Welcome to iGrow News, Your Source for the World of Indoor Vertical Farming
USA - ALASKA: Big Grants & New Ideas
VH Hydroponics has modular growing systems, cabinets, and shipping containers for scalable vertical farming to meet the needs of anyone
Customized Vertical Farming
VH Hydroponics has modular growing systems, cabinets, and shipping containers for scalable vertical farming to meet the needs of anyone - individuals, organizations, communities, hotels, and schools - who want fresh, healthy choices and food security.
Multiple Delicious Options
Micro-Grant Scoping Pre-Application
Due February 15th
$1.8 million dollars in Mico-Grants for Food Security are available in 2021.
Full details at the State of Alaska Department of Natural Resources Division of Agriculture
The first step is to submit the Pre-Scoping Application by the February 15th deadline.
Signify Adds Automatic Intensity Adjustment Plus Year-Long Recipe Modulations To Horticultural Controls
There’s something for both the greenhouse and the vertical farm in the GrowWise tweaks, which in some cases rely on tying to other systems’ sensors.
The Signify toplights at Belgium’s De Glastuin lettuce greenhouse automatically dim or brighten as daylight levels changes. (Photo credit: All images courtesy of Signify.)
Signify has enhanced the control system for its greenhouse LED lighting so that toplights can react immediately to changes in daylight conditions and adjust brightness accordingly. The company has also added year-long control settings intended to allow vertical farmers — but not greenhouses — to program seasonal variations in LED spectral content over a 365-day period.
Both upgrades are intended to reduce manual labor and improve overall cost efficiencies, Signify said.
Until now, greenhouse farmers could dim or brighten their Signify toplights by instructing the lights to do so via the control system, called GrowWise. Signify has now modified GrowWise software so that it can take readings from daylight sensors that are part of separate systems. GrowWise then instantly and automatically adjusts artificial light intensity emitted by the toplights, called Philips GreenPower LED.
“The lighting can be used much more efficiently since it gives us the flexibility to reduce light levels at any moment we need to,” said Wouter de Bruyn, the owner of Belgian lettuce grower De Glastuin, an early user of the new automatic feature.
Whereas Signify is known in office settings to build sensors into its smart luminaires, the GrowWise controls make use of sensors that are part of climate control systems and greenhouse management systems from companies such as Priva, Hoogendern Growth Management, and Ridder, all based in Holland.
Planet Farms’ Luca Travaglini backs up Signify’s point that prescribing a year of spectral content improves efficiency and helps keep down manual labor costs in controlled environment agriculture (CEA) operations such as vertical farms.
“The climate computer is equipped with a daylight sensor that sends actual light measurements to the GrowWise Control System so we can adapt our light levels automatically to ensure an even light level throughout the day and season,” de Bruyn said at De Glastuin, based in Kontich.
“Dynamic lighting in a greenhouse is the next step in improving the cost efficiency and quality for the cultivation process,” said Udo van Slooten, business leader, horticulture LED solutions at Signify. “It allows growers to effortlessly maintain a consistent level of light throughout the day to produce the best possible crops. The system compensates for cloudy weather and creates a more controlled growing environment for your crop.”
In another upgrade to GrowWise, vertical farmers who want to prescribe modulations in spectral content are no longer limited to 24 hours of looped recipe cycles. Rather, they can order up a year’s worth of shifts for controlled environment agriculture (CEA) operations.
The year-long programming feature is aimed at vertical farmers rather than at greenhouses because the lights that Signify provides for vertical farms support controllable spectral changes, whereas the greenhouse toplights do not. Signify refers to its GreenPower LED vertical farm lights as “production modules” rather than as “toplights.” Toplights and production modules can both be programmed for intensity over a year, but the intention of the year-long feature is oriented toward spectral content.
Compared to greenhouses, vertical farms tend to make much less, if any, use of natural light. In vertical farms, the lights are mounted much closer to the crop in stacked shelves.
One of the first users of the year-round feature is Italy’s greens and lettuce grower Planet Farms.
“Now we can easily create custom light recipes and set them to run year-round to provide the right light recipe with the right light intensity at the right time throughout the crop’s growth cycle,” said Planet Farms co-founder Luca Travaglini. “By automating our full light strategy during the growth cycle, for the whole year, we can run our operations very efficiently and keep our manual labor costs low. That makes it easier for us to maintain consistent quality as we scale up our production.”
The horticultural market is a key growth sector for Signify, especially as it maps out a strategy to maintain profits in the pandemic economy, in which last week it reported a yearly rise amid rigorous cost controls that now include a small number of layoffs. CEO Eric Rondolat is targeting a big chunk of what he has quantified as a $2 billion general horticultural lighting market by 2023.
MARK HALPER is a contributing editor for LEDs Magazine, and an energy, technology, and business journalist (markhalper@aol.com).
Advice For New Vertical Farmers: Grower Spotlight on Andrew Worrall
Andrew is LettUs Grow’s Farm Manager, he manages two of our sites across Bristol and has brought a wealth of knowledge into the company through his previous experience in indoor farming roles across the UK including at Grow Up, Raynor Foods & RootLabs. In this three part interview, we explore what it’s been like to move from animal husbandry to indoor farming, the lessons he’s learned along the way, what it’s like working at LettUs Grow and his advice for those new to indoor growing.
Last week we spoke about running a farm at LettUs Grow. What excites you about vertical farming?
It’s the future of the industry. Also, the amount of salad that these farms can produce for their local community. We want to be able to eat salad all year round and we import to make that happen. However, just a small farm can easily provide for its local community, very efficiently and all year round. The sustainability element is also exciting: with our salad there’s no food miles, it’s very minimalistic. You could use an electric van or bike to distribute this crop if you wanted to. It’s a step forward in terms of what we need to do to take care of our planet.
What do you think are the biggest downsides to vertical farming?
It’s still a new technology and it can be expensive. The biggest roadblock facing the industry is that we need more people and companies to collaborate together to make sure we can build these farms at a sensible rate, so we can provide farms to anyone. We want to be able to provide farms to people, communities and countries that don’t have a lot of money, so that they can provide affordable fresh produce to local people.
How has vertical farming impacted your life?
Massively! I wanted to find my passion, a job that I loved - that was very important to me. It’s satisfying to be in a position now where I’m very happy to be doing what I do and I look forward to going into work. I was happy to make the move from London to Bristol. I would have moved even further if it meant being able to continue working within this industry.
Image from: LettUs Grow
How do you see vertical farming playing a part in the future?
When indoor farming first came about, it had a reputation of being competition for outdoor farming, which just isn’t the case. There’s so much we can’t grow that outdoor farming can provide, such as cereal crops. I’m glad we’re at a stage where indoor and outdoor farms can start to work together to optimise both methods. With these new relationships, there should be a good increase in the amount of indoor farms you’ll be seeing. What LettUs Grow offers with DROP & GROW™ is an exciting project because that’s a 40ft shipping container which can be placed pretty much anywhere. It’s not that big - it could go in a car park or behind a restaurant, but actually provide quite a lot of salad to that area.
How much of our food should be grown this way?
Good question. If you had asked me a while back I would have just said salad, but now I’ve changed my mind. Indoor farming can have a massive impact on propagation, especially aeroponics, because of how we aerate and nourish our roots. We could start lettuce for greenhouse projects and we can also propagate tomatoes, strawberries and tree whips. Propagating trees in this way could potentially be hugely beneficial and it’s something we want to do more of.
We can also quickly grow large amounts of microgreens, baby leafs, herbs and we can grow fruiting crops like strawberries. We are slowly chipping away and it’s really exciting. I’m waiting to see if I can ever say I’ve grown or propagated every crop that can be grown in these farms!
What do you think are the biggest benefits of vertical farming?
How fast these crops can grow! The turnover can be as short as 5 days from seed, depending on the crop. Also how clean it can be - I’m very dedicated to making sure these farms are built to ensure they are easy to be maintained and clean. The most exciting part is the crop growth rate though - it’s incredible how fast our crop grows from seed to plate. In a very well maintained growing calendar, which Ostara® is great for supporting, you can optimise your beds so that the day you harvest can also be the day you germinate onto that same bed. Your farms can be forever providing salad at very fast rates.
Image from: LettUs Grow
What was the biggest change you encountered during your years indoor farming?
Moving from being a production grower to an R&D grower. It has been a great change! As a production grower I knew what I needed to know about growing the plant safely and getting it onto a plate so it was good for the consumer. Now I’m fully optimising, learning and understanding the plants completely, so that I can help the grower that I used to be. We spend a lot of time on crop recipes to make sure that whoever we sell our farms to can start up very quickly and they won’t have to spend months developing their crops. If they have the customers and clients behind them, they can buy DROP & GROW and start producing salad as soon as it's been commissioned.
What was the biggest change you encountered in the industry?
More and more people are speaking about what’s going on in the industry and getting involved. I get so many messages on LinkedIn with people who want to get into this career. It’s exciting to see that indoor growing is a career people can access now. When I was developing my skills I didn’t know I would end up in indoor farming. There are more opportunities than ever before. For example, our Crop Technician is doing a placement here for 2 years. The aim is that they can gain the skill sets and knowledge they need to then go off and do the same practice in any farm they want.
What advice do you have for people who are looking to start a career in growing?
Reach out to companies who are already out there. You could start off part-time or as an assistant. If you are patient and dedicated then it’s a journey I promise you won’t regret. It takes a lot of work, but the outcome is amazing - you’ll be learning so much about this new technology. You’ll also build great relationships: there are so many amazing people in this industry who are so interesting, with different backgrounds, who are willing to share their knowledge. You can always learn more and other people are a great source of that.
What about for those looking to start a vertical farming business?
Do your homework. There are people out there who you can reach out to and it’s very easy to get information. It’s very easy to get excited about the idea and jump straight into it, because it is exciting and can be very rewarding, but it’s really important to do it step by step. Know how to scale properly, learning the differences between a small and larger farm. Understand how many people you’ll need and the logistics. I’d also advise people to get some practical work experience before you buy. You want to start the company knowing the tricks of the trade.
Image from: LettUs Grow
LettUs Grow Blog: www.lettusgrow.com/blog/advice-for-vertical-farmers
US - NEW MEXICO: ‘Farm in a Box’ Coming To Grants
The Farm in a Box operates inside a 40-foot shipping container, shown here in Moffat County, Colo. A similar one will be set up at New Mexico State University branch campus in Grants. (Courtesy of Tri-State Generation and Transmission)
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — Fresh, locally produced vegetables will soon sprout from hydroponic beds in an enclosed, converted shipping container parked at New Mexico State University’s branch campus in Grants.
The 40-foot “Farm in a Box” will provide hands-on education and workforce training for local students and others interested in studying the emerging science of “indoor agriculture” as a new, potentially sustainable, enterprise that could offer fresh economic development opportunities and job creation in an area hard hit by the transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy.
NMSU, the Tri-State Generation and Transmission Association, and the National Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) are collaborating on the project.
It’s one of several initiatives under development with local, state, and federal backing to diversify economic activity in Cibola, McKinley, and San Juan counties, where coal-fired power plants and associated mining have provided a financial mainstay for workers and communities for decades.
Both Cibola and McKinley counties are reeling from last year’s shutdown of the coal-fired Escalante Generating Station near Grants, plus the closure of Marathon Petroleum’s oil refinery in Gallup, which together eliminated hundreds of stable, high-paying jobs in those northwestern communities.
Unemployment hit 10.8% in Cibola County in December and 10.2% in McKinley County, according to the state Department of Workforce Solutions. That compares to an 8.2% average statewide unemployment rate.
To ease the impact of Escalante’s closure and assist in transitioning local communities, Tri-State provided $5 million in grants in January to four local economic development organizations. It is also now sponsoring the Farm in a Box initiative, providing $250,000 to set up and equip the high-tech container unit that houses the indoor agricultural operation, with forthcoming grants for NMSU faculty and student assistants to work on the project.
“We realize that closing such coal facilities as the Escalante plant that have traditionally employed significant workforces creates very difficult challenges for local communities to replace those jobs,” Tri-State spokesman Mark Stutz said. “Our goal is to find opportunities in support of economic development with new technologies when we can.”
Tri-State permanently closed the 253-megawatt Escalante power plant in Pruitt last summer as part of the association’s long-term plan to completely withdraw from coal generation over the next decade. It laid off about two-thirds of the plant’s 107 employees, Stutz said.
TriState also plans to close a much larger, 1.3-gigawatt coal facility in Craig, a municipality in Moffat County, Colorado, where the company sponsored another Farm in a Box project that EPRI set up last November.
“We don’t want to just walk away from these communities that we’ve been a part of for decades,” Stutz said.
High tech
EPRI has set up similar Farm in a Box projects in 13 states, said its principal technical leader Frank Sharp, project manager for the institute’s indoor agriculture-and-lighting research efforts.
It’s part of an emerging concept of indoor farming for urban areas and isolated rural communities where food could be grown year-round right where it’s consumed. It could lead to huge energy and water savings through efficient, high-tech growing processes, contributing to carbon reduction by using electricity rather than fossil fuels in agricultural operations and by eliminating long-haul transport of produce to market.
For economically stressed communities such as Cibola and McKinley counties, it could be scaled beyond shipping containers to retrofit under-used or abandoned buildings and to construct new facilities, such as greenhouses, on empty plots, Sharp said.
“It all translates into community impact, job creation, and beneficial use of electricity,” Sharp told the Journal. “Vacated buildings with the infrastructure already in place can be retrofitted, with opportunities to also build new facilities.”
Electric Power Research Institute principal technical leader Frank Sharp, left, with Tri-State Generation and Transmission Association CEO Duane Highley, inside the Farm in a Box agricultural container that was set up in Moffat County, Colo., last November. (Courtesy of Tri-State Generation and Transmission)
Research needed
Research is still needed to maximize efficiency and production, measure benefits, make contained farming systems profitable, and train the workforce. That’s where NMSU comes in, said Jay Lillywhite, agricultural economics professor and co-director of NMSU’s center of Excellence in Sustainable Food and Agricultural Systems.
NMSU faculty and students will study the entire container system, which includes vertical, hanging plastic enclosures to grow crops connected to a closed-loop plumbing system to recycle all water. Researchers will monitor all energy and water use, plant productivity, the impact of red and blue LED lighting spectrums on plant growth, and the economics of the whole operation, Lillywhite said.
“We’ll record everything and transmit all the data wirelessly to EPRI,” Lillywhite said. “It needs to be profitable. Indoor agriculture has had mixed reviews in terms of profitability, so we’ll look at a model that makes sense for New Mexico and the Southwest.”
Other applications
Opportunities extend into many disciplines beyond agriculture, including electrical engineering focused on energy efficiency and renewable generation as alternative systems, such as solar panels, are added to indoor operations, said Rolando A. Flores, dean of NMSU’s College of Agriculture, Consumer, and Environmental Sciences.
“The project has excellent potential to address social, environmental, and economic facets of sustainability, and become a resource-efficiency model for urban agriculture, provided that renewable energy can be incorporated from the beginning,” he said.
State Rep. Patricia Lundstrom, D-Grants, said indoor agriculture can offer significant opportunities alongside other initiatives to diversify the local economy.
Lundstrom sponsored legislation last year that now allows counties with coal plants that are closing to set up special economic districts with bonding and taxing authorities to invest in infrastructure, business recruitment, and retention to create jobs and promote economic development.
That led to the launch in December of the McKinley County Electric Generating Facility Economic District, which is focused on converting the Escalante site in Pruitt into a new industrial zone to recruit more businesses to the area.
“Value-added agriculture is one of the opportunities we can work to develop there with help from the partners on this project,” Lundstrom said. “It can have a significant impact as we work to recruit new, sustainable industry to the local community.”
Columbia Vertical Farm Uses Technology To Cut Plastic Pollution And Boost Sustainability
The new packaging comes at no extra cost to the customer and will be cheaper in the long-run for Vertical Roots
Vertical Roots is the largest hydroponic container farm in the country. They grow and package lettuce varieties and have recently implemented a packaging process that reduces plastic with a resealable film. TRACY GLANTZ TGLANTZ@THESTATE.COM
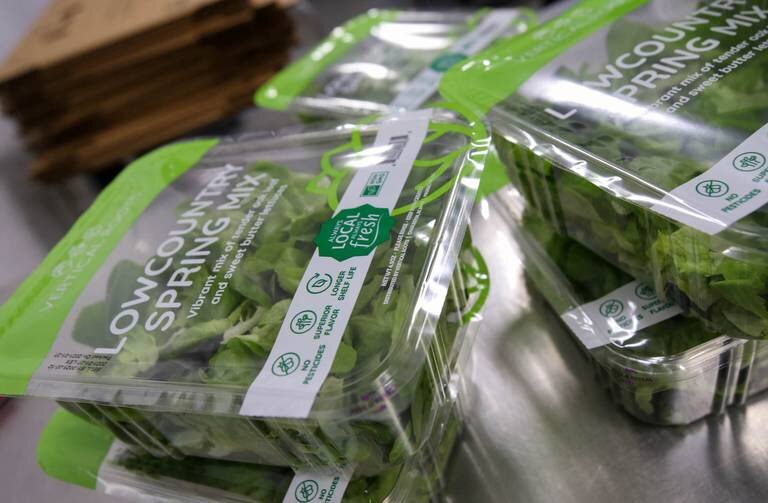
With the use of agricultural technology, Vertical Roots farm in West Columbia created a packaging system for its leafy greens that cut down the company’s plastic usage by 30% and extends the shelf life of the lettuce.
In 2015, high school friends Andrew Hare and Matt Daniels created the idea for Vertical Roots, now the largest hydroponic container farm in the country. Hare is the general manager of the company and Daniels acts as the chief horticulturist.
The first Vertical Roots opened in Charleston and expanded with its second farm site in West Columbia in 2019. Vertical Roots parent company, AmplifiedAg, manufactures the container farms and farm technology of which Vertical Roots operates.
The farms are part of a growing industry called controlled environmental agriculture (CEA) that uses technology to ramp up nutrient-rich food production year around.
Hydroponics helps the farm uses 98% less water than traditional farming, according to Hare. Their technology creates an indoor environment to grow lettuce on the East Coast. Most lettuce in the U.S. comes from California and Arizona, where temperatures do not fluctuate much throughout the year, travelling 2,000 miles from farm to table. Vertical Roots offers a solution for local lettuce.
“Our mission is to revolutionize the way communities grow, distribute and consume food,” said Hare. As populations grow, Hare said the ability to produce enough food is a global concern.
VERTICAL ROOTS AGRICULTURAL INNOVATION
As a company committed to sustainability, Vertical Roots had to address its plastic usage and the consumer demand for environmentally friendly products.
“I think everyone can agree that the amount of plastic that’s consumed and used globally is a bit of a problem,” said Hare.
If Vertical Roots were to completely opt-out of using plastics, as much as 40% of the lettuce would be damaged in transportation to the retailers, Hare said. So the company decided to still use plastic containers in order to cut out food waste, but it changed the amount and type of plastic used.
By replacing the conventional “clamshell” plastic lids that you see on a container of lettuce at the grocery store, Vertical Roots cut down more than 30% of plastic usage by creating a resealable film lid. The new packaging comes at no extra cost to the customer and will be cheaper in the long-run for Vertical Roots, according to Hare.
The farm also uses recycled plastic that can also be recycled again after use. Tiny perforations in the film lid of the packaging allow air to leave the lettuce container and extends the product’s freshness, making Vertical Roots lettuce last around 14 days on the shelf.
“We tested respiration and condensation with each lettuce variety, and ultimately found that we could extend the freshness and shelf life of our salad mixes even more,” said Hare.
Vertical Roots, at the S.C. Farmer’s Market, is the largest hydroponic container farm in the country. They grow and package lettuce varieties. Tracy Glantz TGLANTZ@THESTATE.COM
GROWTH IN THE AGRICULTURAL TECHNOLOGY INDUSTRY
In the first three quarters of 2020, a record $754 million of venture capital was invested in the vertical farming industry, according to PitchBook data. This was a 34% increase from the entire previous year, Bloomberg reported in a January article.
A 2019 report from Global Market Insights showed that the vertical farming market size, or the number of potential customers or unit sales, surpassed $3 billion in 2018 and said it, “will exhibit a massive compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 27% from 2019 to 2026.”
In vertical farms, crops are harvested on several vertical layers indoors, where farmers can grow year-round by controlling light, temperature, water and other factors, according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
Vertical agriculture is also seen as a growing industry because it “could help increase food production and expand agricultural operations as the world’s population is projected to exceed 9 billion by 2050,” according to the USDA.
However, some are skeptical about the future of vertical farming for several reasons. The farms use LED light bulbs to grow crops, which require a lot of energy and money to operate.
Also, the farms mostly produce greens, which are low in calories because they take less water and light. The new farming technology is marketed as a way to combat world hunger, but in poorer countries, low-calorie greens are not as beneficial, according to Bloomberg.
THE FUTURE OF VERTICAL ROOTS
Despite a tough year due to COVID-19, Vertical Roots will open two more indoor, container farms in Georgia and Florida in 2021.
The company lost revenue from foodservice customers like restaurants, schools and universities during the pandemic, said Hare.
Those food service customers accounted for about half of Vertical Roots’ business, Hare said. Grocery store business stayed steady and even grew during the pandemic. As schools and restaurants are slowly reopening, Vertical Roots is gaining business back.
The West Columbia farm location produces about $1.5 million pounds of produce per year, said Hare. Vertical Roots lettuce is in 1,200 different grocery stores in 11 states, including Lowes Foods stores, Publix, Harris Teeter and Whole Foods Market chains.
Hare said the company is constantly working on sustainable initiatives, including figuring out a way to reduce light energy consumption by 20-25%, thinking about compostable packaging systems and finding ways to use less water at the farms.
In the future, Vertical Roots hopes to offer a larger variety of produce. The team is experimenting with growing foods like tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, herbs and mushrooms to see if they could be viable products.
At 25,000 square feet, the world's first indoor vertical farm is also one of the largest farms. Located 120 miles south of Seoul, South Korea, fruits and vegetables grow without soil, bathed in light from pink LEDs. BY META VIERS
1 of 3
Vertical Roots, at the S.C. Farmer’s Market, is the largest hydroponic container farm in the country. They grow and package lettuce varieties. TRACY GLANTZ TGLANTZ@THESTATE.COM
VIDEO: Kentucky Greenhouse Company AppHarvest Goes Public On Nasdaq As It Prepares To Grow
AppHarvest has estimated it will generate net revenue of $21 million in 2021. The company is expected to produce 45 million pounds of tomatoes annually. AppHarvest employs 300 Eastern Kentuckians
FEBRUARY 03, 2021
AppHarvest has estimated it will generate net revenue of $21 million in 2021.
The company is expected to produce 45 million pounds of tomatoes annually. AppHarvest employs 300 Eastern Kentuckians.
David Wicks, Nasdaq’s vice president of new listings, said he was “incredibly proud to be your partner and look forward to supporting your innovation as a NASDAQ listing company” in a video message Monday.
Founder and CEO Jonathan Webb eats an AppHarvest tomato in a video message displayed in Times Square on Monday.
Two weeks ago, AppHarvest shipped its first bundle of tomatoes from its flagship location in Morehead.
“All this noise that is happening around us — listing on the Nasdaq and being shown in Times Square, selling our tomatoes to the largest grocers in the U.S. — all that is resonating back on the ground inside of our facility where our employees are feeling the positive impact of the work we’re all doing together,” Webb said.
The beefsteak tomatoes are selling out at grocers around the country.
“We can’t grow fast enough,” he said. “Our tomatoes are hitting store shelves and flying off the store shelves. It’s not just Kentucky, it’s everywhere from Indiana, all the way down to Florida.”
Webb said the company’s job now is to build faster and grow more vegetables to get on store shelves.
The company continues to look throughout Eastern Kentucky for building sites, Webb said, but there are challenges.
“We just have to find a place to build,” he said. “We have the capital. We want to build there, but building on these reclaimed coal mine sites are incredibly challenging and very expensive to try to make work. We would love to be there.”
The first greenhouse was originally planned for Pikeville, but AppHarvest said the site, a reclaimed strip mine, was not feasible for construction. After about two years of delays, AppHarvest announced its decision to relocate to a 350-acre parcel about two miles off I-64 near the Sharkey community of Rowan County.
Webb said they continue to invest in Pike County with a container farm at Shelby Valley High School. AppHarvest has two other farms at schools in Rowan and Breathitt counties.
The company aims to have 12 facilities growing and supplying fruits and vegetables by 2025. AppHarvest already announced a Berea facility to grow leafy greens and a Richmond facility to grow vine crops.
“One massive impact of 12 facilities is we’re going to have hundreds of millions of pounds of fresh fruits and vegetables pouring out of our region,” Webb said. “Not only the economic benefits of that, but the health benefits are tremendous. We’re in a situation where not many companies can say they feel incredibly proud of the product they produce and we do that.”
The first AppHarvest tomatoes will be in grocery stores by Wednesday, Jan. 20, 2021.
Photos: COURTESY OF APPHARVEST
Liz Moomey is a Reporter for America Corps member covering Eastern Kentucky for the Lexington Herald-Leader. She is based in Pikeville.
Israeli Agritech Company, Vertical Field In UAE Project
Vertical Field develops vertical agricultural farms that enable crops to grow in the city
27 January 2021
Israeli agritech company Vertical Field, which specializes in vertical farming, has signed an agreement with Emirates Smart Solutions & Technologies (ESST) a company that develops innovative agricultural projects in the Persian Gulf, to deploy pilot vertical farms as a first stage to full-scale deployments in the United Arab Emirates.
Vertical Field develops vertical agricultural farms that enable crops to grow in the city. Vertical Field’s technology enables produce to grow on a bed of soil (geoponically) inside repurposed shipping containers. Vertical Field claims that its advanced technologies enable high-quality crops to grow quickly and efficiently in optimum conditions without the use of chemical fertilizers or pesticides. These customizable urban farms can grow a range of fresh crops for supermarkets, restaurants, urban farmer’s markets, and distribution centers. Vertical Field says that its technology is more efficient and less wasteful than conventional agricultural methods, using 90% less water, and growing precise quantities of produce in a controlled environment.
Produce inside Vertical Field’s containers can therefore grow 365 days a year, are not limited to seasonality constraints, weather conditions, extreme climate events, or geographic location. The farms are modular, expandable, and moveable, and can be managed automatically. Produce is grown in a sterile container with minimal human interference. Crops that are currently grown in the farm include: several varieties of lettuce, basil, parsley, kale, mint, and more, which are sold at competitive prices.
Under the UAE agreement, Vertical Field will conduct a pilot project that will ascertain the most suitable crops for the local market. The first stage of the project will be launched in the United Arab Emirates, and is expected to expand into a multimillion-dollar partnership that will include deployments in additional states of the Gulf region. The first farm will be installed in Umm Al Quwain as part of a research, development, and training center, which is expected to support additional projects in the rest of the Gulf states.
According to market research firm Markets and Markets, in 2020, the vertical farming industry reached $2.9 billion, and it is expected to reach $7.3 billion by 2025. Approximately 80% of the agricultural consumption in the Emirates is imported from around the world, equivalent to over $10 billion (2018). The rising costs of shipping food as well as an increased desire for food security and regional independence has played a strong role in the development of the ESST-Vertical Field partnership.
Vertical Field CEO Guy Elitzur said, "This collaborative project is a first-of-its-kind partnership that offers Vertical Field’s innovative agricultural technologies to the Emirates and the Gulf Region. The Makalde Group brings forty years of experience and wide knowledge in the field of agricultural inputs and resources and we bring innovative technology.
"Arid desert regions face many challenges surrounding the production of high-quality agricultural produce at low prices. With the help of various agricultural technologies and new developments we believe that we can successfully align the demands of the market with competitive prices without compromising quality- and most importantly with increased access and availability."
Maher Makalde, CEO and Partner of ESST said, "Our goal is to establish food security that is independent of imports and to develop a high-quality agricultural infrastructure that reaches the retail market."
Published by Globes, Israel business news - en.globes.co.il - on January 27, 2021
© Copyright of Globes Publisher Itonut (1983) Ltd. 2021
Hydroponic Indoor Farm Plans To Be Among First Tenants In Downtown Piqua's Zolo Building
It was strategically placed in front of the Zollinger's building, a 40,000-square-foot former grocery warehouse planned as a mixed-use development with 16 loft-style residential units, a roof deck, community market/kitchen incubator and co-working space.
Fifth Season Farm, founded by a local brother-sister duo, has launched a hydroponic indoor farm inside a shipping container along Main Street in downtown Piqua.
By John Bush – Senior Reporter, Dayton Business Journal
A unique farming business has set up shop in downtown Piqua, and if all goes to plan the concept will be among the first tenants in an historic building being redeveloped in the city core.
Fifth Season Farm, founded by brother-sister duo Britt Decker and Laura Jackson, launched a hydroponic indoor farm inside a shipping container along Main Street. It was strategically placed in front of the Zollinger's building, a 40,000-square-foot former grocery warehouse planned as a mixed-use development with 16 loft-style residential units, a roof deck, community market/kitchen incubator and co-working space.
While the farm has been operating there for months, the long-term intention is to occupy space inside the the century-old building, which will be renamed the "Zolo." Chris Schmiesing, Piqua's community and economic development director, said the community market concept fits well with Fifth Season's business, and would be a welcome addition to the building.
"Part of the Zolo concept is the community market space, where local growers and producers can come and put their product on the shelves and begin to grow their business," Schmiesing said. "We're really excited to have Fifth Season Farm in there because we think it really represents the kind of innovative, entrepreneurial activity we want to see more of."
Unlike some traditional farms, Fifth Season does not use pesticides or herbicides, and utilizes non-GMO seeds. Powerful LEDs create a specific light recipe for each plant, allowing control over size and shape. There is no dirt, meaning the crops are free of bugs. The hydroponic system uses 90% less water by recycling the nutrient rich infused water in a loop system. Since it is weather controlled, temperature, relative humidity and CO2 levels remain constant all year.
"It is a complete, self-contained unit," Decker said. "The products also have a much longer shelf life because they are harvested to order."
Fifth Season currently grows about half-a-dozen varieties of lettuce, as well as specialty greens such as Swiss chard and kale. Decker said they are also growing small root vegetables such as radishes.
Currently, Fifth Season offers delivery through its website. Orders can be delivered up to five miles from its farm location, where customers can also come to pick up their products. Fifth Season produce can also be found on the Miami County Locally Grown Virtual Market. Decker said they are in discussions with local grocery stores, restaurants and gyms to carry their product as well.
When their space in the Zolo building is ready, Decker said they plan to open a marketplace and pickup location inside. He added the entire reason they placed the farm in that location was to be ready for when the redevelopment project is complete.
In June 2020, the Piqua Planning Commission unanimously approved a zoning change that allows for residential use within the building. The rezoning was a big administrative hurdle the project needed to cross, but the project still needs to be fully financed. The project missed out on the latest round of Ohio Historic Preservation Tax Credits, though Schmiesing said additional funding sources are being finalized.
Gamble Associates, a Massachusetts-based urban design and planning firm, is taking the lead on the Zolo project. Gamble Associates Principal David Gamble previously said the interior build-out will take between nine and 10 months to complete once it gets started.
Assuming everything aligns, Gamble said this project will create a "critical mass" that could have ripple effects throughout the city of Piqua.
"Piqua, in my mind, has reached an inflection point," he said in July 2020. "While there may not be a lot of transformation to date, there's been a lot of good planning and the city has very good leadership. Piqua is due for that next phase of growth. We like working here, and we're excited about this opportunity and what it can do for the city."
2020 Shone A New Light On The Need For Container Farming
For us here at Freight Farms, the COVID-19 pandemic became a pivotal moment
Even A Pandemic Couldn’t Stop Us!
When the COVID-19 pandemic came to a head in March, we all felt a deep sense of trepidation. At the time, the future looked beyond bleak. We were all at the forefront of a completely new experience and it was up to us to figure out how to stay safe and continue to thrive in the ‘new normal’ world. For us here at Freight Farms, the COVID-19 pandemic became a pivotal moment. Would people still care about their source of food in the midst of a health crisis? Would individuals be looking to shift careers and lifestyles during such uncertainty?
The answer came right away: yes. The pandemic shone a spotlight on the key flaws within our food system and the need for a workplace revolution. We saw a tremendous growth of interest from people looking to make a positive and needed impact on their communities. We reflect on the year with immense gratitude for our community of farmers that continue to help us address pressing issues of sustainability and food security–we can’t wait to see all we can accomplish together in 2021!
AppHarvest, USDA Partner To Expand Educational Container Farm Program
Located at Breathitt High School in Jackson, Ky., the retrofitted shipping container allows students to grow and provide fresh leafy greens to their classmates and those in need in their community
In partnership with the U.S. Department of Agriculture, we’ve opened a new high-tech educational container farm in Eastern Kentucky to offer students a hands-on AgTech experience.
Located at Breathitt High School in Jackson, Ky., the retrofitted shipping container allows students to grow and provide fresh leafy greens to their classmates and those in need in their community. The U.S. Department of Agriculture provided a majority of funding for the container farm through its Community Facilities grants program.
The Breathitt County container farm is the third in our program, which started in 2018 in Eastern Kentucky to excite students about growing their own food.
“This amazing project will not only put fresh vegetables on the table but, more importantly, it will teach tomorrow’s agribusiness leaders — and do all of that right here in Eastern Kentucky,” said U.S. Department of Agriculture Rural Development State Director Hilda Legg.
Click here to learn more and here for coverage of the container farm’s opening.
CubicFarms Announces Change of Financial Year End And Change of Auditor
CubicFarms is a local chain, agricultural technology company developing and deploying technology to feed a changing world. Its proprietary technologies enable growers around the world to produce high quality, predictable crop yields
VANCOUVER, B.C., January 19, 2021 – CubicFarm® Systems Corp. (TSXV:CUB) ("CubicFarms" or the "Company"), a local chain, agricultural technology company, today announced that it has changed its financial year-end from June 30 to December 31. The change in financial year-end has been made to coincide with the financial year-ends for the parent corporation and all its subsidiaries.
For details regarding the length and ending dates of the financial periods, including the comparative periods of the interim and annual financial statements to be filed for the Company's transition year and its new financial year, reference is made to the Notice of Change in Year-End filed by the Company on SEDAR pursuant to Section 4.8 of National Instrument 51-102, a copy of which is available electronically at www.sedar.com
In addition, the Company has changed its auditor from MNP LLP (the "Former Auditor") to KPMG LLP (the "Successor Auditor"). At the request of the Company, the Former Auditor resigned as the auditor of the Company effective January 7, 2021, and the Company appointed the Successor Auditor as the Company's auditor effective January 7, 2021, until the next Annual General Meeting of the Company.
"We would like to thank MNP for their expertise and guidance and we are pleased to announce that KPMG will be our auditor going forward," said Dave Dinesen, CubicFarms' CEO.
There were no reservations in the Former Auditor's audit reports for the period commencing at the beginning of CubicFarms' two most recent financial years and ending at the date of the resignation of the Former Auditor. There are no "reportable events" (as the term is defined in National Instrument 51-102 – Continuous Disclosure Obligations) between the Company and the Former Auditor.
Neither TSX Venture Exchange nor its Regulation Services Provider (as that term is defined in the policies of the TSX Venture Exchange) accepts responsibility for the adequacy or accuracy of this release.
About CubicFarms
CubicFarms is a local chain, agricultural technology company developing and deploying technology to feed a changing world. Its proprietary technologies enable growers around the world to produce high quality, predictable crop yields. CubicFarms has two distinct technologies that address two distinct markets. The first technology is its CubicFarms™ system, which contains patented technology for growing leafy greens and other crops indoors, all year round. Using its unique, undulating-path growing system, the Company addresses the main challenges within the indoor farming industry by significantly reducing the need for physical labour and energy, and maximizing yield per cubic foot. CubicFarms leverages its patented technology by operating its own R&D facility in Pitt Meadows, British Columbia, selling the system to growers, licensing its technology, and providing vertical farming expertise to its customers.
The second technology is CubicFarms' HydroGreen system for growing nutritious livestock feed. This system utilizes a unique process to sprout grains, such as barley and wheat, in a controlled environment with minimal use of land, labour, and water. The HydroGreen system is fully automated and performs all growing functions including seeding, watering, lighting, harvesting, and re-seeding – all with the push of a button – to deliver nutritious livestock feed without the typical investment in fertilizer, chemicals, fuel, field equipment, and transportation. The HydroGreen system not only provides superior nutritious feed to benefit the animal but also enables significant environmental benefits to the farm.
For more information, please visit www.cubicfarms.com
8 Easy Steps To Start Your Farm
Whether you want to sell to restaurants, hotels, or members of your local community, The Greenery™ makes it possible for anyone to grow local food on a commercial scale.
We’ve worked with farmers across the globe to help them establish successful businesses, so we know what you’ll need to do to launch a successful business.
Here’s what you’ll need to get started:
STEP 1
Understand hydroponics and your local food market.
STEP 2
Build your business plan.
STEP 3
Secure financing for your farm.
STEP 4
Find your perfect farm site and research your municipality’s zoning laws.
STEP 5
Get trained - join us at Farm Camp or in Farmhand Academy
STEP 6
Prepare for arrival - our Client Services team will take care of all the logistics!
STEP 7
While your crops start to grow, develop your marketing, packaging and other facets of your business.
STEP 8
Launch your farm and join the community of growers. Read advice from others like you.
The Freight Farms team will be there to support every step of the way.
Schedule a call today to get all your questions answered
and take the first step towards building a successful business.
Book A Consultation
US: KENTUCKY: Breathitt Students Join AgTech Farming, Will Feed The Community
The retrofitted shipping container will serve as a hands-on agricultural classroom for students at Breathitt High School, allowing them to grow and provide fresh leafy greens to their classmates and those in need in and around Jackson
By Steve Rogers
January 15, 2021
JACKSON, Ky. (WTVQ) — AppHarvest and the United States Department of Agriculture announced the expansion of the company’s educational high-tech container farm
program for Eastern Kentucky high school students, unveiling a new container farm unit at Breathitt High School in Jackson.
The program demonstrates the company’s ongoing commitment to fostering interest in high-tech farming, as it seeks to create America’s AgTech capital from within Appalachia.
The retrofitted shipping container will serve as a hands-on agricultural classroom for students at Breathitt High School, allowing them to grow and provide fresh leafy greens to their classmates and those in need in and around Jackson.
The U.S. Department of Agriculture provided the majority of funding for the unit through its Community Facilities grants program.
The educational container farm’s arrival was formally celebrated Friday, Jan. 15, with U.S. Department of Agriculture Rural Development State Director Hilda Legg and Appalachian Regional Commission Federal Co-Chairman Tim Thomas among those attending.
Attendees toured the container farm and learned about its high-tech tools.
“This amazing project will not only put fresh vegetables on the table, but, more importantly, it will teach tomorrow’s agribusiness leaders — and do all of that right here in Eastern Kentucky,” Legg said. “This public-private partnership is exactly what we need more of, and I’m proud to have been a part of it.”
The container farm is 2,880 cubic feet, weighs 7.5 tons and includes space to grow up to 4,608 seedlings and 8,800 mature plants all at once using 440 vertical crop columns. The container’s unique design utilizes cutting-edge LED lighting and closed-loop irrigation systems to allow students to grow far more than traditional open-field agriculture.
For instance, they can grow up to 940 full heads of lettuce, or 1,570 miniature heads, per week, as part of a single crop.
“We are excited to partner with the USDA and AppHarvest to bring a new container farm to our students and community members of Breathitt County,” said Breathitt County Schools Superintendent Phillip Watts. “Our goal is to teach the students how to grow fresh vegetables and support the local food supply. The inspiration, excitement and innovation that AppHarvest brings to Eastern Kentucky is a blessing for our region.”
Breathitt High School Agriculture Educator Taylor Masters teaches more than 200 students, who will utilize the container farm as part of their studies. “Our students will now be able to work hands-on yearround and the food they grow will help our community in addressing food deserts,” she said.
The Breathitt County container farm joins AppHarvest’s inaugural container farm serving Pike County’s Shelby Valley High School students and its second unit at Rowan County Senior High School.
All three containers are part of AppHarvest’s high school AgTech program, which provides Kentucky students with hands-on experience growing leafy greens and other nutritious foods in a high-tech environment.
Leafy greens from the inaugural Shelby Valley High School program have fed the surrounding community through a backpack program and donations to a food pantry.
A similar food distribution program is planned for the Breathitt County container farm.
AppHarvest is an applied technology company building some of the world’s largest indoor farms in Appalachia. The company combines conventional agricultural techniques with cutting-edge technology and is addressing key issues including improving access for all to nutritious food, farming more sustainably, building a home-grown food supply, and increasing investment in Appalachia.
The company’s 60-acre Morehead, Ky. facility is among the largest indoor farms in the U.S.
The Farm of The Future Could Be Hiding Inside This Shipping Container
It's called The Cube and could bring farming to urban environments
It's Called The Cube And Could Bring Farming To Urban Environments
The Cube's crops are powered by LED lights. N.Thing
As we head into 2021 facing a number of dire existential threats -- pandemics and climate change to name a few -- one of humanity's encroaching issues is population rise.
How on earth (literally) are we going to feed all these people?
Traditional farming methods could be problematic in the long term. It's not just an issue of space but a problem of sustainability. We're currently damaging our environment with current farming techniques -- and eradicating existing species and their habitats to the point where many are calling it the sixth extinction event.
In short, we have some problems to solve. Part of the solution could be found inside this 40-foot refrigerated shipping container.
They call it The Cube: A modular smart farm, designed to be built in urban spaces in pretty much any configuration you like.
The containers can be stacked vertically or horizontally, with potentially dozens or even hundreds of Cubes fitting together to make one giant farming system, capable of cultivating and growing tonnes of produce. The hope is to bring sustainable, efficient, year-round farming to spaces that can't traditionally support agriculture.
"The human populations are growing quite fast," explains Seungsoo Han, the COO at N.thing, "and we need to come up with some kind of very efficient solution that can actually support that fast-growing population, also at the same time, we shouldn't actually damage the environment that that population lives in."
At the heart of the Cube, the farm is an automated operating system known as Cube OS. The system takes in data from sensors inside each farm, measuring readings like humidity, ph levels in the water, temperature, carbon dioxide -- everything that's needed to grow a healthy plant. And each of these variables can be tweaked and optimized, depending on the plants you're growing.
N.Thing has already partnered with Korea's largest supermarket chain to supply greens and, last year, it rolled out a farm in the United Arab Emirates, where summer temperatures regularly climb over 100. Next, N.Thing plans to expand into other territories like Singapore and Qatar.
Vertical Field Prepares To Launch its Topsy-Turvy Farms In Ukraine
Agtech company Vertical Field, which specializes in vertical farming, has signed an agreement with one of Ukraine’s largest agricultural distributors Moderntrendo S.R.O to deploy its vertical farms
The country’s national distributor, Moderntrendo SRO, will promote the fields to more than 260,000 daily customers
James Spiro | 01-06-21
Agtech company Vertical Field, which specializes in vertical farming, has signed an agreement with one of Ukraine’s largest agricultural distributors Moderntrendo S.R.O to deploy its vertical farms. The initial pilot will be conducted at Varus, one of Ukraine’s largest supermarket chains, which currently serves more than 260,000 customers from its 95 stores in 25 cities.
“We are extremely excited about our partnership with Moderntrendo S.R.O which has led to the project with Varus and will lead to more projects in the near future with more chains in Ukraine,” said Guy Elitzur, the CEO of Vertical Field. “One of the realizations that have surfaced during the Covid-19 crisis is the need to develop solutions that allow urban residents access to healthy food, with minimal human handling and without depending on transportation and shipping from remote locations. We are delighted to be able to provide- and expand access to- healthy, and high-quality vegetables grown right outside the consumer’s door."
An inside look at the vertical farms. Photo: Vertical Field
Vertical Field produces commercialized, soil-based vertical farms in containers that produce locally sourced vegetables. The indoor ‘farms’ can grow a variety of greens such as lettuce, basil, parsley, kale, and mint all year round, making them ideal for supermarkets, outdoor markets, and distribution centers.
Related Stories:
Israeli supermarket chain to feature in-store vertical farms
“It’s about making the world a better place,” says multilateral investor in Israel’s SeeTre
“Today, we are creating a pilot project together with Vertical Field, which in the future will only benefit society, because the introduction of innovative and proprietary technologies for vertical cultivation of products for the urban ecosystem by Vertical Field is a new level in the Ukrainian market,” added Bondar Denis, Director of Moderntrend S.R.O.
Last month, Vertical Field signed an agreement with Rami Levy, Israel’s largest supermarket chain, to install its farms at multiple locations across the country. The company was formed in 2006 by Guy Barness who serves as its VP of Product.
Israel’s Vertical Field To Deploy Smart Vertical Farms In Ukraine
Vertical Field’s agreement with the Czech Republic-based Moderntrend SRO, one of the largest agricultural distributors in Ukraine, will see the Israeli company’s solutions set up at Varus, a local grocery chain with 95 stores across 25 cities nationwide
Vertical Field's farms are grown on 'green walls.' Garu Nalbandian
Israeli company Vertical Field, the developer of smart vertical growing solutions for fresh produce, announced a new agreement on Wednesday to deploy its vertical farms in Ukraine, starting with a pilot program with one of the country’s largest supermarket chain.
Vertical Field’s agreement with the Czech Republic-based Moderntrend SRO, one of the largest agricultural distributors in Ukraine, will see the Israeli company’s solutions set up at Varus, a local grocery chain with 95 stores across 25 cities nationwide.
Founded in 2006, the Ra’anana-based Vertical Field uses advanced IoT software, embedded sensors, and in-house monitors to ensure its indoor vertical farms, which grow fresh vegetables, greens, and other plants, are nurtured in controlled conditions regardless of geography, physical location, weather, and climate conditions. The company says its soil-based vertical growing systems make the most efficient use of spaces, both indoors and outdoors, for both agricultural and smart landscaping.
Vertical Field CEO Guy Elitzur said the company’s solutions are ideal for urban environments where land is scarce and access to fresh produce may be more limited. He also indicated that the COVID-19 pandemic has heightened the need for reduced contact and a more efficient supply chain.
“One of the realizations that have surfaced during the COVID-19 crisis is the need to develop solutions that allow urban residents access to healthy food, with minimal human handling and without depending on transportation and shipping from remote locations,” Elitzur said in a company statement. “We are delighted to be able to provide – and expand access to – healthy, and high-quality vegetables grown right outside the consumer’s door.”
Elitzur said the agreement with Moderntrend SRO will lead to partnerships with additional chains in the future.
Moderntrend SRO Director Bondar Denis said the pilot project introduces “innovative and proprietary technologies for vertical cultivation of products for the urban ecosystem by Vertical Field” and represented “a new level in the Ukrainian market.”
Last month, Vertical Field finalized a multi-million-dollar agreement with Israeli grocery chain Rami Levy to install vertical farms at dozens of the supermarket company’s branches across the country over the next five years.
By NoCamels Team January 06, 2021
SEE ALSO: Israeli Grocery Chain To Offer Fresh Produce Grown On-Site
What 8 Indoor Farming Companies Plan For 2021
By Jesse Klein
January 6, 2021
When the pandemic exposed major issues with our lengthy food supply chain — in the form of shipment delays and inadequate demand forecasting — local vertical farms and indoor growing organizations were called upon to fill in the gaps in a way that was unprecedented.
With 2020 in the history books and hopes for an end to the COVID-19 pandemic rising, these companies seek to build on their newfound momentum in 2021. With revenue for vertical farming alone estimated at just $212.4 million in 2019, one forecast calls for the industry to hit $1.38 billion by 2027, a compound annual growth rate of 26.2 percent from 2021 to 2027.
Here are what eight indoor-growing leaders are planning in the year ahead. The list is presented alphabetically and represents a slice of the marketplace activity cropping up in late 2020.
AeroFarms
The Aerofarms facility in Jersey City, New Jersey. Photo courtesy of Aerofarms
AeroFarms’ four New Jersey vertical farms produced 2 million pounds of produce in 2020. And this year that number likely will skyrocket with the company’s April announcement of construction on a 90,000-square-foot indoor vertical farm in Abu Dhabi, the world’s largest vertical farm.
In 2021, Aerofarms is taking on the issue of food waste more explicitly. It invested in Precision Indoor Plants (PIP) to help understand and prevent lettuce discoloration, experiment with ways to increase lettuce yield, and level up leaf quality.
AppHarvest
AppHarvest's farm in Morehead, Kentucky. Photo courtesy of AppHarvest
Appalachian company AppHarvest has launched three indoor farms in Kentucky. It chose the state specifically because it’s within a day's drive of 70 percent of the U.S. population.
In early 2021, AppHarvest will harvest its first crop of tomatoes, a move meant to help reduce reliance and emissions from imported tomatoes. In 2019, 60 percent of America’s tomatoes were imported. The farms use a closed-loop system that runs entirely off recycled rainwater to eliminate agricultural runoff and reduce water usage.
Bowery Farming
Bowery Farming's second farm in Kearny, New Jersey. Photo courtesy of Bowery Farming
Bowery Farming, based in New York City, plans to invest its 600 percent increase in sales last year into a new vertical farm in Bethlehem, Pennsylvania, in 2021.
By working with the Pennsylvania Department of Community and Economic Development and the Governor’s Action Team, Bowery is turning an arid industrial site into 8.7 acres of modern farmland that also should help the economic recovery of the area. Bethlehem once was a thriving steel town with Bethlehem Steel Corporation once employing around 60 percent of the local workforce at its peak before shutting down in 1998.
Since then, the city has had to transition into different sectors. Bowery Farming hopes to be part of that evolution. Its farm will create 70 jobs and feature LED lighting, recapture water from the plants using a water transpiration system, and collect data on a massive scale to inform future farming choices.
BrightFarms
This BrightFarms greenhouse produces more than two million pounds of leafy salad greens per year. Photo courtesy of BrightFarms
With $100 million in new funding raised in 2020, BrightFarms plans to construct indoor farms in every major market by 2025. This year marks the start of that journey with the construction of two new facilities in North Carolina and Massachusetts.
Both farms will be six to seven acres, or almost double the company’s current facilities in Ohio, Illinois and Virginia. In 2021, BrightFarm, which makes its headquarters in Irvington, New York, also plans to roll out its proprietary AI System, Bright OS, which will use machine learning and analytics to make operations from seed to shelf more efficient.
Gotham Greens
Gotham Greens operates a network of greenhouses across the Northeast, Mid-Atlantic, Midwest, New England, Mountain West, and beyond. Photo courtesy of Gotham Greens
Gotham Greens has been at the forefront of urban farming for over a decade. After starting in New York and expanding across the northeast, 2021 will be the year Gotham tries to take over the rest of the country.
As the COVID-19 pandemic shuttered so many businesses, Gotham Greens was able to expand into Aurora, Colorado, just outside of Denver. The Colorado location is Gotham’s eighth indoor farm. It also expanded to Baltimore.
Finally, in December, the company announced an $87 million funding round. The funding will support Gotham Greens products in Whole Foods Market, Albertsons Companies, Meijer, Target, King Soopers, Harris Teeter, ShopRite, and Sprouts.
Infarm
An Infarm installation at French retailer, Metro. Photo courtesy of Infarm
In 2021, Infarm is hopping on a hot industry trend — bringing the vertical farm to the grocery store.
In late December, the Berlin-based company announced a partnership with Sumitomo, a Japanese company that owns Summit Store, one of Tokyo’s leading supermarket chains. The partnership will bring Infarm’s modular vertical farm directly to grocery stores.
With this move, Infarm is expanding on its in-store strategy first experimented with Kroger in Berlin in 2020. Brick Street Farms also partnered last year with Publix to bring its vertical farms closer to the consumer.
Infarm will install its first farm at Summit’s Gotanno location and products are scheduled to be ready for sale at the end of January.
Kalera
Kalera's new farm in Houston will be the largest such facility in Texas. Photo courtesy of Kalera
Kalera also plans a rapid expansion in 2021. The Orlando-based vertical farm company is pushing into Atlanta, Denver and Houston this year. This will be the company's third, fourth and fifth farms and the first ones outside Florida.
The Houston facilities will be the largest vertical farm in Texas while the Atlanta location will be the highest production volume vertical farm in the Southeast. The Atlanta one will be more than double the size of the company's Orlando facilities — able to produce 11 million heads of lettuce.
And in December Kalera announced it is expanding into the Pacific Northwest in Seattle. These new facilities will help Kalera support partnerships with grocers and restaurants in the area.
Plenty
Most vertical farms, including Plenty, have initially focused on leafy greens like kale. Photo courtesy of Plenty
Plenty, based in San Francisco, had an eventful final quarter of 2020 and is riding that momentum into 2021.
In August, the indoor farming company announced a partnership with Albertsons to expand into more than 430 stores in Southern California. It followed up that move in October with a $140 million funding round led by Softbank and a historic partnership with Driscoll's to give consumers fresh sweet strawberries year-round.
This year, Plenty plans to begin construction on the world's largest output vertical farm in Compton, California. Upon completion, the farm will be the size of a big box retail store and will grow over 700 acres of leafy green crops.
Share this article Twitter Facebook Linkedin
Jesse Klein
Contributor
Indoor Ag Fintech Startup Contain Raises Investment Round, Adds Industry Veteran To Team
We have plans to introduce new ways to support the burgeoning indoor agriculture industry in 2021, and this funding round will allow us to do just that.”— Nicola Kerslake, Founder, Contain Inc
NEWS PROVIDED BY Newbean Capital
January 04, 2021
Image from Contain Inc
A Techstars graduate, Contain Inc works with industry vendors and more than 20 lenders to facilitate access to capital for North American indoor growers.
We have plans to introduce new ways to support the burgeoning indoor agriculture industry in 2021, and this funding round will allow us to do just that.”— Nicola Kerslake, Founder, Contain Inc
Image from Rooted Global
RENO, NV, UNITED STATES, January 4, 2021 /EINPresswire.com/ -- Contain Inc, a fintech platform dedicated to indoor agriculture, today announced that it has closed a round of funding from investors in the US and Europe. They represent investments from indoor agriculture, food and beverage, entertainment, and financial industries. The funds will enable further technology development as well as new initiatives that support indoor agriculture. The industry has become ever more relevant in the time of COVID as consumers and produce buyers alike recognize the benefits of local secure produce supply.
Image from Contain Inc
A Techstars graduate, Contain Inc works with industry vendors and a pool of more than 20 lenders to facilitate access to capital for North American indoor growers of all sizes. In 2020, Contain collaborated with Singapore family office ID Capital to introduce a microlearning platform, Rooted Global, that enables corporate employees to grow a little of their own food at home. Its clients include tech and food majors, such as Danone and Dole. Nicola Kerslake, founder of Contain Inc, added: “We have plans to introduce new ways to support the burgeoning indoor agriculture industry in 2021, and this funding round will allow us to do just that.”
In addition, Chris Alonzo, President, and CEO of Pietro Mushrooms, will join Contain Inc to provide consulting services to future leasing clients. Chris brings a wealth of experience in planning, constructing and managing indoor farms across two continents. He is a third-generation mushroom farmer in Kennett Township, PA, an area that supplies half of the US’s mushroom supply. Nicola Kerslake said: “we’re frequently approached by indoor farmers planning large new projects and are delighted to be able to offer the services of such an experienced grower to those looking to bolster their plans before seeking financing.” Chris Alonzo added: “I’m excited to bring my expertise to Contain Inc’s fast-growing team and to engage with a startup that has long supported indoor farmers”.
The Company will also be expanding its team in business development, marketing and product development over the coming weeks, and encourages those seeking roles in this exciting space to visit its website at contain.ag for more details.
About Contain, Inc.
Contain Inc is a US-based fintech platform dedicated to indoor agriculture, growing crops in warehouses, greenhouses, and container farms. The Company works with leading equipment vendors and with an expanding pool of lenders to aid indoor growers in finding funding for their farms. It is also home to microlearning platform Rooted Global, which works with majors such as Danone and Dole to enable employees to grow a little of their own food at home. The Company graduated from the 2019 Techstars Farm to Fork program, backed by Cargill and Ecolab.
More information: https://contain.ag, https://rooted.global
Nicola Kerslake
Contain Inc.
+1 7756237116
email us here
Visit us on social media:
Twitter
LinkedIn
Things To Think About Before Purchasing A Freight Farm
In this article, I will detail all the steps, hurdles, and bureaucracy I endured trying to start and bring a Freight Farm into my local community in Canada
Connor McGoran
In this article, I will detail all the steps, hurdles, and bureaucracy I endured trying to start and bring a Freight Farm into my local community in Canada. While this may not be the same experience for everybody, I will share what I learned and how I failed at starting a Freight Farming business. This process took me approximately three months to go through. The goal of this article is not to dissuade anyone from trying to start a Freight Farm business but to learn from my shortcomings so that the next individual who embarks on this journey will succeed and know what to expect.
Background
I had just finished my degree in Technology Management from NAIT and the early phase of COVID-19 hit which caused community lockdowns across Canada. During the lockdown, I stumbled upon an article from the MIT Technology Review about a unique way to grow roughly 1.5 acres of food in a retrofitted sea-can using LEDs, hydroponics, and specialized HVAC. My curiosity got the best of me and I asked myself if there was a feasible business case for this type of innovation in my home town. This to me seemed like a well-timed idea due to the broken food supply chain across North America due to COVID-19. With further research, I even found that Elon Musk’s younger brother Kimbal used multiple Freight Farm’s to grow his produce for his restaurants. This led me to read more to see if this magic box would be feasible from an economics and business perspective.
Step 1 : Research
The first thing I did was reach out to Freight Farms in Boston where I had a wonderful experience dealing with the Freight Farm Team. They gave me all the documentation I would need to get started detailing the cost of a brand new unit to be 115,000 USD. I also reached out to another company called FarmBoxFoods to see how their technology differed and what their price was set at 125,000 USD. Due to the high cost and the poor CAD-USD currency conversion (1.4), I looked at purchasing a used Freight Farm from the iGrow Group which re-sells used units online.
LGM Freight Farm Operating Costs
Step 2: Business Spreadsheet
I then created my own spreadsheet-based upon the numbers provided to me by the Freight Farm team and my own research to see if it would be feasible from a business perspective. There are some numbers included in this spreadsheet which I will talk about later in the article.
LGM Calculator Tab 1
LGM Calculator Tab 2
LGM Calculator Tab 3
After building my spreadsheet, I determined that the only way for me to make money and pay off any debt in Canada with the CAD-USD conversion rate was to purchase a used unit through the iGrow Group. Different brands of hydroponic growing sea-cans and units ranged from 55,000 USD to 150,000 USD depending on the model and year.
Step 3: Business Plan
After creating my spreadsheet I called other Freight Farmers within Canada to ask about their experience running a company. The expertise of people who already operated their own Freight Farms was extremely insightful because they were able to share their difficulties, what they learned, and what I should anticipate. This helped me write a modified version of the business plan below. I decided to call my company KLC Greens.
KLC Greens Business Plan
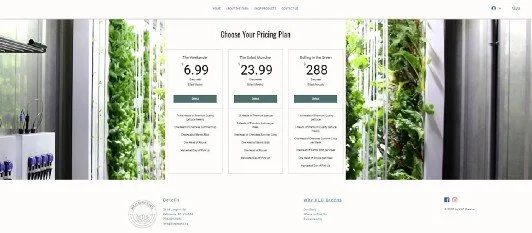
KLC Greens is a hydronic farming company that would provide the highest quality local produce to the local industry in Canada 365 days a year! It has the capability to turn around over 1000 heads of lettuce or other leafy greens after a 6-week initial phase.
Demand for local produce is booming and KLC Greens would be perfectly positioned to increase the availability of “hyper local” foods for our customers. By utilizing the very best hydroponic farming technology, Freight Farms’ Leafy Green Machine would grow high value cash crops year-round with consistent high quality that is not possible with outdoor farming in the local community.
Marketing Strategy:
KLC Greens marketing strategy would focus on selling their produce to wholesale grocery stores, a retail CSA program, and local restaurants that want the best produce available year-round. KLC Greens has been in contact with different local grocery stores that have shown interest to our product.
Company Description
KLC Greens is a hydroponic farming company that would provide fresh produce to the local vegetable industry in Canada. We will grow different lettuce varieties for restaurants, wholesalers, and retail through CSA that would aim to support the growing local food movement in Canada.
Our world is changing. More people than ever are now living in tightly populated, urban areas, and there’s an increasing demand for locally grown and sustainably produced food. People want to know the story behind the meal on their plates. And even city dwellers want their food to be fresh and full of nutrients, not pre-packaged and shipped from thousands of miles away.
Our climate is also continuing to evolve. Extreme weather conditions are becoming more common, and land and water are becoming scarcer. Large-scale food production and distribution has had a significant impact on the earth’s ecosystem, and it’s continuing to affect our water levels and biodiversity.
Transparency is key to understanding where and how food is produced and KLC Greens is committed to improving transparency in the produce industry by growing ‘hyper-local’ produce in one of the most innovative hydroponic system available, Freight Farms’ Leafy Green Machine. Growing in the Leafy Green Machine enables us to provide unparalleled transparency in all operations from seed to harvest and provides our customers with the certainty that they are eating, receiving, buying Okanagan produce grown via the best agricultural practices available.
Our Product
We will initially grow different lettuce varieties and sell it to wholesalers and restaurants at an expected price of 2$ per head of lettuce. This type of cash crop takes 6 weeks to reach maturity and we estimate harvesting 4044 heads per month. For details on harvest volumes, see Appendix A for revenue calculation data and assumptions.
Our lettuce is hyper-local, meaning that our lettuce is grown in the community where it will be consumed, and is thus considered a premium and differentiated product by the market, commanding a higher price point than even organic foods. This differentiation is what enables us to command the higher price of 2$ as opposed to the general wholesale price of 1.50–1.75$.
Market Breakdown
KLC Greens will specifically target high-end restaurants in the Canada area. Our target customers are chefs and restaurant owners in the farm-to-table movement who already provide information to customers about their sourcing policies and chefs and restaurant
owners in the ethnic cuisine space who require specific fresh greens for their dishes that are not available year-round through traditional farming.
Our competitors in the restaurant industry include direct competition from other local farmers, and wholesalers who source exclusively from local farms but are constrained by seasonality, and indirect competition from larger wholesalers who bring in low cost produce from around the world and in all seasons. KLC Greens will compete by providing “hyper local” produce to the restaurant industry regardless of season.
KLC Greens plans to sell its lettuce into the wholesale market in Canada. We will target smaller wholesale companies who specialize in local produce as opposed to working with the larger, national companies where we will struggle to meet sufficient volumes to be a relevant partner.
Our competitors for local wholesale are other local farmers growing vegetables and different varieties of vegetables (traditionally or hydroponically). During the summer months, traditional farmers will be KLC Greens greatest competition as the supply of local Lettuce is significantly increased and the price is driven down. During the non-summer months, regional, large-scale hydroponics producers are the greatest competitors for KLC Greens. In both instances, KLC Greens will rely on its freshness and consistent availability to appeal to our wholesale partners.
KLC Greens will sell its produce in farmers markets in the Canada area. We will target markets in middle to upper-middle class areas in order to gain access to consumers who are dedicated to eating fresh, local produce and have the disposable income to purchase our premium Lettuce.
Our competitors fall into two categories, direct competitors from the farmers market community and indirect competitors from outside the farmers market. To date, KLC Greens does not know of another hydroponic farmer participating in farmers markers in the Canada area, meaning that our primary direct competitors will be local farmers growing Lettuce in the traditional way. Outside of the farmers market, our competitors are traditional food retailers who may or may not stock local Lettuce. In both instances, KLC Greens has an advantage as we can differentiate on freshness and availability all year.
KLC Greens will also target middle to upper-middle class customers who already participate in CSA programs and demonstrate a commitment to eating local produce.
While most of KLC Greens competitors are not “hyper local” producers, it is worth briefly discussing the different methods of urban farming that may eventually enter the market as direct competitors. The four main competitors to KLC Greens Leafy Green Machine growing method in the urban farming space are indoor warehouses farms, urban greenhouses, rooftop farms, and small plots of land transformed into farms. Each have their benefits, however KLC Greens firmly believes that the Leafy Green Machine provides the best combination of protection from natural elements, cost effective production, and reliable crop yields that will make urban farming a profitable venture now and into the future.
Competitive Advantage
KLC Greens main competitive advantages are the farming technology we will use to produce our lettuce and the support of a network of small business hydroponic farmers.
We are in the process of purchasing a Leafy Green Machine from Freight Farms to use as our primary farming tool. A Leafy Green Machine is a turnkey hydroponic farm built inside of an insulated shipping container, enabling it to produce fresh vegetables in any climate for a full 365 days per year. To help ensure success, the Leafy Green Machine is equipped with sophisticated environmental controls which allow KLC Greens to easily grow consistently high-quality lettuce while simultaneously eliminating the guesswork inherent in traditional farming. The Leafy Green Machine only requires 20 hours a week to operate.
In addition to the benefits of the Leafy Green Machine itself, our purchase of a Leafy Green Machine provides us with access to the many resources Freight Farms offers to its extensive and ever-growing network of small business farmers. Freight Farms’ commitment to KLC Greens success includes:
· Comprehensive in-farm and online training
· A resident plant expert who is available to all beginning farmers
· Monthly shipments of customized nutrients and seeds
· Software designed to optimize harvest yields and allow remote monitoring of crops and control of the Greenery
· And most importantly, access to Freight Farms’ very active network of small business farmers who are available for assistance and advice
The strength of the Freight Farms network cannot be overstated. Each small business farmer has faced similar business challenges to those that KLC Greens will inevitably face. By leveraging the solutions of fellow Greenery farmers, KLC Greens can significantly reduce the risk associated with a new venture and move through challenges quickly and successfully.
Marketing and Sales Plan
KLC Greens sales plan is to target Restaurants, Retail (CSA) and wholesalers. Our company will target chefs and owners of high-end farm-to-table restaurants who have already demonstrated a desire to provide customers with transparency in food sourcing. Our Retail CSA program will target middle to upper-middle class customers who already participate in CSA programs and demonstrate a commitment to eating local produce. KLC Greens will also target wholesalers who are looking for consistent quality produce that can be supplied year-round.
KLC Greens has discussed our hyper-local lettuce with Natures Fare, Sysco, and Valley Green Foods and they are very excited about the possibility of buying year-round, local lettuce.
In order to obtain customers KLC Greens will implement the following marketing strategies of utilizing digital marketing tools, word of mouth, social media campaigns, and attending local regional industry events. KLC Greens will use a combination of digital marketing, via add words and a company website, and networking at industry events to identify and network with farm to-table restauranteurs, grocery chains and wholesalers. We will operate a booth at local conferences to better spread the word about our hyper-local lettuce, give potential customers the opportunity to try the lettuce for themselves, and direct further inquiries to our website for more information about the benefits of hydroponic produce.
KLC Greens will have a variety of different packaging for products depending on industry or consumer needs. If wholesalers require clam shell or hard plastic containers for packaging, our business will source that out. KLC Greens will package its lettuce in grams or kg in either rectangular clamshell packages or hard plastic containers for it’s wholesale partners.
Management Team
Key Partners:
· Accounting/Tax Partner: TBD
· Legal Advisor: TBD
· Insurance Provider: TBD
Use of Funds
KLC Greens is requesting $150,000 CAD for the purchase, transportation, and installation of a Greenery and for the cash flow necessary to get started. In addition to the requested loan amount, Farm Credit Canada has granted KLC Greens 80% of the funds to purchase the Leafy Green Machine. The 80% of the funds provided by Farm Credit Canada would be paid back to the loan.
A detailed breakdown of our planned use of funds is below:
· Greenery Purchase: $88,000
· Greenery Transportation: $9000
· Customs Tax (5%): $4375
· Greenery Installation: $3000
o Leveling: $1000
o Electric: $1000
o Plumbing: $1000
· Training: $4000
o Cost of training: $2500
o (if applicable) Cost of flight to Boston: $1000
o (if applicable) Cost of hotel in Boston: $500
· Business Materials Purchase: $1000
Financial Projections
KLC Greens financial projections are derived from the proven operations and profit models of fellow Leafy Green Machine small business farmers. Based on their experiences, collected, and consolidated by Freight Farms, we have constructed the following financial projections forecasting our first five years of operations.
Key Assumptions of Projected Financial Statements
· One month is 31 days (the Leafy Green Machine operates every day) or four weeks
· Year 1 begins on the day of Leafy Green Machine purchase
· Tax payments are not included in our calculations
· KLC Greens is a cash-based business so we will not offer terms to our customers and pay our bills upon receipt, therefore we have not calculated for Accounts Receivable or Accounts Payable
· We have elected to exclude inventory from our asset calculations however, there will be a nominal amount of work-in-progress and materials inventory at any given time
Step 5: Finding a Freight Farm
After creating my business plan I was ready to try and find a used unit that would fit within my budget through the iGrow Group. The team at iGrow was also super helpful and narrowed down the best unit that was close to where I lived to reduce shipping costs and help pair me with another business owner. I had to WhatsApp call the seller multiple times to ask questions and to inspect the unit due to COVID-19 as I was unable to cross the border. I was able to put a down payment on the unit until I secured further funding.
Step 6: Finding Capital (Funding)
In order to fund my business venture, I had to try and find different avenues for funding which led me on a rabbit trail for approximately two months. At the time of trying to obtain funding I was 22 and had no assets in my name but actually had little difficulty in getting approved funding. The only problem that occurred was that no bank in Canada would give me a bridge loan to bring the used Freight Farm into Canada. I called every single bank over the span of two months that I could possibly think of and tried to brainstorm creative ways to bypass the process. My seller was growing impatient so this led the seller to agree to send the unit across the border on the condition I would pay the remaining 90% and provide letters from the different financial institutions that I was approved for funding. I was able to obtain funding three different financial institutions called Farm Credit Canada, Community Futures, and RBC. Farm Credit Canada is a farm lender that is subsidized by the government which has a special young farmers loan for ages under 40 that can approve loans of up to a million dollars. Community Futures is a community-based organization that helps aspiring entrepreneurs within the Okanagan and RBC is a bank within Canada.
I reached an agreement with Farm Credit Canada after dealing with their business analyst’s and scrutinizing my business plan they would grant me 80% funding for the Freight Farm once it crossed the border, Community Futures would provide the operating expenses and other equity, and RBC would provide me a business account with an operating line of credit. Once I obtained the letters from all three financial institutions I was able to bring the Freight Farm across Canada.
Step 7: Logistics, Logistics, Logistics
Growing up in the Okanagan Valley in Canada which has an abundance of agriculture land and plenty of farming, I did not think I would have such a difficult time finding a place to put the Freight Farm. I reached out to numerous farmers, tried my contacts, and tried door knocking to try and find some land. What I found was that majority of old farmers did not want the hassle of having this on their property, did not understand the technology or it was not worth their time for the money. Being on a budget and knowing where I wanted my profit margins it was proving to be quite difficult. The Leafy Green Machine I was purchasing also required a certain power supply, access to water and it has to be leveled. If the land did not have these pre-requisites I would have to pay to have a sub-meter installed, the piping for water, and a contractor to have the unit leveled.
I ended up using a service called Young Agrarians which is a farmer educational resource network for new and young ecological, organic, and regenerative farmers in Canada. They had a local representative that assisted me with their land matching program and helped guide me through making a lease agreement. I ended up finding a landowner by door knocking who would allow me to put my Freight Farm on his land for a reasonable price and had the Young Agrarian Organization help build the lease agreement.
Step 8: Incorporation and Accounting
Due to my limited expertise and from the wisdom of other mentors I thought it would be best to get the advice from an accountant and lawyer to help me best set up my business. I know from other experiences that the CRA is not the most forgiving and can cause major headaches if you do not submit the proper paperwork. I consulted my local accountant where he advised me on the pros and cons of doing a sole proprietorship or incorporating and helped draft me a letter to my lawyer. I chose to incorporate and then sent the letter to my lawyer who set up the business to best suit my companies needs. A few weeks later KLC Greens was approved and incorporated.
Step 9: Website and Logos
While I was trying to find suitable land and was waiting for my business to be incorporated I decided to design my company logo and build a website. I utilized Fiverr as a platform to build my logo as it cost 60 CAD and was created within 48 hours. These were some of the designs created within 48 hours.
To build my website I decided to go through Wix. I used Wix because it was the most reasonably priced 25 USD and it had the best functionality for what I needed. I was able to create this website.
Step 10: Apply for a City Business License
Applying for a city license was an easy process as there was an online portal where I had to describe my business and what I was planning on selling. The estimated time to obtain a response was approximately 48 hours. I contacted my local city a few months prior to ask if there would be any concerns with having a Freight Farm within the city limits. So I expected my business license to be approved without any obstacles.
Step 11: Customs Broker/Shipping/Crane
While completing the last few steps I had to find a customs broker that would deal with the transaction so that the Freight Farm would come across the border without any difficulty. I also contacted numerous shipping companies with the IGrow Group to find the best deal. Once this was secured I could then schedule the crane companies in the seller's city and my home town. Now that everything was set, my Freight Farm was scheduled to come in three weeks' time.
Step 12: Bureaucracy
My assumption that obtaining a city business license was going to be easy proved to be wrong due to my city’s bylaws and bureaucracy. My application was forwarded to the agriculture department, the city planner, and the building inspector where I was met with the following response. I had numerous conversations about if there was any variance that could happen and how someone at the city three months ago told me they did not see anything wrong with my Freight Farming idea.
Hi Connor,
I was forwarded your email to help answer. The Planning Department and ALC both allow hydroponics to be grown on site (A1/ALR), however, the sea-can is not permitted. We only allow sea-cans/shipping containers on a permitted basis if they meet BC Building Code, which will require an engineer or an architect to make the sea-can structural sound. Sea-can’s are not permitted structures and won’t be given a Building Permit unless they are altered to meet the BC Building Code.
Please let me know if you have any other questions, I’m happy to help.
This was my response to the email above
To whom it may convern,
I talked with an associate at the city of Canada about three months ago about my business plan and any concerns I should foresee in the future, this associate saw no problems with my business and freight farm being in Canada. When I went to apply for a business license a week ago I ran into a few hurdles with the City about the freight farm meeting the BC Building Code and certain bylaws and obtaining a building permit. My understanding was that this container would be deemed a temporary unit on ALR land and should not need a building permit.I have reached an agreement with the business license team at the City and planners that this will be deemed a temporary structure for 6 months (as it can be moved readily at any time).
My container will be delivered in the next two weeks and I did not foresee these hurdles and I am looking for guidance on what to do next. I am a young entrepreneur and have taken a loan to start this business and would love to reach an agreement with the City and make the necessary legal changes to make my business work. I really appreciate how supportive the City has been and the amazing staff I have dealt with.
I have attached a pdf describing the leafy green machine, as well as the bylaw pdf on steel containers.
Here was the city’s reply;
Hi Connor,
I see from the web site link that you provided that this product comes from a USA based manufacturer. Do you have any support documentation from the supplier/manufacturer that references a Canadian standard for the electrical system, water system and building standard(s) that these are built to? We will require this information as part of a Building Permit & Plumbing Permit application along with a site plan showing where this container will be installed on the property
The bulletin that you have copied and referenced as allowable under exception, clearly identifies the exception for the use of the container as storage and not as an occupied/semi occupied building for the production of plants with a dedicated water system and electrical system. The British Columbia Building Code (2018 edition) is the Provincial standard that needs to be meet once the structure is being used as a building, which is what you are proposing. The A277 standard in BCBC 2018 is for factory built units, similar to modular homes that are factory inspected for compliance during construction and certified as compliant. The storage container can be stored on the site if approved by City of planning staff for 6 months, but would not be allowed connection to city water or electrical without meeting the minimum standard set by BC BC 2018. I would suggest that you reach out to the modular factory representatives to see if they can have a factory inspector come to do an on-site evaluation of the container unit to certify it or help provide information to cross reference Canadian to the USA based standards, so that you can apply for a building permit. https://www.kelowna.ca/homes-building/agricultural-land/dwellings is the link to the requirements for Building Permit application. A plumber will be required to apply for a plumbing permit if/when the building permit is issued and a proper back flow preventor will be required to protect the city water source.
This process may seem overwhelming but is no different than importing a USA built car into the Canadian market. The car would need to meet the standards set in Canada for the car to be registered and used in Canada. If the USA company has built these containers to meet or exceed Canadian standards and can prove this with valid documentation, the application process should be straight forward. An application for building permit can be made at 2nd floor city hall and the permit would be for an accessory building on farm land.
This response led me on another rabbit trail of trying to figure out if the Freight Farm I was purchasing would meet any of the building standards in Canada and so forth. At this point in time, my container was two weeks away, I had already purchased all my supplies for the Freight Farm and was going to sign my lease agreement. Freight Farm’s provided me with the following information below through an email and was able to confirm their shipping containers were ISO certified.
All LGMs are upcycled reefer containers. What this means is that they were previously used to ship produce to and from other countries. Once the refrigeration unit no longer worked, they were decommissioned. We would remove that unit, and retrofit our equipment. I bring this up, because the container itself will likely have some dents and marks from its usage as a freight container. This does not impact the structural integrity of the container at all. We have frequently had these container re-certified to be seaworthy, and safe for use from a structural standpoint. Additionally, the company that would have manufactured the farm has a number of certifications (CE, UL, etc.) that would apply to the actual assembly.
With this information, I called a few inspection agencies about what it would cost to bring the Freight Farm up to the BC Building Code or CSA standards where I got numerous replies saying it would cost thousands of dollars and be a very time-consuming process. On top of this, I would then have to be certified by the local building inspector and make sure the Freight Farm was conforming to any local bylaws.
Where it all went wrong
Just as I was confident about my business and thought I had everything prepared, I was hit with the bombshell from the city about bringing the container up to the BC Building Code and the numerous inspections I would have to go through. Also last minute the landowner of the farmland I was going to lease decided he did not want me on his land anymore or to sign a lease. This led me to call off the shipment 10 days before my container was supposed to arrive which caused me to call of the shipment. From my further conversations with the BC Building Inspectors and other consultants who specialized in shipping container homes, they said that any other Freight Farms located in BC that were not CSA approved or up to the BC Building code were illegal. They further elaborated that the only reason they were operating was that the local city or bylaw was turning a blind eye. This was the turning point where I had to decide if the current risks were worth taking with the knowledge that it would cost much more than expected to get the Freight Farm certified and if I didn’t it could be shut down by the city. I went back to crunch the numbers and realized I could not financially risk having the Freight Farm nonoperational for a few months due to the loans payments from the bank. I could not wait to have my container certified by the proper governing bodies and inspections to take place. This led me to painfully decide to not pursue my business plan anymore. I had to contact my seller and the IGrow Group about my situation and unfortunately, three months' progress was now void.
Where I Failed
I did not properly do my due diligence in contacting all the necessary channels in my local city to ask about the local bylaws. I trusted one individual's opinion at the city who did not have the proper knowledge to give me the advice that I relied on.
I did not think of the construction standards of the Freight Farm at the early phase of my business plan. This led to more hurdles when I was asked for information by the city.
I put a 10% down payment on the container before I had secured funding from other financial institutions. This caused the process to take longer than expected and caused my seller to wait over two months to get my finances in order only to have to cancel last minute.
Due to my limited assets, I had to borrow from numerous financial institutions to obtain the financial capital to purchase the Freight Farm. In the last two weeks, before my Freight Farm was expected to arrive, RBC called to inform me that there was too much conflict between the financial agreements between Farm Credit Canada, Community Futures, and RBC. This caused me to have to re-negotiate all my letters with my lenders delaying the purchase further.
I did not sign a lease agreement before arranging the shipment of the container causing the landowner to back out the last minute.
I purchased supplies for the container before it arrives.
I rushed the entire process in three months, leaving little time to carefully think out everything.
What I learned
Before starting the process make sure you know what your city’s bylaws are and talk to a few local representatives to make sure the information you are being told is true.
Read the bylaws to ensure your Freight Farm is up to local standards.
Obtain financing early on before contacting a seller if you have limited assets or can only afford a small down payment.
Make sure that if you borrow from numerous financial institutions there is no conflict of interest between them if they require equity of your Freight Farm until the loan is paid off.
Sign a lease agreement from a landowner, do not go off of their word.
If you want to disregard the city bylaws the best scenario would be to know someone who has land or own it yourself. That way you can hide the Freight Farm and won’t have any complaints, thus reducing the risk of your business being shut down in British Columbia.
Have more certainty of your business before purchasing supplies, creating logos, or a website.
Leave more time to think through each step, because once you are in the chaos it is harder to take a bird’s eye view of your business
Do not be dissuaded by hurdles that come out of nowhere, this is a natural occurrence in business. Learn how to navigate them and reflect on how to make sure they do not happen again. I went through what seemed hundreds of hurdles and learned how to navigate them. Even though I had to decide to give up in the end it was due to huge financial risk and my limited access to capital. The risk of not running my business for four months while making bank payments and the uncertainty of the financial amount to bring the Freight Farm up to BC building code were my deciding factors.
You learn 110% more when you stick your neck out and go through the process. Going into business is not easy and requires a certain mental fortitude and resilience.
Know when to give up and know when to keep on persevering. At certain times you may feel like giving up but that is also where the most learning can be achieved and later on you’ll laugh at the thought that you almost gave up. The flip side is don’t let your ego cause you to make bad business decisions, use logic, and periodically review your business plan and current state of affairs.
Even though I failed to start my company the amount of learning I went through the last three months was invaluable.
Conclusion
My hope is that this article will help the next entrepreneurs who embark on purchasing a Freight Farm and help them build off of my experience. I still believe there is a strong business case for a Freight Farm within my community but currently, I lack the financial capital and political power to cut through the bureaucracy. I hope my three months of trials and tribulations will save you time or help you in your journey.
WRITTEN BY
Connor McGoran
Edumacated Writer, Aspiring Blogger
Technology Farming Hydroponics Farming Startup Entrepreneurship
Urban Crop Solutions Solidifies Presence In North America With The Appointment of Douglas Gamble As Sales Manager
He joins UCS from the more traditional side of agriculture – having been raised on a dairy farm, which later transitioned into a large-scale Greenhouse operation
Urban Crop Solutions (UCS) is pleased to announce the appointment of Doug Gamble as their North American Sales Manager. Doug has spent over 25 years in management, sales, and business development roles; and brings his own entrepreneurial experiences and spirit to the position. He joins UCS from the more traditional side of agriculture – having been raised on a dairy farm, which later transitioned into a large-scale Greenhouse operation.
As the company’s first North American Sales Manager, Doug will lead the supply and delivery of UCS’s latest solution – the ModuleX plant factory; and ramp up the export of the company’s technology and environmentally beneficial solutions to urban farming in Canada and the United States. Doug will lead the operation from the small town of Sackville, New Brunswick in Canada – where his office, home, and family are located.
Urban Crop Solutions is a Belgium based pioneer in the fast-emerging technology of indoor vertical farming. It has developed over the past five years, 220 plant growth recipes, for which all drivers for healthy plant growth – such as optimal LED spectrum and intensity, nutrient mix, irrigation strategy, and climate settings – are tested and validated daily in its Indoor Farming Research Lab in Waregem (Belgium). To date, UCS has delivered over 25 projects for clients throughout Europe, North America, and Asia-Pacific. Its commercial farms are being operated for vegetables, herbs, micro-greens for food retail, foodservice, and industrial use. Research institutions are also operating UCS’s grow infrastructure for scientific research on banana seedlings, flowers, and hemp.
For more information:
Urban Crop Solutions: www.urbancropsolutions.com
For more information on this press release, or on Urban Crop Solutions and their products and services, you may contact Doug Gable, Sales Manager - North America; or Brecht Stubbe, Global Sales Director.
Doug Gamble, Sales Manager doga@urbancropsolutions.com
Brecht Stubbe, Global Sales Director brst@urbancropsolutions.com
European headquarters: Regional headquarters:
Grote Heerweg 67 800 Brickell Avenue, 1100 Suite
8791 Beveren-Leie (Waregem) Miami, FL, 33131
Belgium USA
(+32) 56 96 03 06 +1 (786) 408-6027
Facebook: www.facebook.com/urbancropsolutions
Twitter: www.twitter.com/U_C_Solutions
LinkedIn: www.linkedin.com/company/urbancropsolutions
YouTube channel: http://www.youtube.com/c/UrbanCropSolutions