.
‘By having a completely controlled environment, we could grow produce that are typically imported—our contribution to reducing the carbon footprint of having to keep importing these vegetables.’
What are the imported vegetables you cultivate?
Kristine: We currently grow a handful of produce that has to be imported. Some examples include garland chrysanthemum, domiao, sangchoi (Chinese lettuce), wawachoi (Chinese cabbage) and even for those that can be grown locally like mizuna, kale, arugula, watercress, etc. Our produce is far superior than what you can normally get in the market.
How important is sustainability for the brand?
Kristine: Of course, sustainability of the brand is important so we can carry out our ethos which is to provide our market with the freshest and healthiest vegetables without sacrificing social responsibility. We are constantly trying to improve our system to work toward this.