Welcome to iGrow News, Your Source for the World of Indoor Vertical Farming
"We’re Retrofitting With The Variables We Have In Place"
Planted Detroit introduces new 20.000 sq. ft. growing facility
“The Square Room is a big block of pink lights with eight levels, where all our growing is done. Everything after germination is done in the same room, both harvesting of our baby greens and microgreens. Because we’re almost done with our PARS (Planted Automated Racking System), which is the big automation,” says Megan Burritt, Managing partner at Planted Detroit.
From a mix-fused downtown neighborhood in Detroit, daily deliveries of ready-to-eat salads and fresh greens are transported to local retailers and restaurants. Planted Detroit makes a large contribution to the city’s share of fresh produce.
New facility
Planted Detroit has been in the middle of the construction of its new 20.000 sq. ft growing facility. The growing space has been a massive update to the company compared to its previous 6-level growing facility which was between 1500-2000 sq. ft. The same room was used for processing, packaging, harvesting, and so on. “It was rather crowded, says Megan, but the main goal was to keep everything tight for the construction to continue in the near surrounding. We’re very serious about biosecurity and we have a daily procedure for everyone who sets foot in our grow room to go through. Making sure our greens don’t come into contact with pathogens is our top priority.
The new growing room
The Square Room, one of our growing rooms, is highly automated, including an automatic harvester to ensure work-efficiency. Once everything is big enough to be transplanted out of their plug trays, PARS (Planted Automated Racking System) will be transplanted with gutters and then go into harvesting. On the other side of PARS, the gutters are taken down and harvested through Planted’s new automatic harvester.
Delivering directly to consumers
The company wants to reach a higher volume of customers as it’s aiming to obtain a consumer brand status. Next to that, the company is always on the lookout for finding more customers through other venues. “We want to go directly to consumers via our web-store to shorten food miles as much as possible, delivering the freshest and most delicious greens,” Megan says. In order to do that the company needed to have a bit more scale, trying to maximize the space they already had.
She adds: “Our farm maybe isn’t the square footage which we could have built from scratch, but we’re retrofitting with the variables we have in place. That is why we have done a combination of a microgreen vertical nursery and PARS for baby greens. Our direct customers wanted meal solutions and we’ve been able to deliver them that. We’ve been doing everything from seed to plate basically.”
Megan Burritt, Managing partner
New projects coming up
On the same campus, 10 meters away, a new farm will be constructed, under the company's office space. In this farm herbs and edible flowers will be grown in response to different customers' demands. Megan says that Planted Detroit’s wholesale customers got them to this point as they were very interested in herbs and edible flowers. “However we weren’t able to perfect these as well in the systems that our baby greens were in perfectly. That’s why we’ve been leaning into R&D lately because once finishing the construction of Farm 2 it will have excellent growing conditions that are better than they have been for those crops.”
Edible flowers are an interesting thing, says Megan, but the company has gotten so much interest in it. According to Megan there aren’t many farms in the US that are growing them. “They’re high priced at this point. It sort of sticks to our original innovation, namely what exists here in the food system and what does not. Where can we fill the ‘does not exist niche’ and satisfy the needs of our customers.”
The company is rolling out a subscription program sometime this year and figuring out where it fits into the fresh food subscription system and how they can partner with other parties in order to get produce closer to society. “It’s great to have this ag job, applied science to be able to do. In all the things we’ve been doing is hiring these Detroiters and showing that we can really create a really great culture of work. It’s really great to see we’re contributing to a better Detroit and a better tomorrow,” Megan states.
Team expansion
During 2020 most of the team stayed on by moving around working hours, so the farm could come back in full force. By the time all equipment was in place, 10 to 12 people were added to the team to have them fully trained before the system would be functioning. “It has been really wonderful to expand the team to see what our capacity is,” says Megan.
“Luckily we’ve been able to develop systems that have been resilient. We’ve seen so many different patterns in consumer behavior but they seem to have fallen in our favor. People are eating more at home, shopping for groceries more, and that triggered our pivot focusing on direct consumers. But now, it’s perfectly in line with our strategy on how we go to market. As long as we can supply our customer needs we’ll be on the right path. Nothing but bright hopes for the future right now,” Megan affirms.
For more information:
Planted Detroit
Megan Burritt, Managing partner
megan@planteddetroit.com
www.planteddetroit.com
Author: Rebekka Boekhout
© VerticalFarmDaily.com
Eastern Kentucky Company Growing Local Economy By Growing Vegetables Year-Round
AppHarvest has created 300 jobs in Appalachia, an area not really known for growing tomatoes.
by GIL MCCLANAHAN
MOREHEAD, Ky. (WCHS) — Imagine growing fresh local tomatoes in the dead of winter. A company in Eastern Kentucky is using high-tech agriculture to grow vegetables indoors.
To View The Video, Please Click Here.
AppHarvest checks tomatoes growing inside the company's 60-acre indoor greenhouse.
(AppHarvest ) Courtesy Photo
AppHarvest opened in Rowan County, Ky. last October. They are growing more than just vegetables. They are growing the economy in an area that sorely needs it.
What's growing inside AppHarvest's 2.8-million square foot facility is capable of producing more food with less resources.
"For our first harvest to be on a day where there was a snowy mountainside could not have been any more timely. The fact that we are able to grow a great juicy flavorful tomato in the middle of January and February is what we have been working to accomplish," AppHarvest Founder and CEO Jonathan Webb said.
Webb said five months after opening its Morehead indoor farm facility, the company shipped more than a million beefsteak tomatoes to several major supermarket chains, including Kroger, Walmart and Publix. Those large bushels and bushels of tomatoes are grown using using the latest technology, no pesticides and with recycled water in a controlled environment using 90% less water than water used in open-field agriculture.
"We're just trying to get that plant a consistent environment year round with the right amount of light and the right amount of humidity and the right temperature just to grow, and the vines of our crops the tomato plant end up being 45 feet and we grow them vertically so that is how we can get so much more production," Webb said.
One of the company's more well-known investors is Martha Stewart.
"I said Martha, can I get five minutes and I told her what we are doing. She was like, look we need good healthy fruits and vegetables available at an affordable price. I love the region you are working in," Webb said.
A couple of weeks later, Webb met with Stewart at her New York office, and she decided to become an investor in the company. Some local restaurants are looking forward to the day when they can buy their vegetables locally from AppHarvest. Tim Kochendoerfer, Operating Partner with Reno's Roadhouse in Morehead, buys his vegetables from a company in Louisville.
"It will be another selling point to show that we are a local restaurant," Kochendoerfer said.
Webb points out AppHarvest is not trying to replace traditional family farming. "Absolutely not. We want to work hard with local farmers," he said.
Webb said by partnering with local farmers, more local produce can get on grocery store shelves, because last year 4 billion pounds of tomatoes were imported from Mexico.
"What we are working to replace is the imports from Mexico where you got children working for $5 a day using illegal chemical pesticides in the produce is sitting on a truck for 2-3000 miles," Webb said.
AppHarvest has already started influencing the next generation of farmers by donating high tech container farms to local schools. Students learn to grow crops, not in the traditional way, but inside recycled shipping containers. The containers can produce what is typically grown on 4 acres of land. Rowan County Senior High School was the second school to receive one. It arrived last fall.
"We sell that lettuce to our food service department and it's served in all of our cafeterias in the district," said Brandy Carver, Principal at Rowan County Senior High School.
"When we talk about food insecurity and young people going home hungry, what better way can we solve these problems by putting technology in the classroom. let kids learn, then let the kids take the food home with them and get healthy food in the cafeterias," Webb said.
AppHarvest has created 300 jobs in Appalachia, an area not really known for growing tomatoes. Local leaders believe the company will attract more business to the area.
"I fully expect in time we'll see more and more activity along that line like we do in all sectors," said Jason Slone, Executive Director of the Morehead-Rowan County Chamber of Commerce.
"We will eventually be at the top 25 grocers. Name a grocer. We've been getting phone calls from all of them," Webb said.
AppHarvest has two more indoor farming facilities under construction in Madison County, Ky., with a goal of building 10 more facilities like the one in Rowan County by the year 2025.
To find out more about AppHarvest click here.
BRITISH COLUMBIA: Tomorrow: 2021 BC Economic Summit
Join us tomorrow for a panel discussion with guests from our projects across B.C.! You'll have the opportunity to hear their experiences and discover how you can also take steps forward in food sovereignty with indoor growing
Join us tomorrow for a panel discussion with guests from our projects across B.C.! You'll have the opportunity to hear their experiences and discover how you can also take steps forward in food sovereignty with indoor growing.
REGISTER
Fresh Impact Farms Awarded Arlington's First Agriculture Grant
Arlington County received its first-ever agriculture fund grant from the state, money that will go to county-based Fresh Impact Farms.
Operating since 2018, Fresh Impact Farms uses hydroponic technology to grow a variety of speciality herbs, leafy greens, and edible flowers indoors. (Mark Hand/Patch)
ARLINGTON, VA — Arlington County received its first-ever agriculture fund grant from the state, money that will go to Fresh Impact Farms, an Arlington-based company that plans to double production at its indoor growing facility.
Virginia Gov. Ralph Northam announced Monday that he had awarded an Agriculture and Forestry Industries Development, or AFID, Fund grant to Arlington totalling $15,000 to be given to Fresh Impact Farms. The company will receive a total of $30,000 from the government, with Arlington County matching the state grant with local funds.
"Agriculture continues to be a key driver of our economic recovery in both rural and urban areas of our commonwealth," Northam said Monday in a statement. "Innovative, dynamic businesses like Fresh Impact Farms are demonstrating how exciting new opportunities can grow out of pandemic-related challenges."
"I congratulate the company on their success and am thrilled to award the first-ever AFID grant to Arlington County to support this expansion," the governor said.
In recent decades, Arlington County has grown into one of the most densely populated counties in the nation. Up until World War II, Arlington still had plenty of farmland. But over the past 60-plus years, the only farming in the county has been of the backyard and patio variety or in the community gardens in the Four Mile Run area.
Operating since 2018, Fresh Impact Farms uses proprietary hydroponic technology to grow a variety of specialty herbs, leafy greens, and edible flowers indoors.
"Governor Northam's award to Fresh Impact Farms, Arlington's only commercial farm, is an innovative way to celebrate unique uses of technology to help a small business pivot during the pandemic," Arlington County Board of Supervisors Chairman Matt de Ferranti said. "I am thrilled that Fresh Impact Farms is growing and looking to the future of a sustainable food supply."
The company will invest a total of $137,500 as part of the expansion, which will include a second grow room, a larger production facility, and an educational hub where customers, after the pandemic, will be able to see how their food is harvested.
Fresh Impact Farms' community-supported agriculture or CSA, program focuses on leafy greens and home kitchen-friendly herbs and has grown them steadily since the program's creation last April. Along with residential customers, the company now has smaller wholesale clients in the Washington, D.C., area.
The future is bright for urban agriculture, said Ryan Pierce, founder of Fresh Impact Farms, located in the back of a Lee Highway strip mall. (Mark Hand/Patch)
After the start of the pandemic, Fresh Impact Farms decided to shift its business model to a CSA delivery service in order to continue generating revenue.
"Seizing the opportunity created by more people cooking at home, the company initiated a Community Supported Agriculture program targeting area residents," the governor's office said.
"Now, with vaccinations underway and the restaurant industry poised to rebound, Fresh Impact Farms is expanding, which will allow the company to resume supplying their restaurant customers, while also meeting new demand through their CSA program," the governor's office said.
Over the next three years, the company expects to grow an additional 10,500 pounds of Virginia-grown leafy greens, herbs, and edible flowers for restaurant and CSA customers.
The future is bright for urban agriculture, said Ryan Pierce, founder of Fresh Impact Farms, located in the back of a Lee Highway strip mall.
"The support and generosity from the Commonwealth and Arlington County will be valuable as we expand our production and move towards a hybrid model of serving both the needs of restaurants and consumers," Pierce said in a statement. "As the owner of a local food business, nothing gets me more excited than seeing the community come together in support of local food."
The funds from the Arlington County Industrial Development Authority, together with the state grant, represent "an important investment in urban agriculture, sustainability, and technology," Arlington County IDA Chair Edwin Fountain said in a statement. "This project will advance the County's innovative and forward-thinking approach to developing new sectors of economic activity in Arlington."
US: NEW YORK - Well-Known Investors Water Ellicottville Greens With $1M In Growth Funding
The Series A round of funding will support construction of mobile vertical farming facilities, built inside reused shipping containers, along with the acquisition of Vertical Fresh Farms, an established indoor farming operation in Buffalo.
By Dan Miner
Reporter, Buffalo Business First
March 8, 2021
Ellicottville Greens continues to push forward on its ambition with $1 million in new funding, led by well-known local investors.
The Series A round of funding will support construction of mobile vertical farming facilities, built inside reused shipping containers, along with the acquisition of Vertical Fresh Farms, an established indoor farming operation in Buffalo.
It is a natural progression for the company, which was founded in 2018 by Sal LaTorre and Gabe Bialkowski and seeks to take advantage of the national consumer drift toward locally grown, organic produce.
“We decided to go after a new round of funding because we have a lot more demand coming in than we have capacity to grow right now,” Bialkowski said. “We are focusing on growing the product and sales and that will help define everything else.”
The round was led by Scott Friedman, chairman of Lippes Mathias Wexler Friedman law firm, and Andrea Vossler, a partner at that firm. The duo run Varia Ventures, an investment vehicle and management consultancy aimed at startups in Buffalo. A group of angel investors based in Buffalo participated as well.
Ellicottville Greens raised $250,000 in seed funding last year from Launch NY and other local investors.
Ellicottville Greens has thus far established four shipping containers: three at its Ellicottville home base and one on the Eastern Hills Mall property in Clarence. It sells its products to homes and restaurants through web-based marketplaces that include Produce Peddlers and Off the Muck.
Produce Peddlers is itself a local startup founded by Gary and Gina Wieczorek.
In the long-term, Bialkowski says Ellicottville Greens has a repeatable business model that could be attractive to supermarkets since the company could set up shop nearby and deliver produce at the peak of possible freshness.
He said the firm is set up at the intersection of nationwide consumer shifts in how people consume food.
“People want to buy healthy local products,” Bialkowski says. “They’re getting more health-conscious and they want to know where their food comes from.”
Ellicottville Greens is the third local startup to announce a growth-oriented round of private funding this year. The others include Torch Labs ($25 million) and Circuit Clinical ($7.5 million).
Lead photo: Ellicottville Greens' storage containers
IN THIS ARTICLE
Study On Analytic Tools To Measure Future Plants Stress
The paper also assesses the future outlook, economic potential, and implementation strategies for the integration of these technologies in future farming practices.
New work from the Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology (SMART), MIT’s research enterprise in Singapore, and Temasek Life Sciences Laboratory (TLL) highlights the potential of recently developed analytical tools that can provide tissue-cell or organelle-specific information on living plants in real-time and can be used on any plant species.
In a perspective paper titled “Species-independent analytical tools for next-generation agriculture” published in the journal Nature Plants, researchers from the Disruptive and Sustainable Technologies for Agricultural Precision (DiSTAP) Interdisciplinary Research Group (IRG) within SMART review the development of two next-generation tools, engineered plant nanosensors and portable Raman spectroscopy, to detect biotic and abiotic stress, monitor plant hormonal signalling, and characterize soil, phytobiome, and crop health in a non- or minimally invasive manner. The researchers discuss how the tools bridge the gap between model plants in the laboratory and field application for agriculturally relevant plants. The paper also assesses the future outlook, economic potential, and implementation strategies for the integration of these technologies in future farming practices.
Crop loss
An estimated 11-30 per cent yield loss of five major crops of global importance (wheat, rice, maize, potato, and soybean) is caused by crop pathogens and insects, with the highest crop losses observed in regions already suffering from food insecurity. Against this backdrop, research into innovative technologies and tools is required for sustainable agricultural practices to meet the rising demand for food and food security — an issue that has drawn the attention of governments worldwide due to the Covid-19 pandemic.
Sensors
Plant nanosensors, developed at SMART DiSTAP, are nanoscale sensors, smaller than the width of a hair, that can be inserted into the tissues and cells of plants to understand complex signalling pathways. Portable Raman spectroscopy, also developed at SMART DiSTAP, encompases a laser-based device that measures molecular vibrations induced by laser excitation, providing highly specific Raman spectral signatures that provide a fingerprint of a plant’s health. These tools are able to monitor stress signals in short time-scales, ranging from seconds to minutes, which allows for early detection of stress signals in real-time.
“The use of plant nanosensors and Raman spectroscopy has the potential to advance our understanding of crop health, behavior, and dynamics in agricultural settings,” says Tedrick Thomas Salim Lew SM '18, PhD '20, the paper’s first author. “Plants are highly complex machines within a dynamic ecosystem, and a fundamental study of its internal workings and diverse microbial communities of its ecosystem is important to uncover meaningful information that will be helpful to farmers and enable sustainable farming practices. These next-generation tools can help answer a key challenge in plant biology, which is to bridge the knowledge gap between our understanding of model laboratory-grown plants and agriculturally-relevant crops cultivated in fields or production facilities.”
Early detection
Early plant stress detection is key to timely intervention and increasing the effectiveness of management decisions for specific types of stress conditions in plants. Tools capable of studying plant health and reporting stress events in real-time will benefit both plant biologists and farmers. Data obtained from these tools can be translated into useful information for farmers to make management decisions in real-time to prevent yield loss and reduced crop quality.
The species-independent tools also offer new plant science study opportunities for researchers. In contrast to conventional genetic engineering techniques that are only applicable to model plants in laboratory settings, the new tools apply to any plant species, which enables the study of agriculturally relevant crops previously understudied. Adopting these tools can enhance researchers’ basic understanding of plant science and potentially bridge the gap between model and non-model plants.
Technologies in agriculture
“The SMART DiSTAP interdisciplinary team facilitated the work for this paper and we have both experts in engineering new agriculture technologies and potential end-users of these technologies involved in the evaluation process,” says Professor Michael Strano, the paper’s co-corresponding author, DiSTAP co-lead principal investigator, and the Carbon P. Dubbs Professor of Chemical Engineering at MIT. “It has been the dream of an urban farmer to continually, at all times, engineer optimal growth conditions for plants with precise inputs and tightly controlled variables. These tools open the possibility of real-time feedback control schemes that will accelerate and improve plant growth, yield, nutrition, and culinary properties by providing optimal growth conditions for plants in the future of urban farming.”
“To facilitate widespread adoption of these technologies in agriculture, we have to validate their economic potential and reliability, ensuring that they remain cost-efficient and more effective than existing approaches,” the paper’s co-corresponding author, DiSTAP co-lead principal investigator, and deputy chair of TLL Professor Chua Nam Hai explains. “Plant nanosensors and Raman spectroscopy would allow farmers to adjust fertilizer and water usage, based on internal responses within the plant, to optimize growth, driving cost efficiencies in resource utilization. Optimal harvesting conditions may also translate into higher revenue from increased product quality that customers are willing to pay a premium for.”
Collaboration among engineers, plant biologists, and data scientists, and further testing of new tools under field conditions with critical evaluations of their technical robustness and economic potential will be important in ensuring sustainable implementation of technologies in tomorrow’s agriculture.
For more information:
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
www.mit.edu
New York’s Gotham Greens Plans Solano County Indoor Produce Farm
It will be located on 33.6 acres of agricultural land purchased from the university adjacent to Interstate 80.
GARY QUACKENBUSH
FOR THE NORTH BAY BUSINESS JOURNAL
Example of the greenhouse operated by Gotham Greens which announced plans to open in Solano County (Photo courtesy of Gotham Greens)
Gotham Greens Holdings LLC, a firm with indoor agriculture operations across the U.S., Tuesday, announced plans to build a facility next to the University of California, Davis.
The first phase of this 10-acre Solano County facility is expected to open later this year. It will be located on 33.6 acres of agricultural land purchased from the university adjacent to Interstate 80.
The company stated its plans will provide it with the ability to deliver fresh leafy greens, herbs, plant-based dressings, dips and cooking sauces to more retailers, foodservice operators and consumers on the West Coast.
“… We are partnering with one of the highest-ranked agricultural research centers in the world to advance the entire agriculture system,” said Viraj Puri, co-founder and CEO of Gotham Greens. “California is responsible for growing one-third of the country’s vegetables and two-thirds of the nation’s fruit, yet in recent years, issues surrounding drought, food safety and worker welfare have demonstrated the need for continued innovation.”
The greenhouse will generate 60 full-time jobs and provide UC students with the opportunity to learn first-hand how to sustainably grow produce year-round in a safe, clean, climate-controlled environment. The company stated its facilities use 95% less water and 97% less land than conventional farming. Nationwide, Gotham Greens has 500,000 square feet of greenhouse space at five locations staffed by 400 employees.
The UC Division of Agriculture and National Resources and the UC Davis College of Agriculture and Environmental Sciences has entered into a partnership with Gotham Greens to advance research and innovation in the areas of indoor agriculture, greenhouse technology, and urban agriculture to help advance the science, workforce technology, and profitability of indoor agriculture globally.
“We are building a Controlled Environment Agriculture Consortium to support and advance the indoor farming industry, grow more fresh produce on less land and create new jobs for Californians,” said Gabriel Youtsey, the division’s chief innovation officer. “Gotham Greens is an anchoring partner of this research and industry collaboration that we hope will spur innovation, create a new indoor farming workforce and support industry growth.”
Helene Dillard, dean of the college, said, “This partnership will offer our students the chance to learn best practices from leading experts in indoor farming.”
Gotham Greens recently raised $87 million in new equity and debt capital bringing the company’s total financing to $130 million to fuel the next phase of growth.
Founded in 2009 in Brooklyn, New York, Gotham Greens (gothamgreens.com) owns and operates greenhouses in New York, Illinois, Rhode Island, Maryland and Colorado. Its produce is available in more than 40 states and 2,000 retail stores, including Albertsons Companies (Safeway, Jewel-Osco, and Shaw’s), Whole Foods Market, Target, King Soopers, Harris Teeter, and Sprouts.
The company’s products can also be purchased through e-commerce sites including AmazonFresh, FreshDirect and Peapod.
Lead Photo: Gotham Greens
Kroger Expands Partnership With 80 Acres Farms To 316 Stores
80 Acres Farms latest farm in Hamilton, OH grows10 million servings of fresh, pesticide-free produce annually
80 Acres Farms latest farm in Hamilton, OH grows10 million servings of fresh, pesticide-free produce annually
CINCINNATI - March 8, 2021 - ( Newswire.com )
The Kroger Co. (NYSE: KR) and 80 Acres Farms bring farm-fresh produce to customers across Ohio. Today, the companies are growing their partnership to reach more shoppers in the Midwest - both in-store and online.
“Everyone deserves easy access to fresh, affordable, delicious food,” said Dan De La Rosa, Group Vice President Fresh Merchandising, Kroger. “This newly expanded partnership means more communities will have just-picked produce at their fingertips 365 days a year. We’re proud to partner with 80 Acres Farms as we work together to create a world with Zero Hunger | Zero Waste.”
80 Acres Farms’ breakthrough technology means the company can grow pesticide-free produce all year long. With locations closer to customers, the farm-to-table carbon footprint and overall food waste are low.
“Kroger leads with their commitment to fresh by providing customers access to fresher and more nutritious produce,” said Mike Zelkind, CEO and Co-founder of 80 Acres Farms. “Consumers are looking for more nutrition from their diet and want to trust that their food is safe and chemical-free and it will last longer in their refrigerators. The 80 Acres Farms brand delivers against all those promises.”
Today, 80 Acres Farms has four locations in Greater Cincinnati. Its latest state-of-the-art farm will support the new Kroger partnership, bringing 10 million fresh produce servings to communities across the Midwest.
Beginning March 15, 80 Acres will serve 316 Kroger locations across Ohio, Indiana, and Kentucky.
For further information, please contact us at:
Rebecca Haders
rebecca.haders@eafarms.com / +1 513-910-9089
Related Links
New funding sets up 80 Acres Farms for ‘rapid’ expansion
‘The future of food’: 80 Acres debuts world’s first-of-its-kind indoor farm: PHOTOS
Press Release Service by Newswire.com
Original Source: Kroger Expands Partnership With 80 Acres Farms to 316 Stores
Towards Greater Profitability And Scale In CEA And Vertical Farming
The virtual Indoor AgTech Innovation Summit on June 24-25 will gather the world’s leading farm operators, retailers, food companies, investors, seed companies, and technology providers to meet, network, and cultivate new commercial partnerships
The virtual Indoor AgTech Innovation Summit on June 24-25 will gather the world’s leading farm operators, retailers, food companies, investors, seed companies, and technology providers to meet, network, and cultivate new commercial partnerships.
350+ attendees from the US, Europe, the Middle East, and Asia will participate in live-stream sessions, join roundtable discussion groups and connect directly through 1-1 video meetings and group chats.
By sharing best practices from around the globe, and facilitating new connections and collaborations, the summit offers an invaluable platform to develop new business and accelerate projects across the Indoor AgTech ecosystem.
2021 Key Themes
· Hands-Free Cultivation: Latest developments in robotics, automation and AI
· New Crops: Mapping a pathway to mass production
· Retail Insights: Understanding the drivers behind consumer demand
· Seed Optimization: Breeding a competitive advantage
· Financial Models: The investment models scaling the industry
· Advanced Growing Environments: Blurring lines between lighting and genetics
· Profitability at Scale: The technology driving down OPEX
· Food Systems: Bringing food into urban planning
· Direct to Consumer Business Models: Scaling beyond a city
· Energy Efficiency: Driving down the costs of optimum operations
All participants can schedule video 1-1 meetings with potential partners and clients throughout the summit, and for an extended period before and after the sessions.
By sharing best practices from around the globe, and facilitating new connections and collaborations, the summit offers an invaluable platform to develop new business and accelerate projects across the Indoor AgTech ecosystem.
Summit website: https://indooragtechnyc.com/
Registration:
One Summit Pass: Indoor AgTech Innovation Summit (June 24-25, 2021)
Super Early Bird Price: $195
Register before April 2
Early Bird Price: $295
Register before May 7
Standard Price: $395
Two Summit Pass: Indoor AgTech (June 24-25, 2021) and Future Food-Tech Alternative Proteins (June 22-23, 2021)
Super Early Bird Price: $445
Register before April 2
Early Bird Price: $595
Register before May 7
Standard Price: $695
https://indooragtechnyc.com/register/
To Be or Not To Be? Vertical Farm Standards or Best Practices?
There is a lot of talk these days about standardizing the design of indoor vertical farms. One of the beauties of the vertical farming industry is the lack of regulation that has allowed innovation to flourish
Robert Colangelo, Founding Farmer, Green Sense Farms Holdings, Inc.
There is a lot of talk these days about standardizing the design of indoor vertical farms. One of the beauties of the vertical farming industry is the lack of regulation that has allowed innovation to flourish. Green Sense Farms has been an early adopter building our first vertical farm in 2012. Since that time, we have seen the indoor vertical farm supply chain proliferate with some amazing innovation.
When we built our first indoor farm, we had to make many farm components on our own such as, grow tubs, nutrient fill and drain valves, LED light hangers, air circulation systems, data collection software … Now there is a rapidly developing network of suppliers that make excellent components that can be integrated into a custom farm system to meet the needs of each crop.
I’m a big believer in free-market systems. Standardization is a way to control the market and promote mediocrity. Once a standard is created most organizations will do the minimum amount of work to meet the standard, stifling innovation.
What the industry needs now is collaboration. I propose that we create “Best Practices” for indoor vertical farm design and operation. A Best Practice can be a living document that evolves with technology as the CEA industry matures.
Let me know your thought, please send to Robert@greensensefarms.com
1. Advocate for developing indoor vertical farm standards
2. Advocate for developing best practices 3. Advocate for status quo (do nothing)
Vertical Farms vs Greenhouses – The First Consideration: Location
When and where to use a vertical farm versus a greenhouse, and what factors – both economic and environmental – make the difference.
In just the past decade or so, sustainable farming has seen a high-tech makeover in the form of Controlled Environment Agriculture, or CEA, which consists of two main technologies: Vertical farms and greenhouses.
When it comes to feeding the world, it’s not a choice between vertical farms or greenhouses. We’ll need both to feed our growing global population with healthy, sustainable food, and we need to understand the ideal situation for each.
But as a business decision, it often is a choice between the two – and that’s what we hope to explain in this five-part series of articles: When and where to use a vertical farm versus a greenhouse, and what factors – both economic and environmental – make the difference.
In this first post, we’ll cover the basic differences between vertical farms and greenhouses, and why location matters so much when deciding between the two. Then stay tuned because, in the next articles, we’ll dive deeper into energy and lighting costs, automation and other expenses, environmental and crop considerations, and finally, the future of farming.
Vertical Farms vs Greenhouses: The Basics
The two technologies are often confused, but there are significant differences between them in resource use, cost, output, and, perhaps most importantly, the ideal locations for each.
Greenhouses are the more traditional technology that you’re probably familiar with: A single layer of crops, planted inside an enclosed space with walls and a ceiling made of glass or plastic to allow natural light in. They’re semi-controlled environments.
Vertical farms, on the other hand, are a much more recent invention using trays of usually hydroponic plants, stacked in floor-to-ceiling towers, with LED lights illuminating each layer, and climate control constantly adjusting the temperature, humidity and more.
In the upcoming articles in this series, we’ll dive into each part of these differences in more detail. But for now, let’s start with the first question entrepreneurs always need answering: The price tag.
Henry Gordon-Smith is the CEO of Agritecture, an independent consultancy and software creator that helps clients decide between the two technologies. As he puts it, “Vertical farming represents the most expensive, most controlled form of agriculture.”
At first blush, vertical farms are, in fact, shockingly more expensive than greenhouses – six to 10 times as costly. Gordon-Smith says vertical farming costs 2,200 to 2,600 Euro per square meter of cultivation bed space, while high-tech greenhouses cost 250 to 350 Euro per square meter of cultivation space.
Both offer a year-round source of fresh, pesticide-free, locally-grown produce, which provides better nutrition than the same foods that arrive from far away.
But what else do farmers, entrepreneurs, and investors get for all the added expense of vertical farming?
The answer is pretty simple: A more compact farm with more production per square meter, less water use, and more control over both quantity and quality. (With iFarm, this predictability is part of the package, in the form of a guaranteed yield within a precise time frame.)
For some entrepreneurs or municipalities, the cachet of implementing a high-tech farming technique that’s only been in use for less than a decade is also a factor in favour of vertical farming. But most often, the choice comes down to location.
The Ideal Location for a Vertical Farm versus a Greenhouse
The first step in determining the feasibility of building a vertical farm or greenhouse is to look at the drivers and constraints – many of which are simply location-based.
Places with limited space, such as dense urban areas, and limited access to fresh water are ideal for vertical farms. Doubly so if they have access to low-cost, renewable energy, and if they’re near a market with high demand for the crops vertical farms excel at producing: Leafy-greens, micro-greens, herbs and berries grown locally, without pesticides.
But in areas with unlimited space, lots of natural sunlight, and high-cost and/or high-carbon electricity, greenhouses may be the better option and the extra expenses of vertical farming might not make sense.
How these considerations apply in broad regions of the world is illustrated below:
Urban Agriculture Giant Infarm To Reap $250m From Next Fundraising
The company, which has a partnership with Marks & Spencer, is working with Goldman Sachs, Sky News learns
The Company, Which Has A Partnership
With Marks & Spencer,
Is Working With Goldman Sachs, Sky News Learns
Infarm says it is the fastest-growing urban farming firm with interests including 'cloud-connected growing centres'.
Infarm, one of the world’s fastest-growing vertical farming companies, has picked bankers to line up a mammoth fundraising that will underline burgeoning investor interest in the sector.
Sky News has learnt that Infarm has hired Goldman Sachs to oversee its biggest funding round to date, just five months after raising $170m from a syndicate of blue-chip backers.
Sources said the latest financing was likely to kick off in the coming weeks and would be completed later this year.
Infarm has a partnership with M&S
It is expected to crystallize the so-called 'unicorn' status for Infarm - meaning it would join the crop of European technology companies worth at least $1bn.
Infarm, which is based in Germany, is targeting a vertical farming network of 5m square feet by 2025, it said in a statement last year.
The company is one of a breed of start-ups attempting to address food supply problems, some of which have become particularly intense during the coronavirus pandemic.
Unlike its rivals, Infarm installs modular 'mini-farms which are located within supermarkets and restaurants.
[Webinar] Airing It Out: Clean Production Room Environment
You won't want to miss our next Indoor Ag-Conversations webinar session as our expert panel talks about creating a healthy environment for people and plants
JOIN OUR NEXT CONVERSATION
MARCH 24, 2021 | 2:00 - 3:00 PM EDT
You won't want to miss our next Indoor Ag-Conversations webinar session as our expert panel talks about creating a healthy environment
for people and plants
MODERATOR:
Dr. Nadia Sabeh, Ph.D., President|Founder, Dr. Greenhouse
PANELISTS INCLUDE:
Trent Thiel, Industrial Molecular Filtration Product Manager for North and South America, Camfil Americas
Jeremy Shechter, Director of Cultivation, Buckeye Relief
During the program, our panelists will touch on:
Air Filtration
Sanitation Best Practice
Covid Safety
Much More!
LEARN MORE & SAVE YOUR FREE SPOT!
SPECIAL THANKS TO INDOOR AG-CON MEDIA ALLIES, EXHIBITORS & SPONSORS
Indoor Ag-Con, 950 Scales Road, Building #200, Suwanee, GA 30024, United States
USA: KENTUCKY - Appalachia Rises Telethon To Raise Funds For Flood Relief
MARCH 5, 2021 — MOREHEAD, KY — With Kentucky’s Appalachian counties in distress following historic floods, more than a half-dozen organizations have united to form a large-scale fundraising effort anchored by a 7 p.m. Monday telethon to be broadcast by CBS affiliates WKYT in Lexington and WYMT in Hazard
Nine Organizations Unite To Assist After Historic Flood
Donate Now At AppalachiaRises.org
MARCH 5, 2021 — MOREHEAD, KY — With Kentucky’s Appalachian counties in distress following historic floods, more than a half-dozen organizations have united to form a large-scale fundraising effort anchored by a 7 p.m. Monday telethon to be broadcast by CBS affiliates WKYT in Lexington and WYMT in Hazard.
Within hours of rainfall beginning to slow on March 1, more than a dozen counties had already declared states of emergency. Representing more than 175,000 Appalachians, the counties were soon joined by far more, as the dramatic need became clear as floodwaters wiped out entire communities through Kentucky. Residual effects, including mudslides and infrastructure collapse, have left many residents uprooted and, in some cases, homeless with essential businesses also closed due to damage. Compounding the difficulties, the unemployment rates in several affected counties are among Kentucky’s highest. Evacuations across the state have also driven thousands to overcrowded and underfunded shelters, while hospitals treat flood-related injuries alongside the ongoing pandemic.
Launched by Morehead-based AgTech leader AppHarvest, the Appalachia Rises initiative has brought together more than a half-dozen organizations, including the Foundation for Appalachian Kentucky, Appalachian Impact Fund, Appalachians for Appalachia, Blue Grass Community Foundation, WKYT, WYMT, and New Frontier Outfitters. To donate to the flood relief fund, visit https://appalachiarises.org with all proceeds being distributed by the Foundation for Appalachian Kentucky and Blue Grass Community Foundation. Funds will be targeted to individuals needing emergency relief, farmers, and small businesses.
Building up to Monday’s 7 p.m. telethon, which will feature musical performances and inspirational addresses by notable Kentuckians, Appalachia Rises will be staging a number of community outreach initiatives.
Supporting comments
Foundation for Appalachian Kentucky Executive Director Gerry Roll: “The Foundation for Appalachian Kentucky is the only nationally accredited community foundation located in and exclusively serving Eastern Kentucky. Dollars raised with our partners at the Appalachia Rises Fund will be used to help with immediate long-term recovery. The Foundation for Appalachian Kentucky has already begun making emergency relief grants to individuals in crisis and are gearing up to make grants to small family farmers and small, local businesses with relief efforts that will continue throughout the year. We understand that recovery takes time and different forms of support. We live here and work here. And we will be here for our communities once the floodwaters subside.”
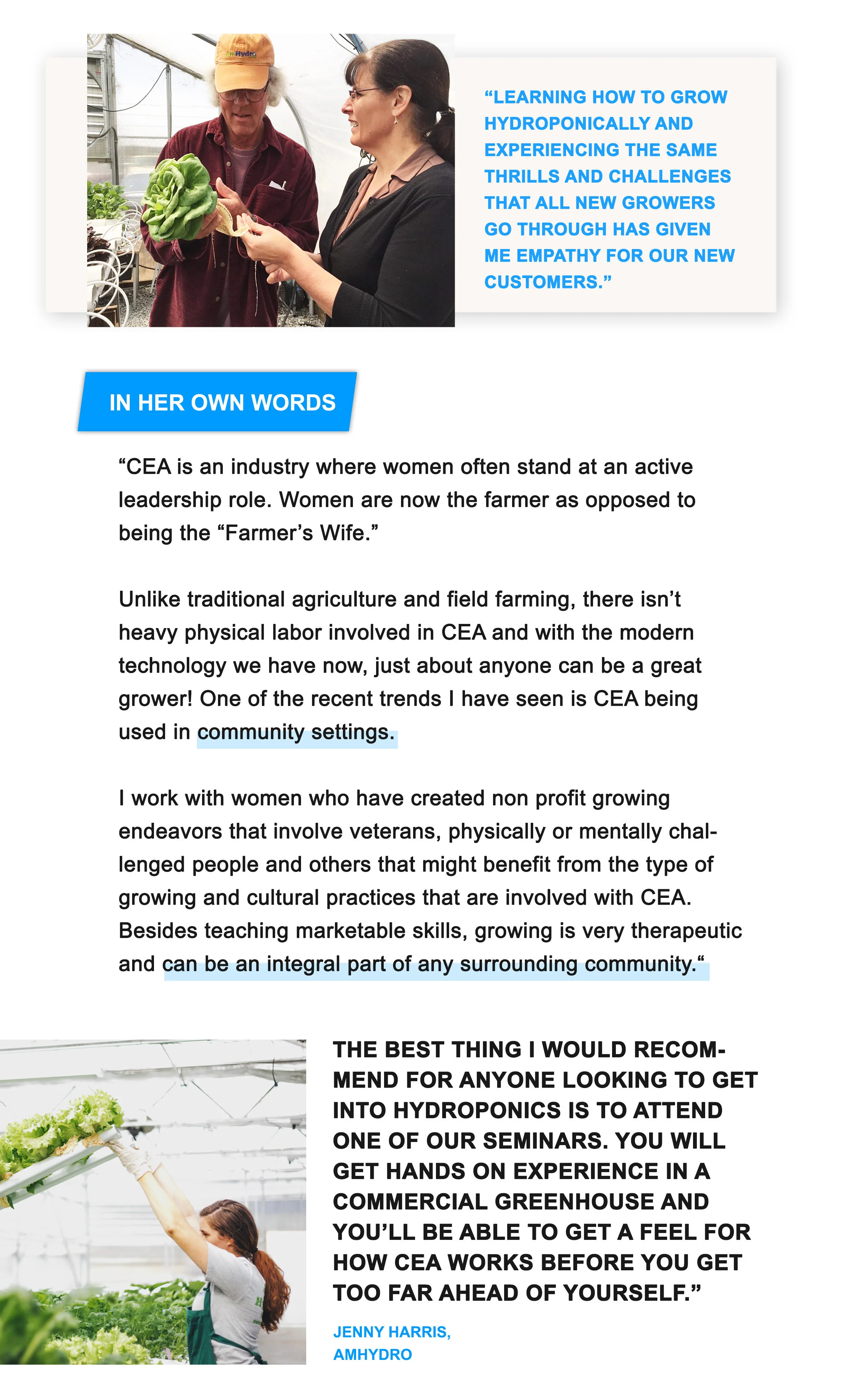
Women In CEA
Are you a woman in CEA, or do you know someone who is? Let us know, we love learning about growers who are working to bring fresh, local produce to their communities!
Are you a woman in CEA, or do you know someone who is?
Let us know, we love learning about growers who are working to bring fresh, local produce to their communities!
You can reach us by email at info@amhydro.com,
or by phone at 1.800.458.6543
Find AmHydro Online, on Facebook, and on Instagram!
SweGreen Becomes Partner In Viable Cities
Viable Cities is an innovation program for smart and sustainable cities. The aim is to accelerate the transition to inclusive and climate-neutral cities by 2030 with digitalization and citizen engagement as enablers
03-03-2021 | Swegreen
SWEDEN- Farming as a Service becomes a new tool in the fight against climate change as the FoodTech enterprise SweGreens joins the Swedish Strategic Innovation Program, Viable Cities.
Viable Cities is an innovation program for smart and sustainable cities. The aim is to accelerate the transition to inclusive and climate-neutral cities by 2030 with digitalization and citizen engagement as enablers.
SweGreen is an innovation company based in Stockholm focused on futuristic, smart, and circular solutions for controlled-environment urban farming. SweGreen own technologies which enables integration of smart vertical farming solutions into real-estate properties. Recently SweGreen has introduced a service for urban production of leafy greens, called Farming as a Service (FaaS), which allows clients to produce greens under their license and close to the city population.
Sweden inspires many other nations and has a leading position in the transition of urbanization context and fighting the climate change through smart and sustainable solutions that could be implemented in cities, says Sepehr Mousavi, member representative, and Chief Sustainability Officer at SweGreen.
Smart urban farming in infrastructure-integrated settings and by harnessing urban resources could be an exponential factor in localizing the food chains in Sweden and cutting back the carbon footprint associated with our food production and supply, he continues.
Viable Cities is growing steadily and new members like SweGreen are joining the current member pool, the likes of Swedish municipalities, Swedish universities and research institutes and other leading innovation companies. Running from 2017 to 2030, the program gathers partners from industry, academia, public and civil society organizations, and jointly funded by the Swedish Innovation Agency (Vinnova), the Swedish Energy Agency and Formas with a total investment of 1 billion SEK (about 100 million EUR).
Viable Cities is coordinated by KTH Royal Institute of Technology.
Together with our member organizations and other stakeholders, we aim to accelerate the transition to climate-neutral cities by 2030 with a good life for all within planetary boundaries, says Olga Kordas, Program Director of Viable Cities and a researcher at KTH Royal Institute of Technology.
Transforming our food systems are one of the key challenges, Olga Kordas continues, and we are happy to be joined by SweGreen to co-create solutions for the future.
Andreas Dahlin, CEO of SweGreen, highlights:
We are honored to be part of such a committed and influential strategic program and partner pool as Viable Cities’. We hope to contribute with innovations around the concept of Farming as a Service, which really could impact food production today and in the future. The ability to produce fresh and nutrient food close to the consumer will be one of the big missions for the food industry in the upcoming decades.
For more information:
Sepehr Mousavi, CSO SweGreen, sepehr.mousavi@swegreen.se +46(0)73-3140043
Andreas Dahlin, CEO SweGreen, andreas.dahlin@swegreen.se +46(0)70-9240032
Åsa Minoz, Head of Communications, Viable Cities, asa.minoz@viablecities.se +46(0)722108826
SweGreen is a Swedish GreenTech company that offers digital, efficient, and circular solutions for urban cultivation in a closed and controlled environment. By combining computer science, advanced technology, and plant sciences, SweGreen contributes to the development of urban sustainable food production. The company was established in 2019 and provides consumer products such as various leafy greens and herbs under the brand of Stadsbondens. www.www.swegreen.com
Source and Photo Courtesy of Swegreen
Advanced Container Technologies, Inc. Joins Clean Food Initiative
Through the use of the company’s GrowPods, ACTX can provide farmers, community groups, investors, and non-profit agencies with a turnkey system to grow ultra-clean and nutritious food that can not only benefit the ecology of the planet and bolster community food security but can also provide new jobs and economic opportunities
March 03, 2021 | Source: Advanced Container Technologies Inc.
Company joins movement toward sustainable alternatives to traditional food production.
CORONA, Calif., March 03, 2021 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Advanced Container Technologies, Inc. (Ticker: OTC:ACTX) stated it is joining the Clean Food Initiative and intends to become a leading force in the drive toward sustainable agriculture.
The Clean Food Initiative is focused on bringing clean, fresh, healthy food to children throughout the world, that is free from pesticides, herbicides, or harmful chemicals. Along with the practice of implementing Sustainable Agriculture Systems (SAS), the aim is to develop a global food system that uses half the water and half the soil as it does today – yet produces twice as much food.
Through the use of the company’s GrowPods, ACTX can provide farmers, community groups, investors, and non-profit agencies with a turnkey system to grow ultra-clean and nutritious food that can not only benefit the ecology of the planet and bolster community food security but can also provide new jobs and economic opportunities.
GrowPods are automated indoor micro-farms that can provide a sustainable supply of affordable safe, clean, nutritious food, while also providing jobs at a local level by promoting the growth of a skilled agricultural workforce in non-traditional settings.
Doug Heldoorn, CEO of Advanced Container Technologies, Inc., said the company’s objectives are to make agriculture sustainable, investable, manageable, scalable, and transparent.
“There is a substantial difference between meeting basic food requirements and meeting optimum nutrition requirements,” he said. “People need access to high quality foods that are rich in nutritional value. Future generations deserve access to a healthy and sustainable food supply, not a diet filled with preservatives, pesticides or chemicals.”
SAS and the Clean Food Initiative represents one of the greatest challenges of the 21st century, as well as a tangible investment opportunity with sound business growth prospects and consistent annual income generation.
“There are few problems facing mankind that are as massive as our need to change our methods of food production and distribution,” Mr. Heldoorn stated. “Fortunately, there are innovative solutions to these challenges, and we are extremely proud to be a vital participant in this agricultural and social evolution.”
For more information, call (951) 381-2555 or visit: www.advancedcontainertechnologies.com.
About Advanced Container Technologies, Inc.
Advanced Container Technologies, Inc. is in the businesses of selling and distributing hydroponic containers called GrowPods; and designing, branding, and selling proprietary medical-grade containers that can store pharmaceuticals, herbs, teas, and other solids or liquids, and can grind and shred herbs; as well as selling other products and accessories, such as humidity control inserts, odor-proof bags, lighters, and plastic lighter holders; and provides private labeling and branding for purchasers of the Company’s containers and the other products. For more information visit: www.advancedcontainertechnologies.com.
Forward-Looking Statements
This release includes predictions or information considered "forward-looking" within securities laws. These statements represent Company's current judgments but are subject to uncertainties that could cause results to differ. Readers are cautioned to not place undue reliance on these statements, which reflect management's opinions only as of the date of this release. The Company is not obligated to revise any statements in light of new information or events.
Company Contact:
(951) 381-2555
info@advancedcontainertechnologies.com
Investor Relations:
Stuart Smith
SmallCapVoice.Com, Inc.
512-267-2430
ssmith@smallcapvoice.com
Related Articles
More articles issued by Advanced Container Technologies Inc.
More articles related to: Product / Services Announcement Food
Hydroponics Farming: Why Hydroponic Farms Are Trending In India?
As per reports, India’s hydroponics market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 13.53% between 2020 and 2027.
Hydroponics is slowly gaining popularity in India and attracting more and more farmers. Basically, hydroponics is a type of horticulture and a subset of hydroculture, which is a method of growing plants, usually crops, without soil, by using mineral nutrient solutions in an aqueous solvent.
Hydroponic farming can be done in a small space also like a balcony which is a soil-less, water-based farming process. Rather than using soil for plant nutrition, crops are fed nutrient-rich water, negating a lot of the baggage that comes with soil-based methods.
Hydroponics is the practice of growing plants in a nutrient-rich solution, skipping the soil. “It has been practised for centuries, so it is not a new technology," points out Akhila Vijayaraghavan, the founder-director of Coimbatore’s Parna Farms, adding the Hanging Gardens of Babylon are believed to have been hydroponically grown. “The Aztecs created vast hydroponic systems using rafts called chinampas," she says.
The film piqued Gopal’s interest, and he began reading about the method to grow plants without soil. “We started working with hydroponics as a project in 2012. At that time, we didn’t know much about the plight of farmers and how a technology like this could add value," said Gopal. The idea was to create awareness among the right audience and sell “through prototypes and hobby kits."
Urban farmers are taking to hydroponics, a water-smart solution to grow pesticide-free produce on rooftops and terraces. As per reports, India’s hydroponics market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 13.53% between 2020 and 2027.
What is Hydroponics
Hydroponics is a branch of hydroculture, in which plants are grown without soil by using water solvent which consists of minerals nutrient solution. Terrestrial plants may be grown with their roots only, roots are exposed to the nutritious liquid, or roots may be supported physically by a medium like gravel.
Plants are also grown through a process called photosynthesis, in which plants use sunlight and a chemical inside their leaves called chlorophyll to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen, as shown in reaction.
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6(Glucose)+ 6O2
The nutrients we use in hydroponic systems may come from different sources, such as fish excrement, duck manure, or chemical fertilisers.
1Advantages of Hydroponics
Plantation without soil
We can grow plants in places where the land is limited, doesn't exist, or is contaminated. In the early time period, Hydroponics was a successful technique used to supply fresh vegetables for troops in Wake Island. It has been considered as the future farming to grow foods for astronauts in space by NASA.
Better use of space and location
All those plants need are provided and maintained in a system, you can grow plants in a small apartment, bedrooms or kitchen as long as you have some spaces.
Roots of plants usually expand and spread out in search of foods, and oxygen in the soil but in the case of Hydroponics, roots are sunk in a tank full of oxygenated nutrient solution and are directly in contact with vital minerals. This means that you can grow your plants closer, and consequently huge space savings.
Climate control
Hydroponic growers can have total control over climate, temperature, humidity, light, the composition of the air. This means you can grow foods all year, regardless of the season. Farmers can produce foods at the right time to maximize their profits.
Water-saving
Plants grown by the process of hydroponically can use 10% of water, as compared to one grown on the field because water is recirculated, in this method. Plants will take up the water they need, while run-off water will be captured and return to the system. Water loss in this system will only occur in two forms - evaporation and leaks from the system.
Use of nutrients
You can have 100% control of the nutrients (foods) that plants need in this method. Before planting, growers can check what are plants requirement and what amounts of nutrients needed at particular stages and at what percentage they should be mixed with water.
Better growth rate
Do hydroponic plants grow faster than in soil? Yes, because you can set conditions favourable to the plant’s growth like temperature, lights, moisture, and especially nutrients. As plants are placed in favourable conditions, nutrients are provided in sufficient amounts and come into direct contacts with the root systems. Therefore, plants do not waste valuable energy in the search for diluted nutrients in the soil and put their complete focus on growth.
A Fully Automated Three-Dimensional Vertical Farm Comes Into Operation
Eponic Agriculture Co. Ltd is a supplier of indoor farming equipment. Alice, the company's director, introduced the recently fully automated production system of a stereochemical vertical farm
Eponic Agriculture Co. Ltd is a supplier of indoor farming equipment. Alice, the company's director, introduced the recently fully automated production system of a stereochemical vertical farm.
"The current three-dimensional indoor farms on the market are based on semi-automated workflow, with some links requiring additional equipment configuration and no continuity in the whole planting system. In order to solve this problem, we developed and designed a complete automated planting system, including the processes from sowing to planting, full-spectrum planting light control, fertilization, harvesting, and cleaning. Which are all done by automated equipment. Whereas all procedures can be controlled by intelligent software with real-time monitoring, data collection, and many other functions."
Benefits of an automated farm
When talking about the advantages of the automated equipment, Alice said, "Take our recently built 20-layer vertical farm as an example. First of all, the mechanical sowing time is 10 times-30 times faster than manual sowing. And on top of that, the use of automated equipment can realize precise planting and efficient communication of multi-layer planting surfaces. The 20-layer vegetable trays are automatically transferred to the ground for uniform watering, harvesting, and cleaning. This greatly improves productivity.
Secondly, the use of lift trucks is required when handling high-level crops. There are certain safety hazards in using lift trucks in a small space. While operating the automated equipment, only a tablet computer is needed to control the whole planting process, which is much safer and more convenient."
Although automated vertical farm systems have many advantages, their application in China is not yet popular. "In terms of production design, we have gone through countless experiments to design the most suitable software program. As well as hardware equipment for practical planting applications. Luckily after a long period of research, we finally chose the most cost-effective and suitable materials. The R&D investment is large and time-consuming.”
From a cost point of view, according to Alice, a fully automatic system is 2-3 times higher in costs than the semi-automatic system which is currently used more often. Most traditional agricultural companies find it difficult to accept such high initial costs. Thirdly, the automated system requires high technical requirements for farm managers. Managers need to have an understanding of both planting technology and software. Alice adds: “It is for these three reasons that the application of fully automated stereoscopic systems is not very common in China and other countries."
Automated planting
"Although the application is not yet widespread, I think fully automated stereoscopic planting is a trend. Urbanization has led to a reduction in arable land and soil pollution has triggered problems with pests and pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables, and the development of three-dimensional agriculture is the only way to maximize and optimize output in a limited area. Currently, stereoscopic planting plants still require a lot of manual labor to operate. As labor costs rise and planting techniques require more precision, the use of automated equipment will be a future trend," Alice notes.
"Automated systems are a trend, not only in China but also globally. Urbanization has been moving forward, in the face of soil pollution, pesticides and pests, etc. The planting area is gradually reduced and three-dimensional agriculture must be developed in order to quantify planting. Three-dimensional agriculture can be located near the city, and reduce the transport distance, people can eat the freshest vegetables, to achieve local supply. Therefore it is necessary to promote automated, intelligent planting systems in order to achieve efficient planting and sustainable development." Alice said.
Industry experience
Eponic Agriculture Co. Ltd's head office, Dahua Intelligent Electronics, has a twenty-five-year history division. The team has been focusing on the development and production of intelligent control systems and industrial lighting. Alice said that based on years of technical foundation, we developed full-spectrum LED planting lights which have been approved and applied by the USDA. Over the years, we have received technical support and affirmation from several agricultural doctors from Europe and the United States, focusing on the development and production of automated stereoscopic planting equipment.
According to Alice, the company has laboratories and showrooms in the US, Australia and Africa. This year, the company is planning on opening new showrooms and laboratories in Europe. “We are expanding our global reach and continue to optimize our growing systems to be a better supplier of fully automated growing equipment."
For more information:
Eponic Agriculture Co. Ltd
Alice Ou, Director
aliceou@eponicagriculture.com
www.eponicagriculture.com
Author: Rebekka Boekhout
© VerticalFarmDaily.com
Vertical Farms Nailed Tiny Salads. Now They Need To Feed The World
Vertical farming is finally growing up. But can it move from salad garnishes for the wealthy to sustainable produce for the masses?
Gartenfeld Island, in Berlin’s western suburb of Spandau, was once the bellows of Germany’s industrial revolution. It hosted Europe’s first high-rise factory and, until World War II, helped make Berlin, behind London and New York, the third-largest city on Earth.
Today’s Berlin is still a shell of its former self (there are over a hundred cities more populous), and the browbeaten brick buildings that now occupy Gartenfeld Island offer little in the way of grandeur. Flapping in the gloom of a grey November morning in 2020 is a sign which reads, in German, “The Last Days of Humanity”.
Yet inside one of these buildings is a company perched at agriculture’s avant-garde, part of the startup scene dragging Berlin back to its pioneering roots. In under eight years, Infarm has become a leader in vertical farming, an industry proponents say could help feed the world and address some of the environmental issues associated with traditional agriculture. Its staff wear not the plaid or twill of the field but the black, baggy uniform of the city’s hipsters.
Infarm has shipped over a thousand of its “farms” to shops and chefs across Europe (and a few in the US). These units, which look like jumbo vending machines, grow fresh greens and herbs in rows of trays fed by nutrient-rich water and lit by banks of tiny LEDs, each of which is more than ten times brighter than the regular bulb you’d find in your dining room. Shoppers pick the plants straight from the shelf where they’re growing.
Infarm crop science director, Pavlos Kalaitzoglou, in his Berlin lab
Credit Ériver Hijano
Gartenfeld Island, however, is home to something more spectacular. Here, in a former Siemens washing machine factory, stand four white, 18-metre-high “grow chambers”, controlled by software and served by robots. These are the company’s next generation of vertical farms: fully-automated, modular high-rises it hopes will scale the business to the next level. According to Infarm, each one of these new units uses 95 per cent less water, 99 per cent less space and 75 per cent less fertilizer than conventional land-based farming. This means higher yields, fresher produce and a smaller carbon footprint.
Agriculture is a £6 trillion global industry that has altered the face and lungs of the Earth for 12,000 years. But, unless we change our food systems, we’ll be in trouble. By 2050, the global population will be 9.7 billion, two billion more than today. Fifty-six per cent of us live in cities; by 2050 it will be 70 per cent. If the prosperity of megastates like India and China continues to soar, and our diets remain the same, we will need to double food production without razing the Amazon to do it. That sign on Gartenfeld Island might not be so alarmist.
Vertical farmers believe they are a part of the solution. Connected, precision systems have grown crops at hundreds of times the efficiency of soil-based agriculture. Located in or close to urban centres, they slash the farm-to-table time and eliminate logistics. New tech is allowing growers to tamper with light spectra and manipulate plant biology. Critics, however, question the role of vertical farms in our food future. They are towering lunchboxes for late capitalism, they argue – producing garnishes for the rich when it is the plates of the poor we must fill. Vertical farms already make money, and heavyweights including Amazon and SoftBank are investing in various companies in the hopes of cornering a market expected to be worth almost £10 billion in the next five to ten years. Infarm is leading that race in Europe. It has partnered with European retailers including Aldi, Carrefour and Marks & Spencer. In 2019 it penned a deal with Kroger, America’s largest supermarket chain. Venture capitalists have handed the firm a total of £228 million.
Not bad for a hare-brained experiment that started in a Berlin apartment.
An Infarm employee tends to a batch of seedlings in a special incubator
Credit Ériver Hijano
In 2011, a year before he moved to Berlin, Erez Galonska went off-grid. He grew up in a village in his native Israel, but the young nation was growing too, and farms made way for buildings. Soon the village was a town, and its inhabitants ever more disconnected from their natural surroundings.
Galonska’s father had studied agriculture, and the son had dreamed of recovering a connection with nature he felt he had lost. The search took him to the mountains of the Canary Islands, where he found a plot of land and got to work. He drank water from springs, drew energy from solar panels, and spent long hours farming produce he then sold or bartered at local markets.
When he met his now-wife Osnat Michaeli, “I traded it for love,” he says. “Love is stronger than anything.” In 2012, the couple, alongside Galonska’s brother Guy, who had studied Chinese medicine, moved to Berlin to work on a friend’s social media project. But the hunger for self-sufficiency remained. It was “a personal quest,” Michaeli says. “How we can be self-sufficient, live off the grid. Food is a big part of that journey.”
We meet at a Jewish restaurant in Berlin’s historic Gropius Bau art museum. It is mid-morning, and Covid-19 has cleared the tables. But a row of Infarm units whirs away quietly along one wall, producing basil, mint, wasabi rocket (a type of rocket leaf with the punchy flavour of wasabi), and other, more exotic herbs. Such produce was a pipedream for the three Infarm co-founders eight years ago. Growing crops when living on a tropical island was one thing. Doing it in a small apartment, located in the tumbledown Berlin neighbourhood of Neukölln, was quite another. Soon after moving from the Canaries, Erez Galonska typed “can you grow without soil” into Google.
Japan had taken to indoor farming in the 1970s, and this bore some helpful information on its techniques. The same was true of illegal cannabis growers, who swapped tips about hydroponics – growing with nutrient-packed water rather than soil – across subreddits.
Several trips to a DIY store later, the trio had what resembled a hydroponic farm. It was a big, chaotic Rube Goldberg machine, and it leaked everywhere. Growing wasn’t simply a case of switching on the lights and waiting. Brightness, nutrients, humidity, temperature – every tweaked metric resulted in an entirely different plant. One experiment yielded lettuce so fibrous it was like eating plastic. “We failed thousands of times,” Erez Galonska says.
Two of Infarm’s co-founders, Osnat Michaeli and Erez Galonska
Credit Ériver Hijano
Eventually, the team grew some tasty greens. They imagined future restaurant menus boasting of food grown “in-farm”, rather than simply made in-house, and founded Infarm in 2013. But there was a hitch: indoor-grown cannabis sells for around £1,000 per kilo. Lettuce for £1.20. Most of the early vertical farms required heaps of manual work and operated in the red. “It simply wasn’t a sustainable business model,” Erez Galonska says.
By 2014, they decided to roadshow their idea and shipped a 1955 Airstream trailer – a brushed-aluminium American icon – to Berlin. The trailer belonged to a former FBI agent, but it was conspicuous in a city of Volkswagens, caravans and Plattenbau buildings. Michaeli and the Galonska brothers transformed it into a mobile vertical farm, then pitched up at an urban garden collective in Berlin’s trendy Kreuzberg district. There they proselytised indoor farming to urban planners, food activists, architects and hackers, handing out salads and running workshops. Fresh, local food – even if it cost a little more – would entice a growing number of foodies who were interested in where their meals came from. The trailer cost nothing but petrol money to move, and emissions from the growing process itself were almost nil.
When the designer of a swanky hotel across town came by trailer, he asked if the team could install something similar in his restaurant. “That was really the trigger,” says Guy Galonska. “We rented a workshop and we got to develop a system for them.”
When they installed their first “farm” in a Berlin supermarket, VCs took notice and visited Infarm’s young founders at their Kreuzberg office-cum-kitchen, where they hosted dinner parties featuring Infarm crops. But a return on investment still seemed distant: some investors thought the farms were an art project. Maintaining locations manually was exhausting, and the team almost went bankrupt “two or three times,” Guy Galonska says. “I think all of us got a lot of white hair during that time,” he adds. “It was a very challenging thing to do.”
A €2 million grant from the European Union in 2016 helped. With it came deals to place Infarm units in supermarkets and restaurants across Germany. Managing them all would require something precise, connected and efficient. To become a sustainable business, Infarm would have to behave less like a farm, and more like a tech startup.
An Infarm kiosk in the Edeka Supermarket E Center in Berlin
Credit Ériver Hijano
For around 2,500 years after King Nebuchadnezzar II of Babylon gifted his wife some hanging gardens, little changed in the world of hydroponic farming. Asian farmers grew rice on giant, terraced paddies, and Aztecs built “chinampa” rigs that floated along the swamps of southern Mexico.
Life magazine published a drawing of stacked homes, each growing its own produce, in 1909, and the term “vertical farming” appeared six years later. The US Air Force fed hydroponically-grown veggies to its troops during World War II, and Nasa explored the tech as a solution for life off-planet. But vertical farming didn’t really capture public imagination until 1999, when Dickson Despommier, a Columbia University professor, devised a 30-storey skyscraper filled with farms. In 2010, Despommier published The Vertical Farm: Feeding the World in the 21st Century, which has become the industry’s utopian testament.
“I had no expectations whatsoever that this would turn commercial,” Despommier says. “We just thought it was a good idea, because we didn’t see any other way out of stopping deforestation in favour of farming, and keeping the carbon dioxide content of the atmosphere at a reasonable level. It turned out to be a crazy idea whose time has come.”
The vertical farming concept is simple: growing produce on vertically-stacked levels, rather than side by side in a field. Instead of the Sun, the vertical farm uses artificial light, and where there is ordinarily soil, growers use nutritious water or, in the case of “aeroponic” farms, an evenly-dispersed mist.
Vertical farms take up a vanishing amount of land compared to their conventional cousins. They use almost no water, don’t flush contaminating pesticides into the ecosystem, and can be built where people actually live. But, by and large, they have not functioned as businesses. Only the black-market margins of weed, and Japan’s high-income, high-import food ecosystem, have catered to profit. It costs hundreds of thousands of pounds to erect a mid-sized vertical farm, and energy use is prohibitively high.
Advances in technology are changing this. By bolting automation, machine learning and cloud-connected software on to vertical farms, firms can trim physical labour, increase capacity and maintain a dizzying range of cultivation variables. Infarm staff at a separate office to the new Berlin farm, located some 23km southeast of Spandau in the Tempelhof district, keep track of “plant recipe” settings at any one of the startup’s 1,220 in-store units, including CO2 levels, pH and growth cycles, via the company’s Farm Control Cloud Platform, a bit like a giant CCTV room. Machine learning finesses recipes, and keeps each plant as uniform as possible.
Inside the new vertical farm, trays of produce are tended by automated systems
Credit Ériver Hijano
Gartenfeld Island’s employees – mechanical and electrical engineers, software developers, crop scientists and biologists – get closer to the produce, but only just. They monitor via an iPad and feed crops into the building’s four massive grow chambers, or farms, each one about the height and width of two London buses, with ventilation systems that whoosh like a subdued turbine hall.
From there on in, robots do the hard work. Inside the farms, a robotic “plant retrieval system” – basically a tricked-out teddy picker – scoots up and down a perpendicular beam, plucking trays of plants in various stages of growth and shuffling them closer, or further, from LED lights at the summit. The firm claims this reduces service time by 88 per cent. A sliver of the window is the only way to see the device in-person: everything is hermetically sealed to keep out pests. “With automation, you invest once and then that price goes down over time,” says Orie Sofer, Infarm’s hardware lab lead. “With human labour, unfortunately, over time the price goes up.”
The number of crop plants varies depending on the produce, but there are usually just under 300 in a “farm” at any one time. Each farm yields the equivalent of 10,000 square metres of land and uses just five litres of water per kilo of food (traditional vegetable farming uses around 322 litres per kg).
Infarm is not alone in this revolution. AeroFarms, a Newark, New Jersey-based startup, feeds an aeroponic mist to roots that are separated from their leaves by a cloth. It’s most recent funding round was led by Ingka Group, the parent of Swedish furniture giant IKEA. New York’s Bowery Farming, like Infarm, focuses on automation and a proprietary dashboard called BoweryOS that, among other things, takes photos of crops in real-time for analysis. It’s £123 million in backing comes from investors including Singapore’s sovereign fund Temasek. Bowery CEO and founder Irving Fain believe his addressable market “is about a hundred billion dollars a year, just in the US, of crops that we think are good candidates for us to grow.”
Leading the vertical farming VC race is Plenty, a San Francisco-headquartered brand that has raised almost half a billion pounds in the capital since it was founded in 2013, including a 2020 Series D round led by Masayoshi Son’s $100 billion SoftBank Vision Fund. Plenty feeds its greens with water that trickles down six-metre-tall poles; infrared sensors pour data into an algorithm that nudges the plant’s growth recipe accordingly.
Plenty co-founder and chief science officer Nate Storey, who works at the company’s test farm in Wyoming, likens these deep-tech solutions to the tools that powered agriculture’s most recent revolution: “The tractor allowed farmers to be freed from constraints. Half of their land was dedicated to raising draft animals, and the tractor came along and freed them from a life where they were basically managing animals just so they could plough their land.”
For them, he says, automation is similar. “It allows us to get rid of the hardest work – the work that is unpleasant, the work [growers] don’t like to do – and focus on the work that really matters.”
Infarm kiosks inside the Beba restaurant in the Gropius Bau museum
Credit Ériver Hijano
Infarm differs from the competition on two fronts. The first is its focus on modular design: each component is compatible and scalable, like a giant, noisy LEGO set. Modularity makes it possible to install Infarm units anywhere in the world in a matter of weeks, no matter the size. That enables the company’s second USP: its business model. Infarm has no stores, selling produce instead via its remote units.
Clients tell Infarm which produce they want, and “create a schedule,” says Michaeli. “You buy the plants. Everything on the farm is controlled by Tempelhof. Everything that’s grown belongs to the client.” A chef may demand pesto that’s made from particular three-day-aged Greek and Italian basil, for example. Infarm can do that (Tim Raue, Berlin’s most famous chef, is a customer). “Everyone stops and asks about the farm,” one Berlin store manager says. “It’s great to have innovation here.”
Infarm has “two big advantages,” says Nicola Kerslake, founder of Contain Inc, a Nevada-based agtech financier. “One is that they’ve figured out how to do product onsite, which is really not very easy. And the other is that they have these great relationships with big purchasers like Marks & Spencer.”
“When you look at where the arms race is in this industry,” she continues, “it’s really been in two areas: How do I get hold of as much capital as possible, and how do I sign up the right partners? Having Marks & Spencer in your back pocket is really useful.”
It has helped encourage investors to open their chequebooks. Hiro Tamura, a partner at London VC firm Atomico, first met Infarm’s founding trio in 2018. A year later he led its £75 million Series B round. “They could roll these things out,” he says. “They worked, and they didn’t need some industrial-sized warehouse to do it. I didn’t lean in, I fell into the rabbit hole. And it was incredible. I was like, wow, these guys are thinking about time and speed to market modularity.”
Infarm ploughs a chunk of its revenue back into research. In a mezzanine-level lab sitting above the farms at Gartenfeld Island, a dozen white-coated analysts conduct tests on herbs to a soundtrack of Ariana Grande, measuring crop sugar levels, acidity, vitamins, toxicity, antioxidants and more. Via a process of phenotyping – the study of organisms’ characteristics relative to their environment – they hope to create more flavourful plants, or new tastes altogether.
“It’s not just about the hardware,” Kerslake explains. “It’s about how the hardware interacts with the rest of your farm system. And we’re starting to see a lot more sophistication on that front because the AI programs these companies started three or four years ago are now starting to bear fruit.”
Infarm’s results are high-quality: juicy lettuce, wasabi rocket that kicks, and basil that’s far more fragrant than the budget variety. “The end goal with almost everything that we’re doing is developing some sort of playbook, some sort of modular and standardised system, that we can then copy-paste to wherever we go,” says Pavlos Kalaitzoglou, Infarm’s director of plant science. Across from the lab, tomatoes and shiitake mushrooms grow in wine cellar-size chambers. They are living proof of how the firm is looking to diversify from herbs and leafy greens, whose low energy and water requirements make them the staple crop of every vertical farming startup today.
Rows of LED-illuminated produce inside one of Infarm’s four massive new grow chambers
Credit Ériver Hijano
We are in danger of farming the planet to death. Agriculture already occupies 40 per cent of all liveable land on Earth, and food production causes a quarter of all greenhouse gases. An area the size of Scotland disappears from tropical rainforests, responsible for up to a quarter of land photosynthesis, each year. Clearing more trees to feed our spiralling population will not help.
“We need to go back to the drawing board and rethink which avenues we can environmentally afford to pursue,” says Nicola Cannon, a professor at the Royal Agricultural University in Cirencester. Nitrogen fertiliser is particularly harmful to the environment, Cannon adds, “and has led us to adopt systems which have grossly exceeded the planetary boundaries.”
Current food systems are wildly inefficient: waste accounts for 25 per cent of all calories. And yet, almost a billion people suffer from hunger worldwide. These are not issues vertical farming will solve, critics, argue. Going local does little beyond satisfying consumers.
Energy is another tricky issue. Ninety per cent of Infarm’s electricity today is renewable, and it wants to reach zero emissions in the next few years. But this doesn’t factor in the environmental cost of building a steel-and-cement facility.
“Vertical farms are a round-off error to the round-off error in terms of contributing to the big levers out there,” Jonathan Foley, an environmental scientist based in Minneapolis, says. “Like most technologies that are getting a lot of venture capital and which come from Silicon Valley kind of thinking, it’s being massively overhyped at the cost of real solutions. There’s an opportunity cost to put all this technology, money and renewable energy – that could be used for other things that we need energy for – into growing arugula for rich people at $10 an ounce.”
More than half the world’s food energy comes from its three “mega-crops”: wheat, corn and rice. They require wind, seasons and micronutrients that vertical farms are unable to replicate today. These are the crops that can prevent famine in Somalia, Bangladesh or Bolivia – not lettuce. “Vertical farms are growing the edge of the plate, not the centre of the plate,” Foley says.
But Despommier says it’s too soon to criticise the young industry for not addressing issues such as crop diversity. “What you’re really seeing is a rush towards profitability to get their feet wet, and to get their ledgers in the black and to pay off their investors, before they start diversifying,” he says.
“In a world where you think that land is unlimited and that resources are unlimited, indoor farming would be nonsensical,” Plenty co-founder Storey says. “As crazy as it seems to replace the Sun with electricity, it makes sense today. And it really makes more and more sense as time goes on.”
Much of the hope vested in vertical farms rests on the light-emitting diode. This tiny bead of light is the industry’s packhorse: it is a farm’s biggest financial layout and the nucleus of its most exciting advances. Modern LEDs are nothing like the ones that powered your childhood TV. They’ve progressed at such a rate, in fact, that they’ve developed their own law to adhere to: “Haitz’s Law”. Each decade, their cost drops by a factor of ten, while the light they generate leaps by a factor of 20.
That curve will eventually plateau, experts say. But not before LEDs improve enough to allow vertical farms to profit from food closer to the middle of the plate. Infarm’s current smart LED set-up is over 50 per cent more efficient than the one that lit its first farms. Haitz’s Law has helped some companies experiment in growing potatoes, which require far more energy and water than leafy greens. Turning profit from a crop that delivers the highest calories per acre would be momentous for the industry.
The cutting edge of LED technology today is smart sensors that can regulate the brightness and spectrum of light to replicate growing outdoors – or enhance it. Much of the planet’s first flora grew only in the ocean, which looks blue because it absorbs blue light at least.
Photosynthesis, therefore, occurs best between the blue and red light spectra. By tailoring LEDs to emit only these colours, or by dimming at intervals meant to mirror a plant’s natural cycle, vertical farmers can further reduce their energy burden – like stripping a road car to its bare bones so it can drive faster.
Recent discoveries have been more surprising. Strawberries, for example, react particularly well to green light. Some spectra can increase vitamin C in concentrated fruits like kiwis, while others extend shelf-lives by almost a week. In the future, says Fei Jia, of LED firm Heliospectra, growers “can get feedback from the lighting and the plants themselves on how the lighting should be applied… to further improve the consistency of the crop quality.”
“If you judge it from what you have today, you understand what [critics] are saying,” Guy Galonska says. “How can you grow rice and wheat and save the world? And they are right. But they can’t see ten years ahead: they can’t see all the different trends that are going to support that revolution.”
Other technological advances are helping agriculture in different ways. Drones and sensors help map and streamline growing. Drip irrigation dramatically reduces the burden on dwindling water supplies. Circular production – where waste products from one process contribute to fuelling another – is becoming more commonplace, especially in livestock farming. Cell-grown or insect-based meat (or vegetarianism) will reduce our reliance on livestock, which consume 45 per cent of the planet’s crops. Infarm, and the broader vertical farm cohort, may not be saving the world today. But it wants to build taller farms, place them in public buildings like schools, and teach people the value of fresh, healthy vegetables. If 70 per cent of us are to live in cities, then cities “can become these communities of growing,” says Erez Galonska.
Ultimately, Infarm wants to build a network of tens of thousands of automated farms, each one pumping streams of data back into a giant AI system in Berlin. This “brain”, as Galonska calls it, will pour that information into algorithms to generate better food at lower costs, each new yield shaving fractions from the water, energy and nutrients required. Then, Infarm could become something closer to the dream Galonska left behind in the Canaries: truly self-sufficient.
It’s a long way from the leaky, DIY gadget he and his co-founders built in their front room. “The way the world is going now, it’s very clear to everyone it’s running in the wrong direction,” Galonska says. “We definitely believe in the power of collaboration: bringing those outside-the-box thoughts to create a new system that will generate more food, better food, much more sustainably, and help to heal the planet – because that’s the main issue on the table.”
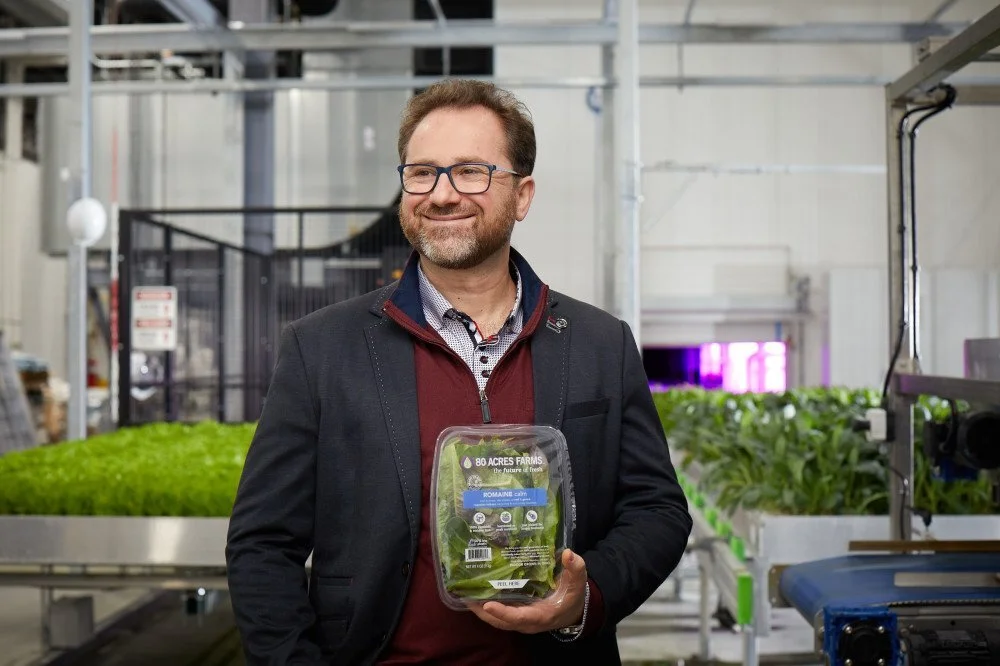
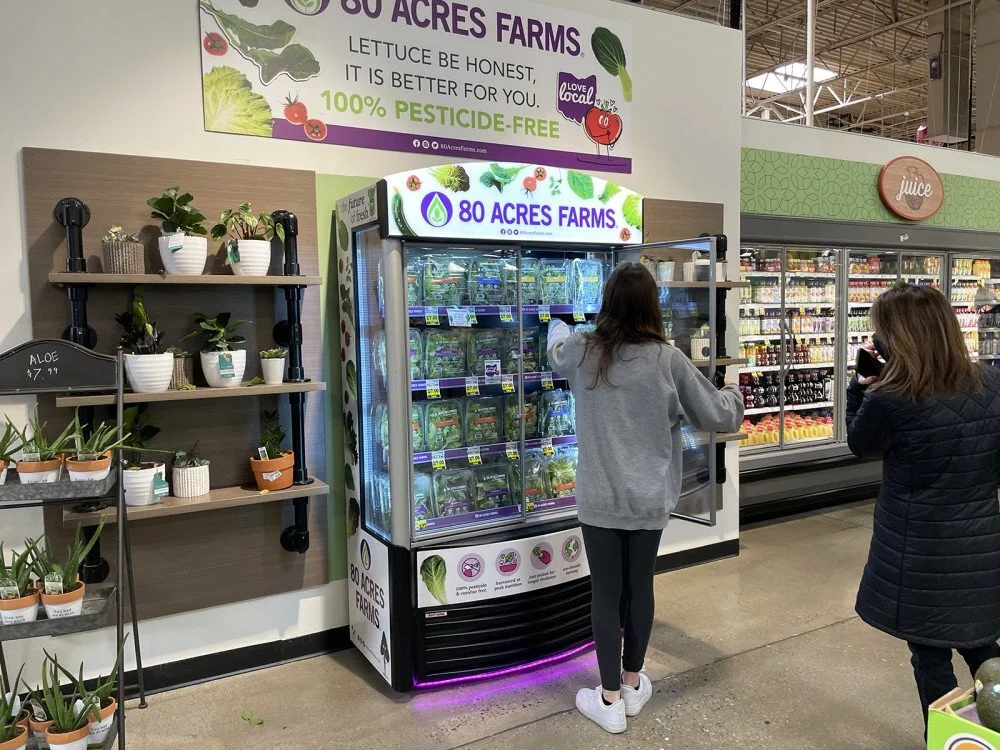
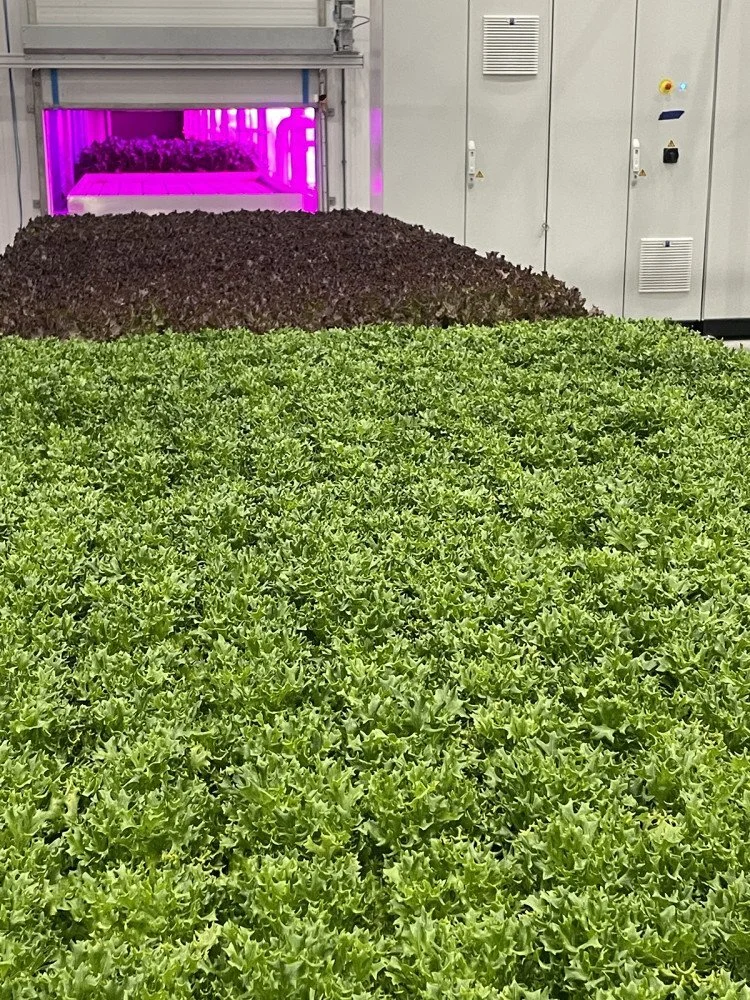

































![[Webinar] Airing It Out: Clean Production Room Environment](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/57c8695d5016e11e71be1d83/1614852225134-U5ZX1JATVG2JIDZ6OD9G/unnamed.png)